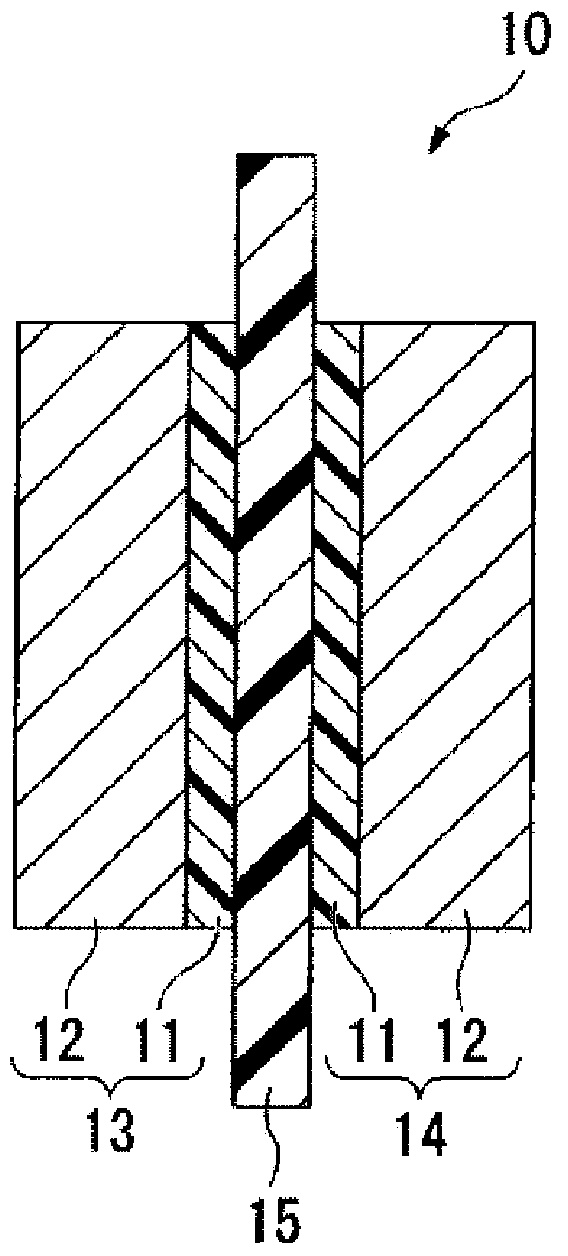
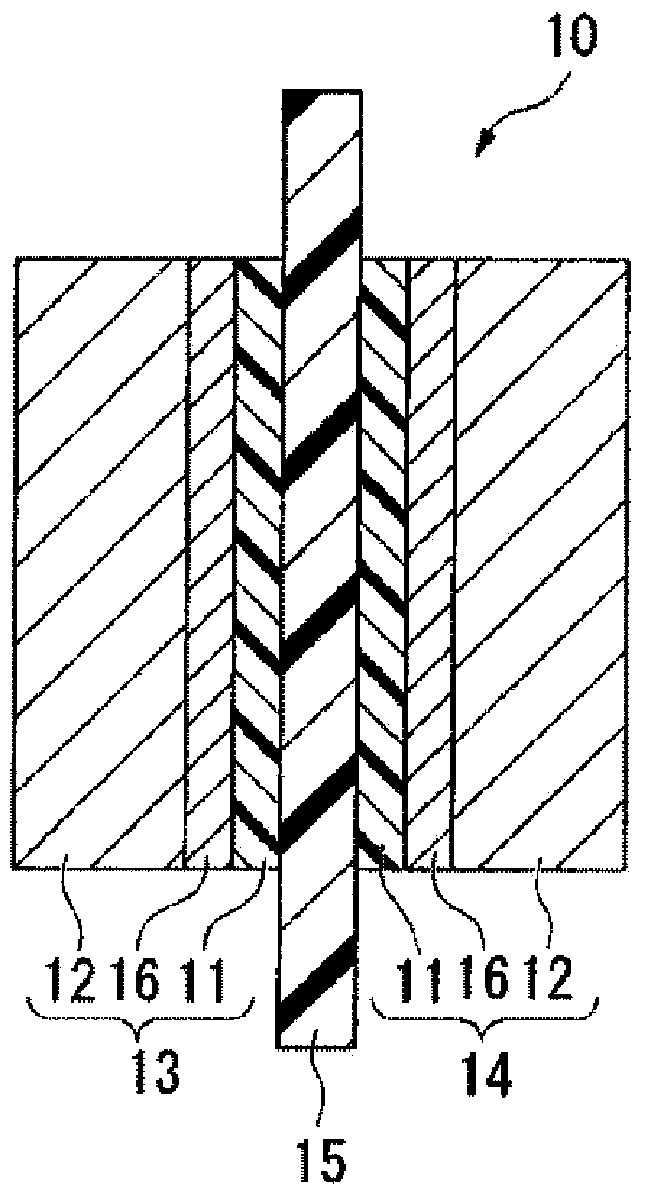
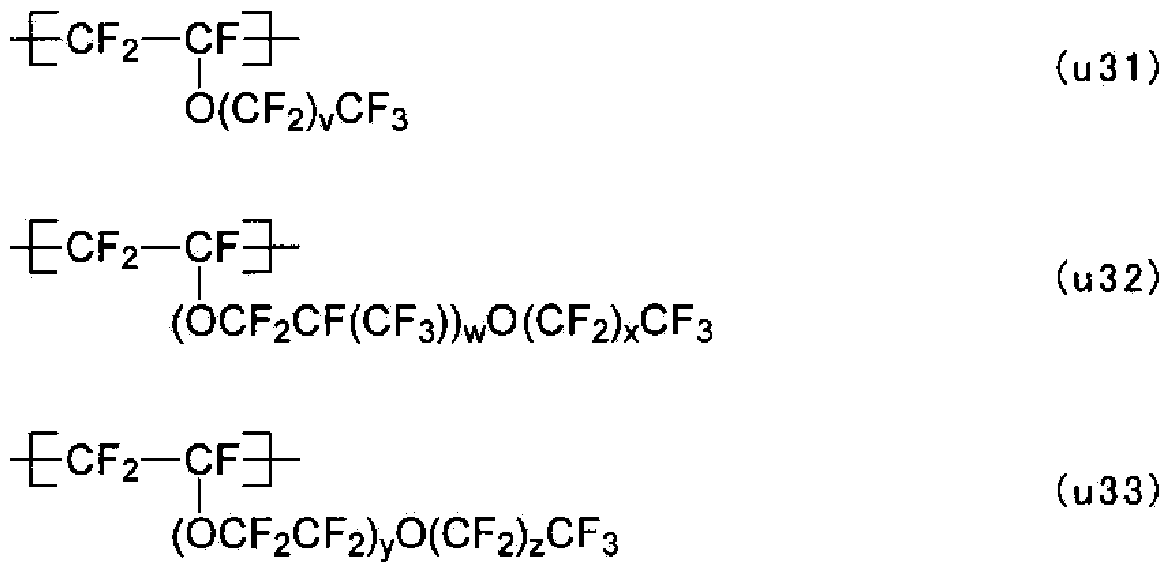Electrolyte material, liquid composition, and membrane electrode assembly for polymer electrolyte fuel cell
An electrolyte material and polymer technology, applied in solid electrolyte fuel cells, fuel cells, battery electrodes, etc., can solve problems such as easy cracking, and achieve the effect of not easy cracking and good power generation characteristics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
manufacture example
[0424] (manufacture of liquid composition)
[0425] A polymer (F') composed of compounds (m12-1), (m11-1) and TFE was obtained by the same method as in Example 5 described on page 29 of International Publication No. 2008 / 090990. Then, by the same method as Example 1 described later, polymer (F') -SO 2 F is converted into a sulfonic acid group to obtain a polymer (H'). The ion exchange capacity of the polymer (H') was 1.5 meq / g dry resin.
[0426] Add 370g polymer (H ') in the heat-resistant and corrosion-resistant nickel-based alloy autoclave of internal volume 2.5L, add the mixed solvent (water / ethanol=50 / 50 mass ratio) of water and ethanol again, solid content concentration Adjusted to 26% by mass. While stirring at a rotation speed of 150 rpm using a double ribbon impeller, the temperature was raised to 120° C. and stirred for 15 hours. Next, 200 g of water was added, the solvent composition was adjusted to water / ethanol=58 / 42 mass ratio, the solid content concentration...
example 1
[0434] (Manufacture of Polymer (F))
[0435] 150.0 g of compound (m12-1), 29.6 g of compound (m32-1), 32.2 g of compound (m21-1) and 63.5 mg of compound (i-1) were charged into a stainless steel autoclave with an inner volume of 230 mL, and the Fully degassed under nitrogen cooling. Then, 8.9 g of TFE was introduced into the system, and the temperature was raised to 10°C. The pressure at this time was 0.15 MPaG (gauge pressure). After stirring at 10° C. for 48 hours, the gas in the system was purged, and the autoclave was returned to room temperature to complete the reaction.
[0436] After diluting the product with compound (s-1), compound (s-2) was added thereto, and the polymer was aggregated and filtered. Then, the polymer was stirred in compound (s-1), re-agglomerated with compound (s-2), and dried under reduced pressure at 80° C. overnight to obtain polymer (F-1). The yield was 42.3g. Table 1 shows the ratio of each unit.
[0437] (Manufacture of Polymer (H))
[0...
example 15
[0450] 231.0 g of compound (m11-4), 13.0 g of compound (m31-2), 8.5 g of compound (m21-1) and 25.3 mg of compound (i-2) were charged into a stainless steel autoclave with an inner volume of 230 mL. Fully degassed under nitrogen cooling. Then, the temperature was raised to 100° C., TFE was introduced into the system, and the pressure was maintained at 0.3 MPaG to start polymerization. During polymerization, TFE was continuously added to keep the pressure constant at 0.3 MPaG. In addition, compound (m21-1) was continuously added at a rate of 1.0 g for 1 hour. After 10 hours, the gas in the system was purged, and the autoclave was returned to room temperature to complete the reaction. After the polymerization, the same procedure as in Example 1 was carried out to obtain a polymer (F-15), a polymer (H-15), a liquid compound (D-15), a catalyst layer (E-15), and a membrane electrode assembly. The results are shown in Table 3 and Table 5.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com