Method for cultivating high-TYLCV (tomato yellow leaf curl virus)-resistant tomatoes
A tomato, high resistance technology, applied in the biological field, to achieve the effect of shortening the breeding cycle
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] Example 1 RNAi vector construction of AV1, AC1 and AC3 gene fragments of TYLCV
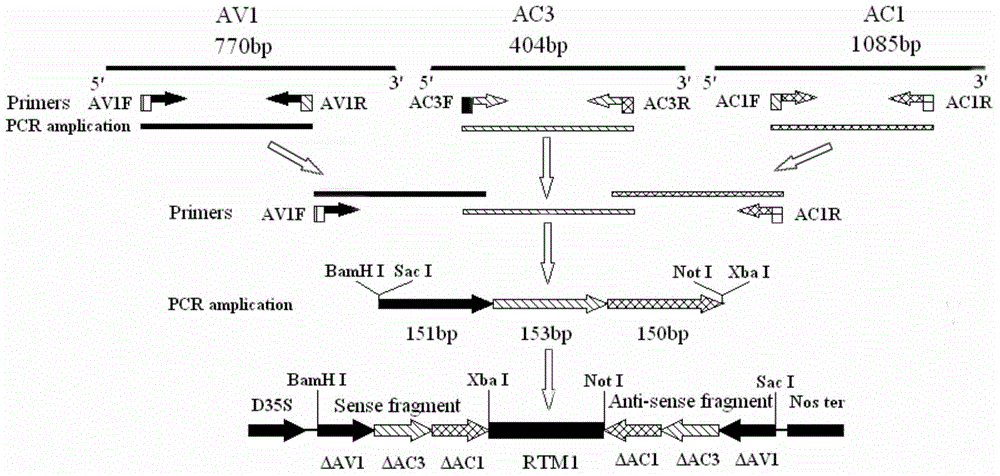
[0041] The construction process of the RNAi vector of the three-gene fragment chimeric gene is as follows: figure 1 As shown, the main steps are as follows:
[0042] 1.1 Genomic DNA extraction of susceptible tomato
[0043] In this example, a modified CTAB method was used to extract the genomic DNA of tomato leaves. The specific experimental steps are as follows: Weigh 2 g of susceptible tomato leaves into a mortar pre-cooled at -20°C, add an appropriate amount of liquid nitrogen, and then quickly grind the leaves into powder. After grinding, put the powder into a 1.5 mL EP tube; add 600 μL of 2% CTAB solution (preheated at 60 °C) to the EP tube, shake and mix well, and take a water bath at 60 °C for 15 min; add 300 μL of chloroform, shake slightly, put in 4 Centrifuge at 13,000 rpm for 5 min. Transfer the supernatant to another new 1.5mL EP tube; add an equal volume of 25:24:1 phenol / c...
Embodiment 2
[0067] Example 2 Agrobacterium-mediated tomato transiently
[0068]2.1 Preparation of Agrobacterium EHA105 competent cells
[0069] Agrobacterium EHA105 was picked and streaked on a YEP solid plate containing 25 μg / mL rifampicin, and cultured at 28 °C for 36-48 h; a single colony was picked and inoculated in 2 mL YEP medium, and cultured overnight at 28 °C and 200 rpm; 2 mL of bacterial solution was inoculated into Continue to culture in 50 mL YEP medium for 6-8 h until OD600 = 0.5, ice bath for 10 min; centrifuge at 7,000 rpm for 5 min at 4 °C, discard the supernatant, and resuspend the bacterial weight in 5 mL of 20 mM CaCl2 solution; centrifuge at 7,000 rpm for 1 min at 4 °C, Discard the supernatant, gently suspend the cells with 1 mL of 20 mM pre-cooled CaCl2, aliquot 100 μL per tube, snap-frozen in liquid nitrogen, and store at -80 °C for later use.
[0070] Note: All steps in contact with air in the experiment are operated in a clean bench. After the preparation of NaCl...
Embodiment 3
[0080] Example 3 Identification of TYLCV resistance of transgenic tomato
[0081] 3.1 Agrobacterium injection inoculation
[0082] 3 weeks after inoculation with RNAi vector, Agrobacterium containing TYLCV infection plasmid was inoculated on the new leaves of transgenic tomato plants, and the tomato plants were infected. The plant transformed with empty load was used as a negative control, and the method was the same as that in 2.3. 5 weeks after inoculation, the symptoms of tomato leaves were observed, and the results were as follows image 3 , 4 , 5 shown. Depend on image 3 It can be seen that A is an untransformed but virus-infecting tomato plant. From the leaf symptoms, it can be found that the tomato has been severely infected with TYLCV; Figure 4 It can be seen that B is a transformed empty tomato plant, and its leaf symptoms are similar to A, indicating that the tomato is also infected with TYLCV; Figure 5 It can be seen that C is a tomato plant transformed wit...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com