Lactobacillus propagation solution preparation method and inoculant preparation method in industrial salted vegetable production
A technology of salted vegetables and lactic acid bacteria, applied in the direction of lactobacillus, food preparation, bacteria used in food preparation, etc., can solve the problems of easy contamination of miscellaneous bacteria, high cost, cumbersome process, etc., and achieve reduced production costs, low cost, The effect of simple preparation procedures
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0020] Example 1: A lactic acid bacteria expansion solution in the production of industrialized salted vegetables: collect 1L of salted water in the radish salted fermentation tank (white radish salted for 2~5d) (scale up according to production needs), and let it stand for about 1h To remove large particles, get 800~900mL of liquid matrix, dissolve it with any one of glucose, lactose, and sucrose at 1%~4% (w / v), heat and boil for 10~40min to sterilize, and cool to 30°C Left and right, measure its pH and salinity.
[0021] It can be seen from the results that the pH of the expansion medium is 6.03 and the salinity is 3.31%, which can be used as a culture medium for lactic acid bacteria.
example 2
[0022] Example 2: A lactic acid bacteria expansion solution in the production of industrialized salted vegetables: collect 1L of salted water in the radish salted fermentation tank (white radish salted for 2~5 days) (scale up according to production needs), and let it stand for about 1 hour To remove large particles, get 800~900mL of liquid matrix, dissolve it with any one of glucose, lactose, and sucrose at 1%~4% (w / v), heat and boil for 10~40min to sterilize, and cool to 30°C about.
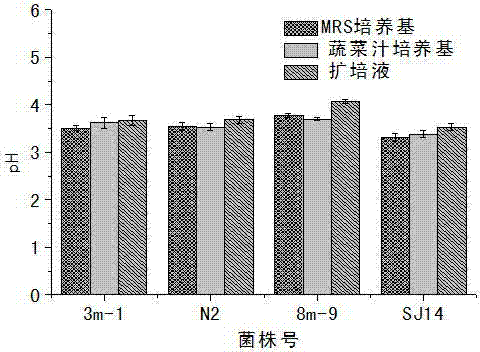
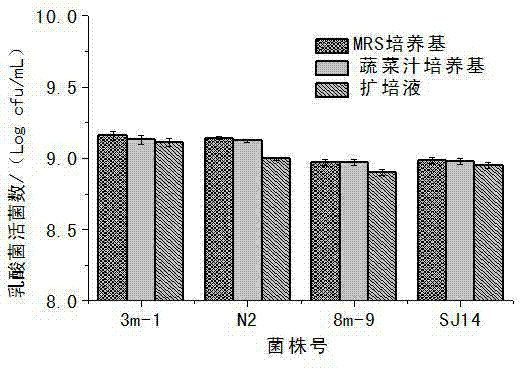
[0023] Inoculate the activated Lactobacillus plantarum 3m-1, Lactobacillus plantarum N2, Leuconostoc enterococci 8m-9, Weissella esophagus SJ14 at the same pH, MRS culture medium, radish juice culture medium and expansion medium with high salinity were cultured at 30°C, and the pH of the fermentation broth and the number of viable lactic acid bacteria were measured for 48 hours.
[0024] It can be seen from the results that the pH and the number of viable lactic acid bacteria were 3.67, 3.67, ...
example 3
[0025] Example 3: A lactic acid bacteria expansion solution in the production of industrialized salted vegetables: collect 1L of salted water in the radish salted fermentation tank (white radish salted for 2~5 days) (scale up according to production needs), and let it stand for about 1 hour To remove large particles, get 800~900mL of liquid matrix, dissolve it with any one of glucose, lactose, and sucrose at 1%~4% (w / v), heat and boil for 10~40min to sterilize, and cool to 30°C about.
[0026] 1) Strain activation: Inoculate the preserved lactic acid bacteria strains (Lactobacillus plantarum 3m-1, Lactobacillus plantarum N2, Leuconostoc enterococcus 8m-9, Weissella angus SJ14) into MRS liquid medium for Activation (30°C, cultured for 24 hours) to obtain activated seed liquid.
[0027] 2) Primary strain cultivation: put the activated seed solution into a conical flask containing 200mL expansion solution at 0.5%~5% (v / v) inoculum, and culture it statically at 30°C for 18~24h to...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com