Zirconium alloy material for light water reactor under higher burnup
A zirconium alloy and weight technology, applied in the field of zirconium alloy materials, can solve the problems of decreased corrosion resistance, uneven growth, poor plastic processing ability of zirconium alloys, etc., to improve corrosion resistance, mechanical properties, and hydrogen absorption. performance effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 2
[0079] The preparation methods of Example 2 and Example 3 are the same, and the only difference is that the components are different, as listed in Table 1. The components of the zirconium alloy in Example 2 are: 0.25% by weight of tin, 1.00% by weight of niobium, 0.10% by weight of iron, 0.13% by weight of oxygen, and 0.05% by weight of copper; the balance is zirconium.
Embodiment 3
[0080] The components of the zirconium alloy in Example 3 are: 0.25% by weight of tin, 1.00% by weight of niobium, 0.10% by weight of iron, 0.13% by weight of oxygen, 0.05% by weight of vanadium, and 0.05% by weight of copper; the balance is zirconium.
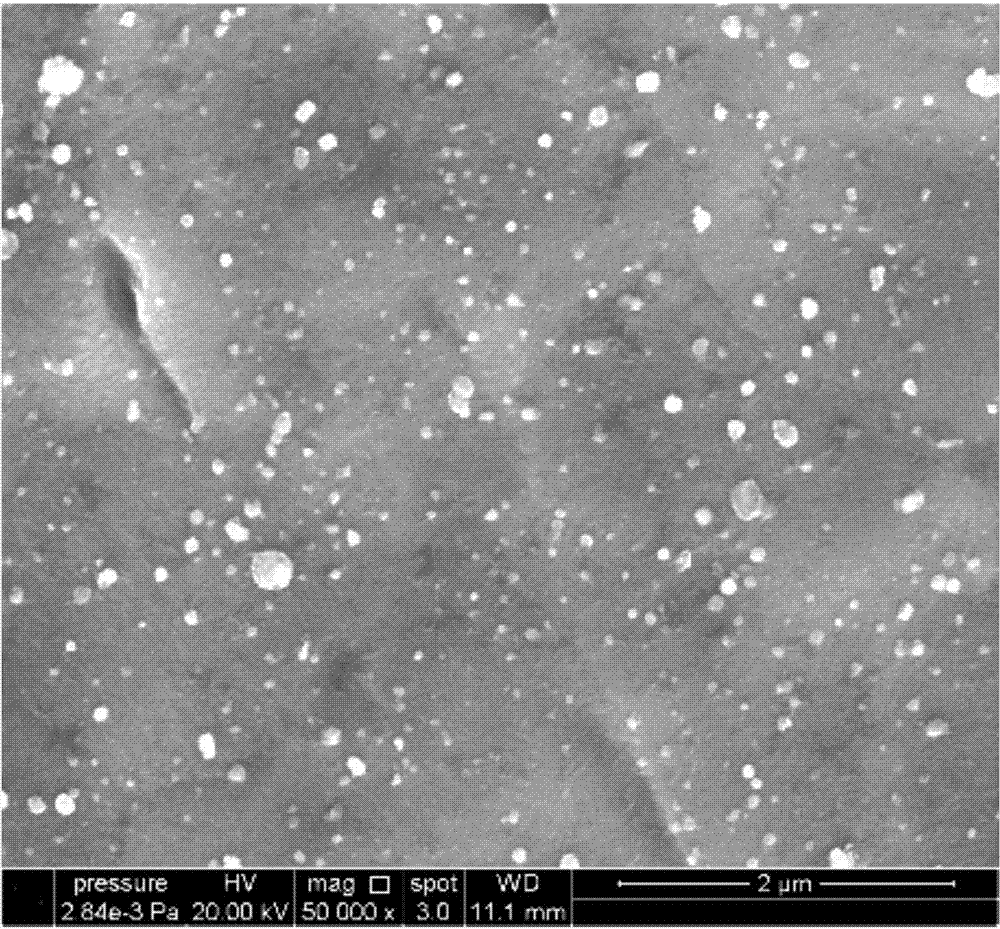
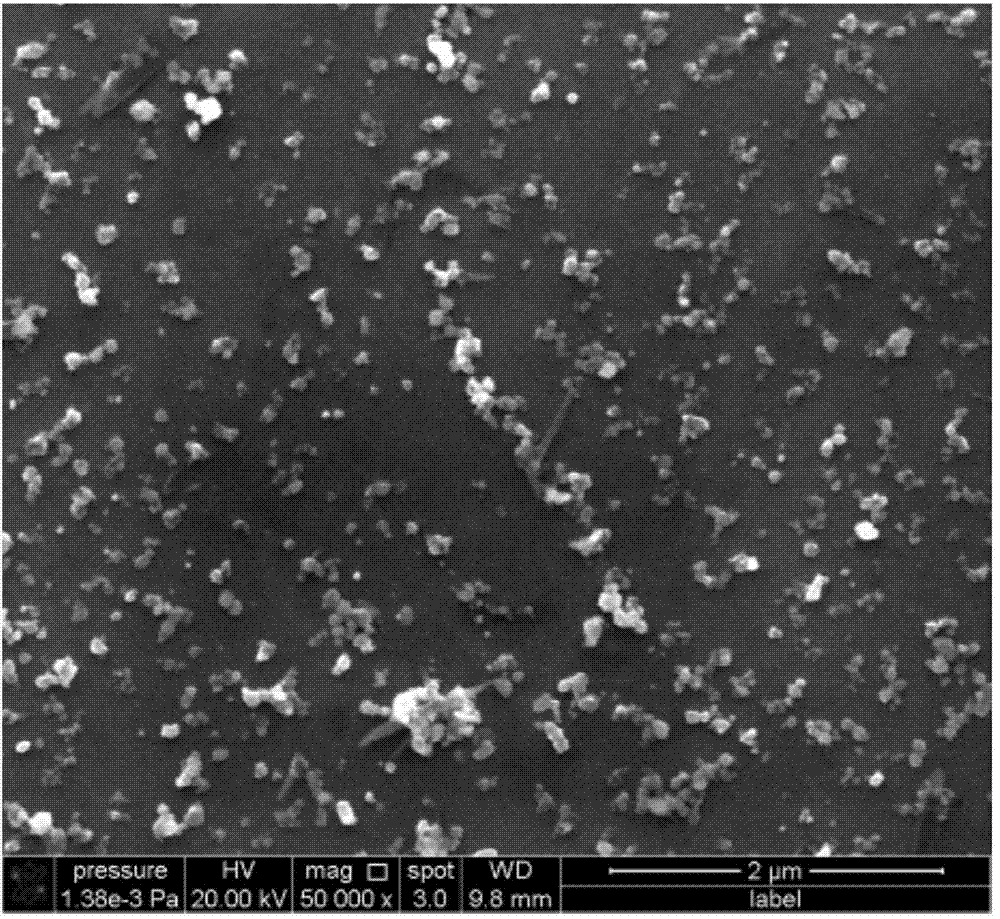
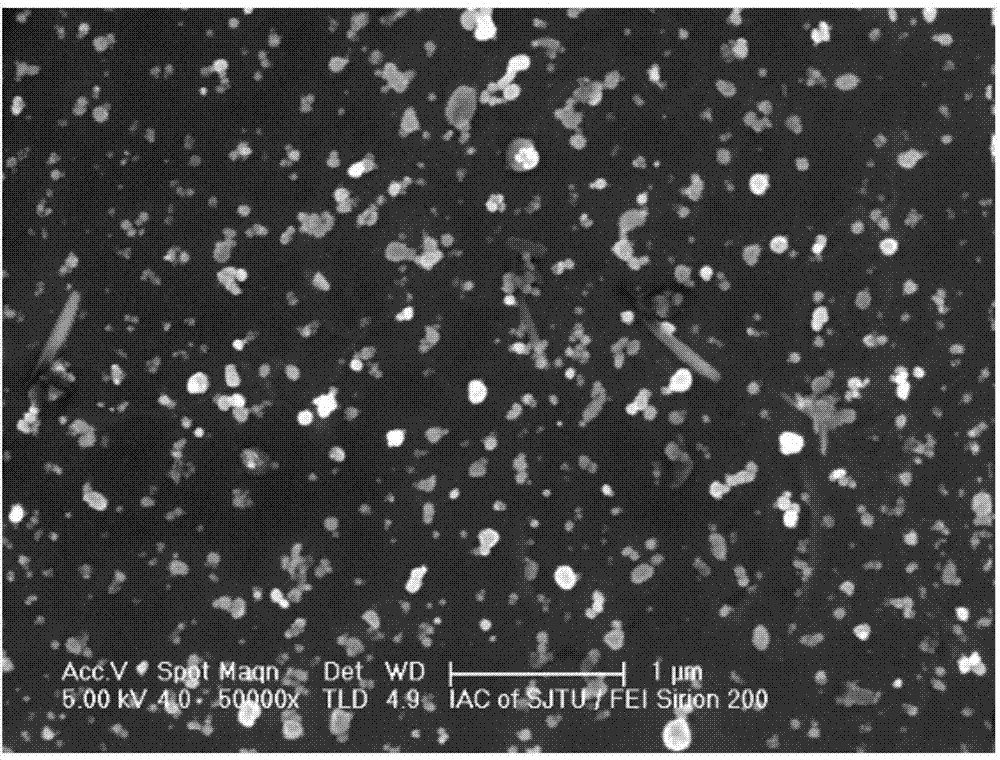
[0081] After the above processing, the performance of zirconium alloy is better. The study found that the average particle size of the second phase particles of zirconium alloys is 50-70nm, and the area share is about 10%, which shows that the second phase particles are small and large in number, which makes the zirconium alloys have better corrosion resistance. The average particle size refers to the average size of the second-phase particles participating in statistics in a plane. For the second-phase particles with irregular shapes, the processing method of measuring from two different directions at the same time and then taking the average value is adopted. The area share refers to the percentage of the area of the s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com