A Desulfurization Bacteria Efficiently Degrading DBTs and Its Application in Desulfurization
A technology for removing sulfur elements, applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, bacteria, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve the problems of poor tolerance to organic solvents, low desulfurization efficiency, etc., and achieve high desulfurization ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] Embodiment 1: strain screening
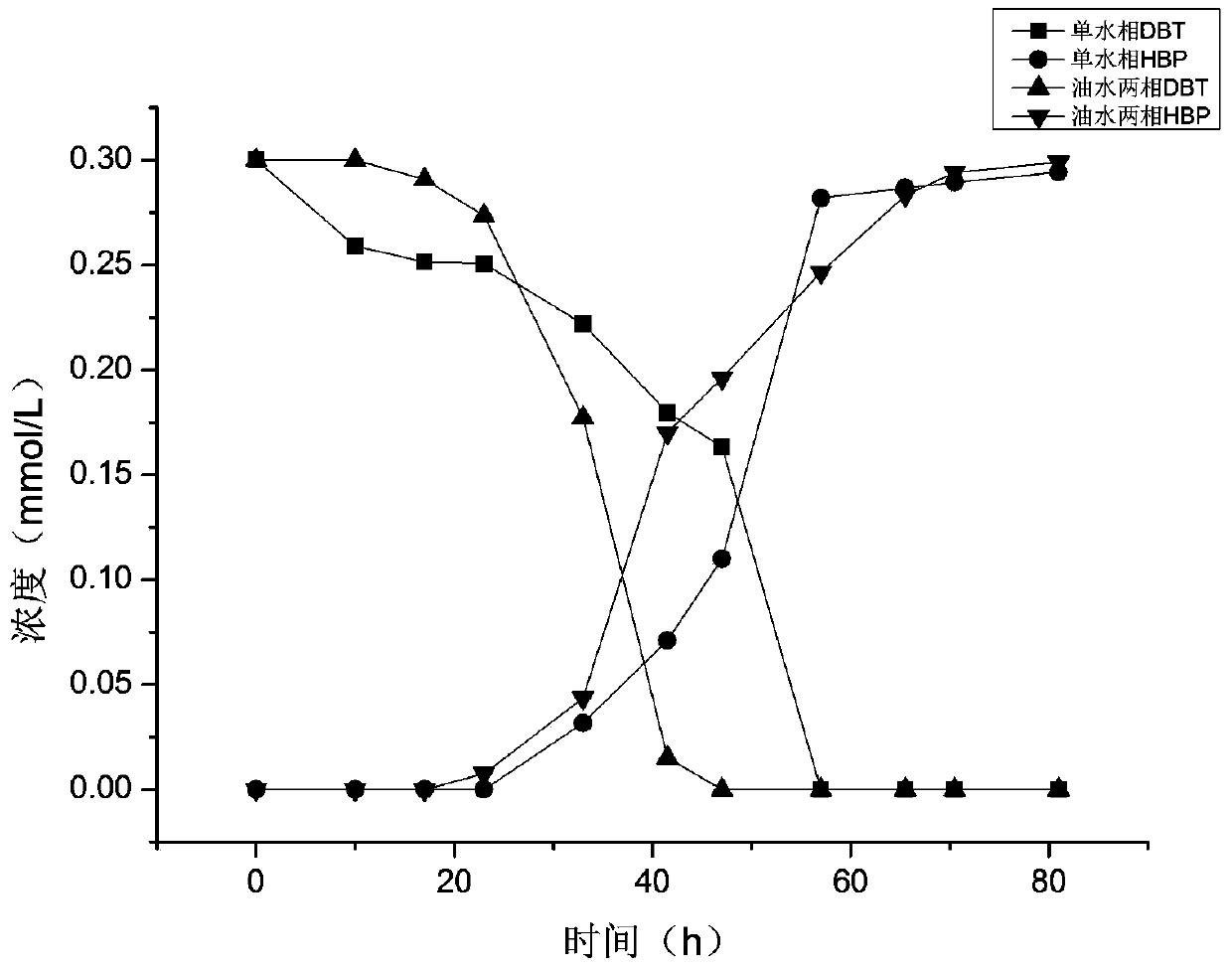
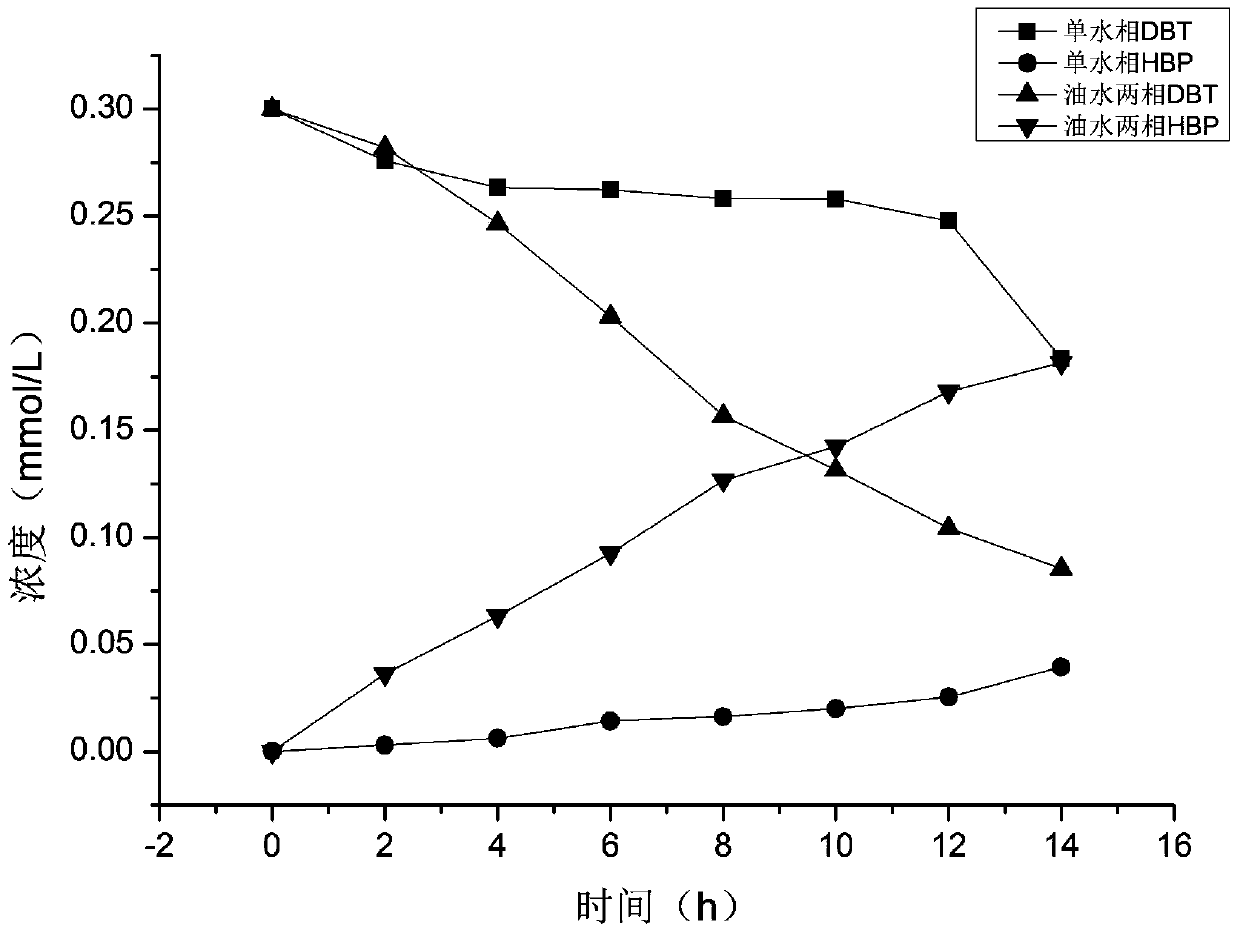
[0024] Dissolve about 2g of crude oil-contaminated soil in Karamay Oilfield, Xinjiang, into 100ml of BSM-DBT culture solution, enrich and cultivate for 4 days, repeat 3-4 times, then take the culture solution and extract it with ethyl acetate for high-pressure liquid phase analysis Its metabolites, for the culture solution containing dihydroxybiphenyl, use the line drawing method and coating method to separate in the BSM-DBT solid selection medium, after 3 days, the colony is formed, pick a single colony and put it into the BSM-DBT liquid Cultivate in the culture medium, and measure the metabolites with the above method after four days of cultivation, and repeat the purification for 4 times to obtain the pure strains of the strains that can metabolize dibenzothiophene and convert to dihydroxybiphenyl.
Embodiment 2
[0025] Embodiment 2: bacterial strain identification
[0026] The entire genome of the pure culture was extracted using a bacterial whole genome rapid extraction kit, and PCR was performed with 16S rDNA universal primers. The strain was identified as Gordonia sp. and named Gordoniasp.JDZX5.
Embodiment 3
[0027] Embodiment 3: Physiological and biochemical studies of bacterial strains
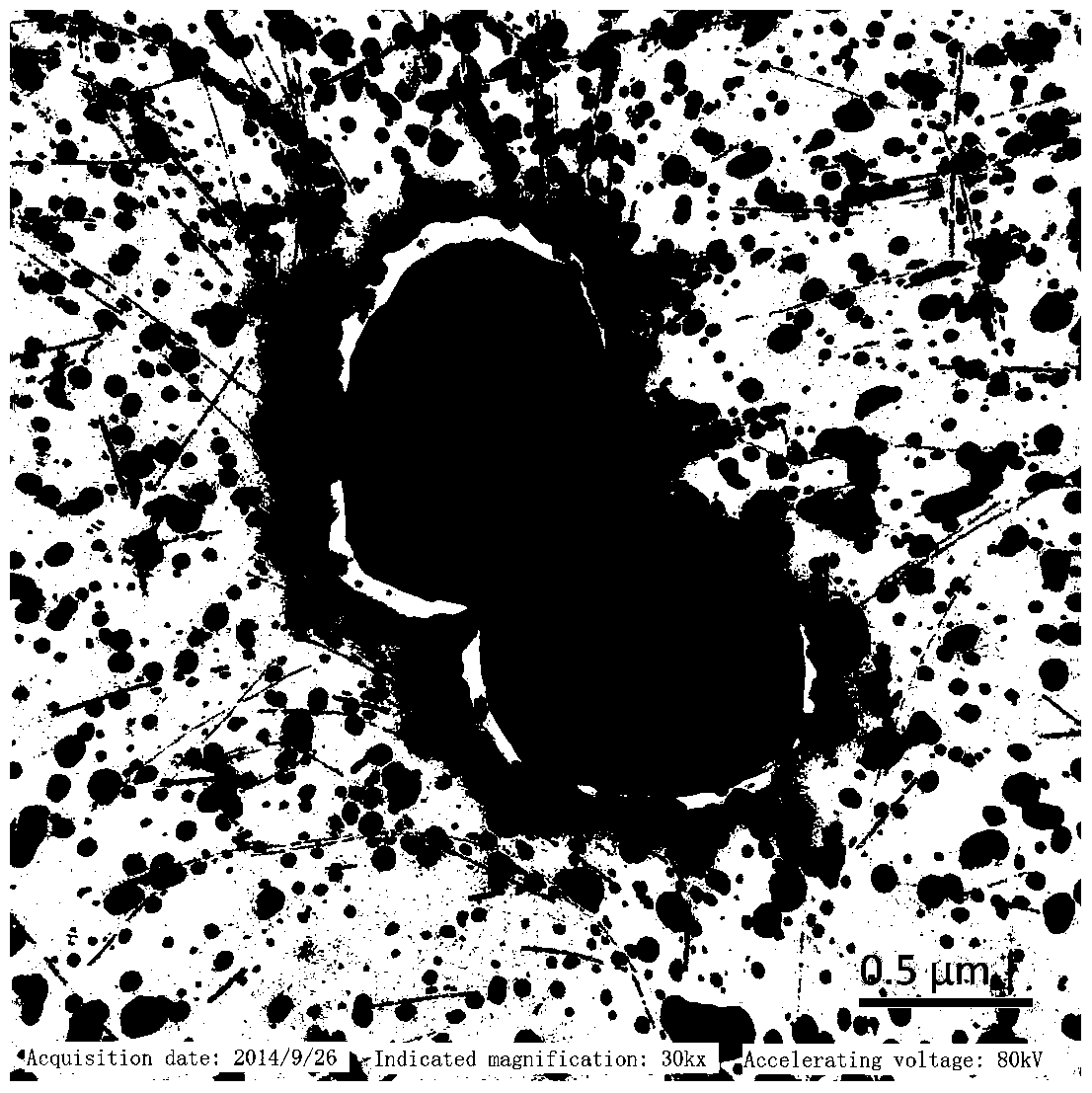
[0028] The morphology of the above-mentioned JDZX5 was observed by transmission electron microscope as follows: figure 1 . It can be seen from the figure that the bacterium is short rod-shaped and has a capsule. The optimum growth temperature of the strain is 30°C, and it can grow well at 28-37°C. Take the initial pH 3.0, 4.0, 5.0, 6.0, 7.0, 8.0, 9.0, 10.0 and 11.0 to culture at the optimum temperature, and determine the optimum growth pH 7.0. The bacterium has stronger tolerance to alkali than acid, and can grow well at pH 6-10. When the pH is below 4.0, the bacterium hardly grows, and when the pH is 11, it can still grow slowly.
[0029] Through the physiological and biochemical experiments such as Gram staining, capsule staining, oxidase test and contact enzyme test, it is determined that the bacteria is Gram-positive, has no flagella, has a capsule, is negative for oxidase, and is positive...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com