Modified process for cellulose fiber
A cellulose fiber modification technology, which is applied in the treatment process of cellulose fiber and the field of modification process of cellulose fiber, can solve the problems of high chroma of dyeing raffinate, large amount of alkali consumption, and difficult treatment of waste water, so as to avoid The effect of dye flocculation, uniform modification and sufficient modification
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0060] Modification process of cellulose fiber:
[0061] Put the cellulose fiber into the container, add water to the container, and then modify the cellulose fiber with two cationic modifiers, the small molecule quaternary ammonium salt cationic modifier and the high molecular quaternary ammonium salt cationic modifier , modified cellulose fibers are obtained after the modification treatment is completed; the small molecule quaternary ammonium salt cationic modifier is the epichlorohydrin parent derivative of the epoxy quaternary ammonium salt, and the high molecular quaternary ammonium salt cationic modified The main chain type polyepichlorohydrin dimethylamine.
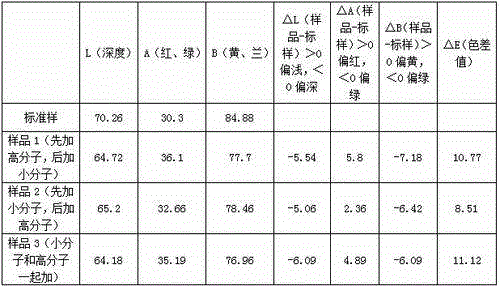
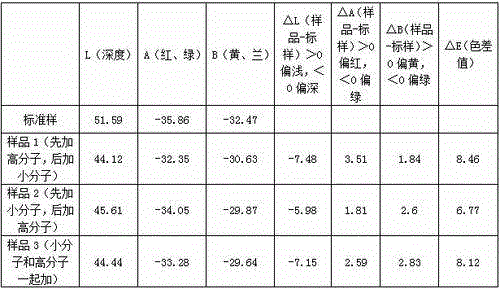
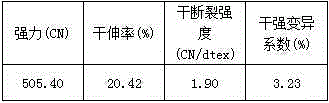
[0062] The above-mentioned process is the cellulose fiber modification process of the present invention, and the modified cellulose fiber with a nitrogen content of 0.16-0.38% is obtained. When the pH value of the fiber is 6.5-8.5, the Zeta electrode potential value is 5-26mV. Due to the small molecular weight of ...
Embodiment 2
[0064] Modification process of cellulose fiber:
[0065] Put the cellulose fiber into the container, add water to the container, and then modify the cellulose fiber with two cationic modifiers, the small molecule quaternary ammonium salt cationic modifier and the high molecular quaternary ammonium salt cationic modifier , modified cellulose fibers are obtained after the modification treatment is completed; the small molecule quaternary ammonium salt cationic modifier is the epichlorohydrin parent derivative of the epoxy quaternary ammonium salt, and the high molecular quaternary ammonium salt cationic modified The main chain type polyepichlorohydrin dimethylamine.
[0066] The cellulose fibers are selected from viscose filaments, viscose staple fibers, modal, tencel, cotton fibers, yarns and fabrics made from the aforementioned cellulose fibers.
[0067] The modification process of the present invention is applicable to all kinds of cellulose fibers, and also includes twisted...
Embodiment 3
[0069] The small molecule quaternary ammonium salt cationic modifier of the present invention is the epichlorohydrin parent derivative of epoxy quaternary ammonium salt;
[0070] The polymer quaternary ammonium salt cationic modifier of the present invention is a main chain type polyepichlorohydrin dimethylamine.
[0071] Epichlorohydrin parent derivatives of epoxy quaternary ammonium salts:
[0072]
[0073] Main chain polyepichlorohydrin dimethylamine:
[0074]
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| electric potential / voltage | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com