Primary separation and culture method of human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells
A technique for stromal stem cells and culturing methods, applied in the field of primary separation and culturing of human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells, can solve the problems of decreased activity, long time consumption, low cell yield, etc., and achieves less cell damage, high cell viability, The effect of a large amount of stem cells
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0051] A primary isolation and culture method of human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells, specifically comprising the following steps:
[0052] 1. Primary isolation of human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells
[0053] Under sterile conditions, the fresh placenta discarded after delivery was placed in a sterile tray, the amniotic membrane was stripped from the placental tissue with surgical instruments, and washed several times with PBS buffer solution to remove residual blood. Cut the amnion tissue into 6×6cm2 in a 15cm glass dish, divide into 50mL centrifuge tubes (each tube contains amnion tissue 10-15cm), add 0.1-0.3% trypsin to 45mL. Transfer the centrifuge tube to a constant temperature shaker at 37°C, 150-300r / min, digest for 30min, and shake vigorously several times every 10min to remove epithelial cells. Transfer the trypsinized amnion tissue to a 250mL storage bottle, add 150mL PBS buffer solution, shake vigorously, and repeat this operation twice. The amnion tissue was ...
example 2
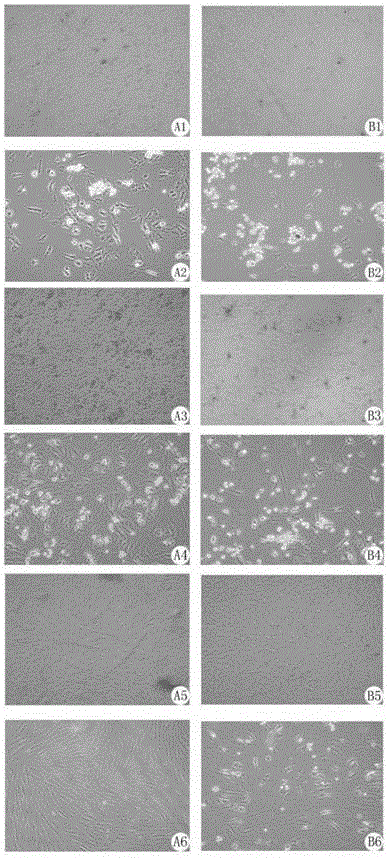
[0057] Flow cytometric identification of isolated amniotic stem cells
[0058] When the primary human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells grow to 80%-90%, collect the cells after trypsinization, take two 1.5ml EP tubes, each tube 1x10 6 Wash two cells with staining buffer (10% FBS+90% PBS), add 200 μl of staining buffer to each tube, add 5 μl of the following four antibodies CD45, CD59, HLADR, and CD90 to the sample, and add no antibody to the negative control. Incubate at 4°C for 20 minutes, wash twice with staining buffer, resuspend with 500 μl 1640 medium, collect 30,000 samples with flow cytometry, and detect the expression of surface markers CD45, CD59, CD90, HLA-DR, etc. . see attached results figure 1 .
[0059] From attached figure 1 It can be seen from the results that the sample expresses CD59 and CD90; low expression of HLA-DR and CD45, which is in line with the characteristics of mesenchymal stem cells. It can also be seen that this method can obtain mesenchymal st...
example 3
[0061] Proliferation curve of isolated stem cells
[0062] The hAMSCs of passage P2 were collected by trypsinization, and the cells were seeded in 96-well plates at 2000 cells / well. at 37°C, 5% CO 2 Continuous culture in the incubator for 7 days. The cells were tested on 1d, 3d, 5d, and 7d respectively. Add 10ul staining agent to the well to be tested, 37°C, 5% CO 2 Cultivate for 2h. The absorbance at 450 nm was measured with a microplate reader, and 6 replicates were made for each sample. The results are shown in Table 1.
[0063] Table 1
[0064]
1
2
3
4
5
6
average
Variance
1d
0.23
0.22
0.2
0.24
0.22
0.21
0.22
0.014142
3d
0.36
0.38
0.38
0.37
0.39
0.36
0.373333
0.012111
5d
0.72
0.69
0.71
0.68
0.69
0.7
0.698333
0.01472
7d
0.82
0.84
0.91
0.88
0.87
0.9
0.87
0.034641
[...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com