DNA analysis method for zooplankton, phytoplankton and zooplankton and phytoplankton specie composition and community structures
A technology for zooplankton and community structure, which is applied in biochemical equipment and methods, and the determination/inspection of microorganisms.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] The amplification effects of zooplankton 18s rDNA primers SSU F04 and SSU R22 and phytoplankton 23s rDNA primers p23SrV f1 and p23SrV r1 were verified:
[0038] The DNA of the cultured eukaryotic phytoplankton Chlorella and the prokaryotic phytoplankton Microcystis were extracted by CTAB method, and the cultured DNA of the zooplankton Hyapha vulgaris was extracted by SDS method.
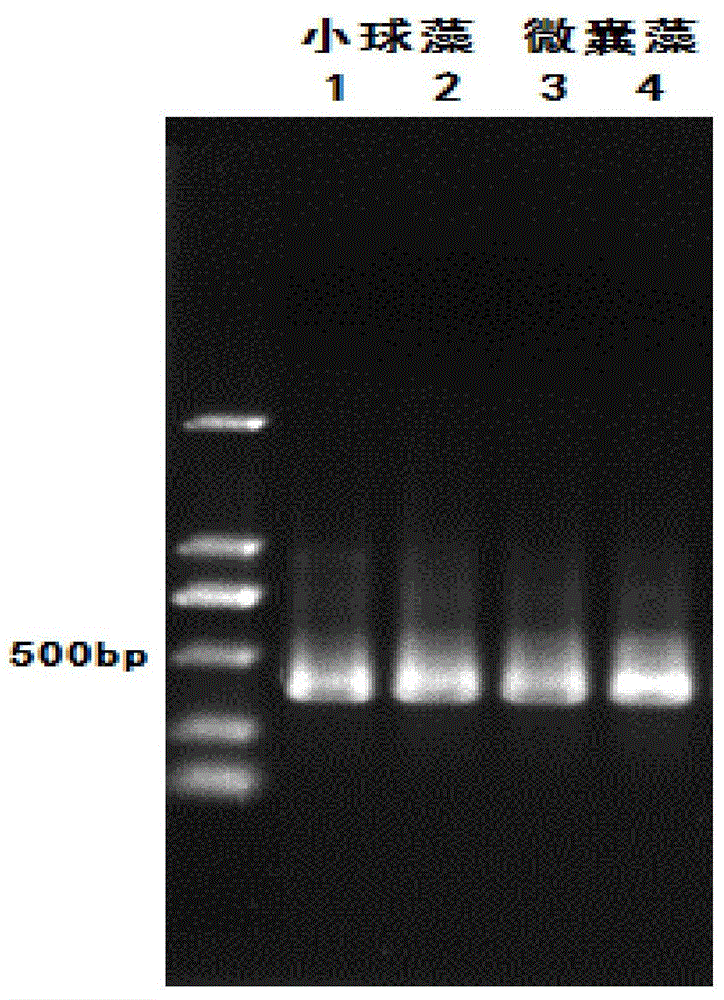
[0039] The phytoplankton 23s rDNA primers p23SrV f1 and p23SrV r1 were used to amplify the DNA of Chlorella and Microcystis. Bands 1, 2 (Chlorella) and 3, 4 (Microcystis) were obtained by gel electrophoresis, respectively. like figure 1 As shown, the amplification effect is good.
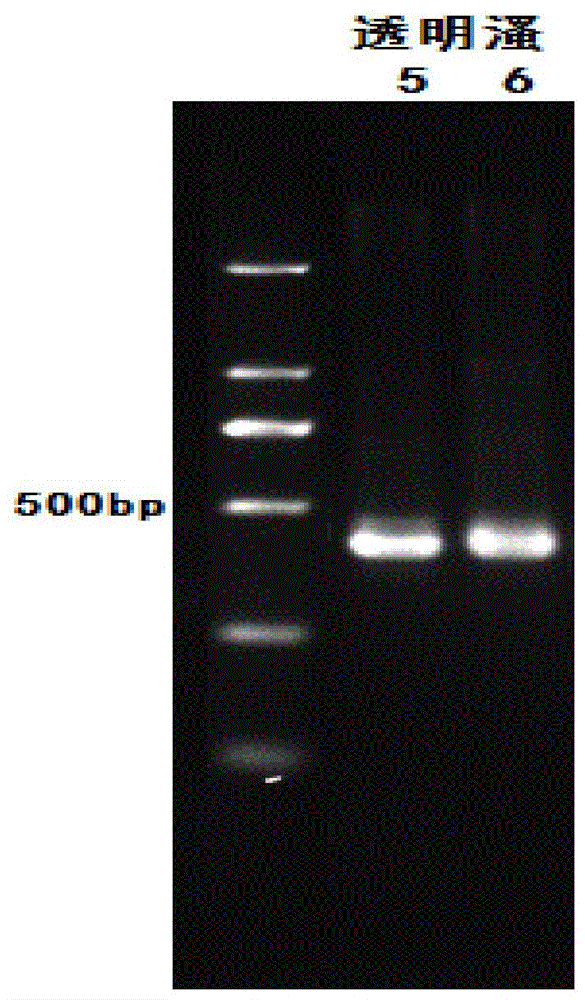
[0040] Use zooplankton 18s rDNA primers SSU F04 and SSU R22 to amplify the DNA of the flea, and gel electrophoresis to obtain bands 5 and 6, respectively, as shown in figure 2 As shown, the amplification effect is good.
Embodiment 2
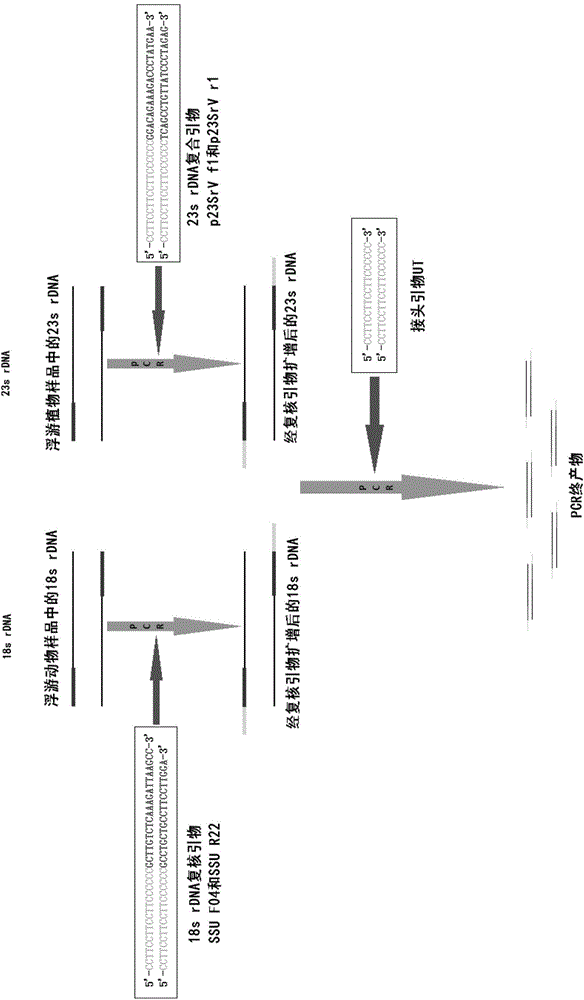
[0042] Verification of the amplification effect of composite primers combined with linker primers to amplify phytoplankton, the principle is as follows image 3 shown.
[0043] The DNAs of the above-mentioned Chlorella, Microcystis, and Phyllostachys vulgaris were mixed at equal concentrations to form an equal-concentration mixed DNA sample. It can be seen from the database query that the target fragments of Chlorella 23s rDNA and Phyllostachys hyalaeum 18s rDNA are about 395bp, The target fragment of Microcystis 23s rDNA is about 420bp.
[0044] The reaction system is 25μl system: 1.8mmol / lMgCl 2 , 200ummol / l dNTPs and 1.5U DNA polymerase, 300nmol / L universal primer UT, 2nmol / L each composite primer (UT-SSU F04 and UT-SSU R22; UT-p23SrV f1 and UT-p23SrV r1), 2.5μl 10×PCR buffer, sterilized H 2 O make up to 25 μl. The temperature conditions of the reaction: pre-denaturation at 94 °C for 2 min; denaturation at 94 °C for 30 s, annealing at 56 °C for 30 s, extension at 72 °C ...
Embodiment 3
[0047] Comparison of feeding habits of silver carp and bighead carp in Qiandao Lake
[0048] Step 1: Sample collection: Take 5 Qiandao Lake silver carp and 5 bighead carp, take the contents of the foregut and mix well, take 0.1 g and store it in a -20°C refrigerator for later use.
[0049] Step 2 DNA extraction
[0050] DNA extraction from foregut contents was performed using Qiagen's Fecal Genome Extraction Kit.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com