Spirulina dehydration method
A technology for dehydration of cyanobacteria and filter press, applied in chemical instruments and methods, dehydration/drying/concentrated sludge treatment, water/sludge/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the disadvantages of increased cyanobacteria volume and high moisture content of algae-enriched water Transportation and final disposal and other issues, to achieve the effect of weight and volume reduction, convenient large-scale industrial production, and fast processing speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] A method for cyanobacteria dehydration, comprising the following steps:
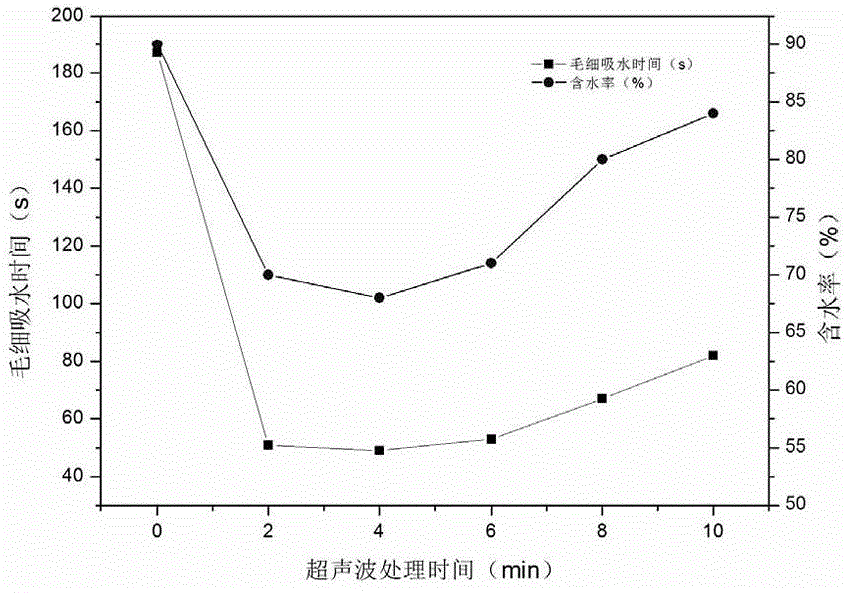
[0035] (1) Ultrasonic: The salvaged cyanobacteria (the initial moisture content of the salvaged cyanobacteria is 98%) is subjected to ultrasonic frequency of 50kHz and sound intensity of 0.7W / cm 2 , Ultrasonic treatment with a sound energy density of 0.8W / ml for 3min.
[0036] (2) Adding a flocculant: adding polyferric sulfate to the sonicated cyanobacteria at a ratio of 2% of the dry weight of the cyanobacteria, and stirring evenly to obtain cyanobacteria added with a flocculant.
[0037] (3) Dehydration by filtration: the cyanobacteria added with flocculant in step (2) are dehydrated by filtration through a membrane filter press, the pore diameter of the filter cloth of the membrane filter press is 20 μm, and the dehydration of cyanobacteria is completed.
[0038] The capillary water absorption time of the untreated cyanobacteria in this embodiment was 89s, and the dry basis calorific value was...
Embodiment 2
[0040] A method for cyanobacteria dehydration, comprising the following steps:
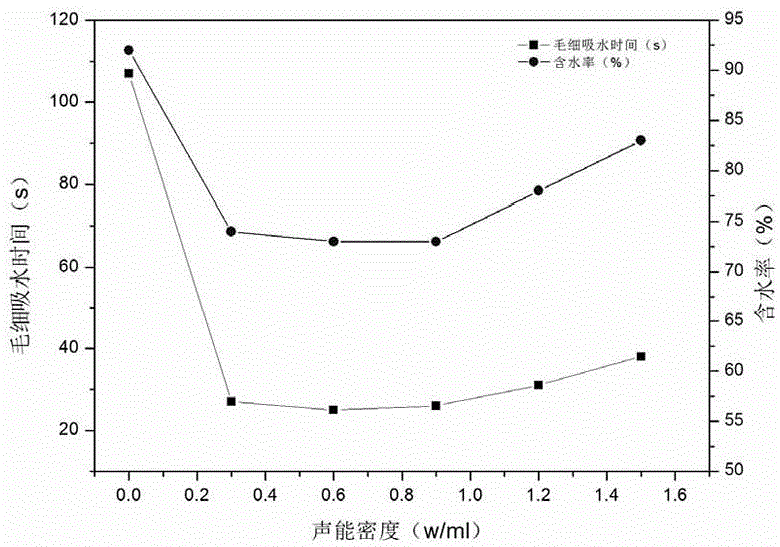
[0041] (1) Ultrasound: the salvaged cyanobacteria (the initial moisture content of the salvaged cyanobacteria is 95%) undergoes a frequency of 80kHz and a sound intensity of 0.6W / cm 2 , Ultrasonic treatment with a sound energy density of 0.5W / ml for 4min.
[0042] (2) Adding flocculant: adding polyaluminum chloride to the sonicated cyanobacteria at a ratio of 4% of the dry weight of cyanobacteria, and stirring evenly to obtain cyanobacteria with flocculant added.
[0043] (3) Filtration dehydration: the cyanobacteria added with flocculant in step (2) are dehydrated through a plate and frame filter press, the pore diameter of the filter cloth of the plate and frame filter press is about 10 μm, and the cyanobacteria dehydration is completed.
[0044]The capillary water absorption time of the untreated cyanobacteria in this embodiment is 365s, and the calorific value on a dry basis is 20.48 MJ / kg. ...
Embodiment 3
[0046] A method for cyanobacteria dehydration, comprising the following steps:
[0047] (1) Ultrasound: the salvaged cyanobacteria (the initial water content of the salvaged cyanobacteria is 99%) undergoes a frequency of 110kHz, and the sound intensity is 0-1.2W / cm 2 , Ultrasonic treatment with a sound energy density of 0.7W / ml for 5min.
[0048] (2) Adding a flocculant: adding polyferric chloride to the sonicated cyanobacteria at a ratio of 1% of the dry weight of the cyanobacteria, and stirring evenly to obtain cyanobacteria with flocculant added.
[0049] (3) Filtration dehydration: The cyanobacteria added with the flocculant in step (2) are dehydrated by pressure filtration through a chamber filter press, the pore diameter of the filter cloth of the chamber filter press is 15 μm, and the cyanobacteria dehydration is completed.
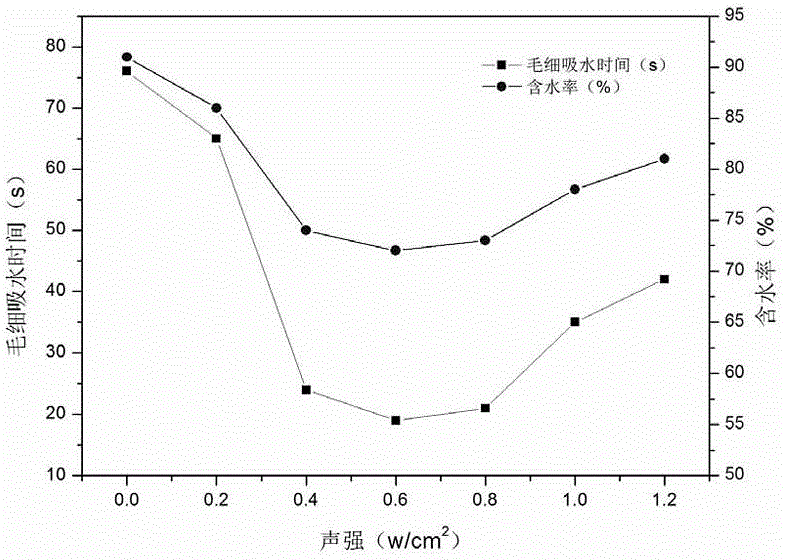
[0050] The capillary water absorption time of the untreated cyanobacteria in the present embodiment was 76s. See figure 1 .
[0051] From fig...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| sound intensity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| heating value | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com