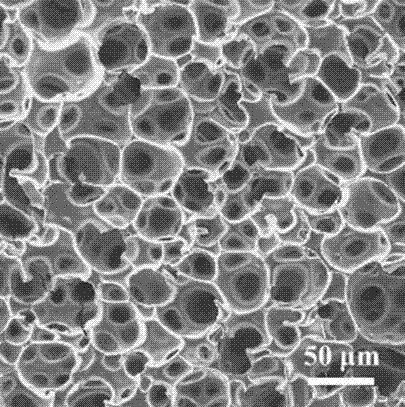
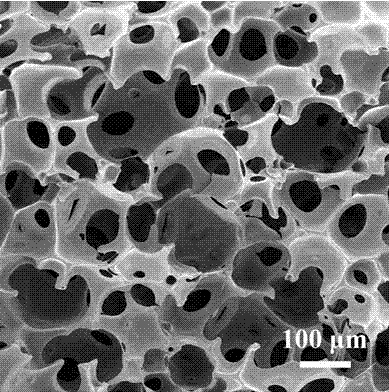
Method for preparing through-hole polymer porous aquagel by using graphene oxide (GO)
A porous hydrogel and polymer technology, applied in the field of materials, can solve problems such as limiting the application of porous hydrogels, and achieve the effects of low cost, good swelling performance and adsorption performance, and wide applicability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] 1. Disperse graphene oxide (GO) in water to prepare an aqueous solution with a mass fraction of 0.5%. The average size of the GO sheet is 1000 nm. The ionic surfactant cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) was added, and its mass accounted for 6% of the GO mass. The reaction was stirred at room temperature for 1 h, then centrifuged and washed three times, and dried in a vacuum oven at 60 °C for 24 h to obtain the modified GO.
[0022] 2. The above modified GO was ultrasonically dispersed in water for 30 min, and the mass of water was 500 times that of GO; acrylic monomer was added to the aqueous dispersion of GO, and its mass was 360 times that of GO; then cross-linking was added. N,N'-methylenebisacrylamide, the mass of which is 15 times the mass of GO; and potassium persulfate, an initiator, whose mass is 12 times that of GO; and finally water is added to control the mass of GO to account for the total amount of water in the water phase. 0.08% of mass.
[0023] 3. A...
Embodiment 2
[0026] 1. The experimental device and operation are the same as in Example 1, except that the GO aqueous solution in Example 1 was changed to GO ethanol solution, and the average size of GO sheets was changed from 1000 nm to 600 nm; the ionic surfactant cetyltrimethyl Ammonium bromide was changed to amino modifier dodecylamine, 6% of GO mass of lipophilic modifier was changed to 80%, and stirring time of 1 h was changed to 12 h.
[0027] 2. The experimental device and operation are the same as in Example 1, except that the mass of water in Example 1 is 500 times that of GO and changed to 100 times that of GO; the monomer acrylic acid is changed to acrylamide, and its mass is 75 times that of GO; cross-linking The agent N,N'-methylenebisacrylamide was changed to polyethylene glycol diacrylate, and its mass was 4 times that of GO; the initiator potassium persulfate was changed to ammonium persulfate, and its mass was 3 times that of GO ; Control the mass of GO to 0.08% of the to...
Embodiment 3
[0031] 1. The experimental device and operation are the same as in Example 1, except that the GO aqueous solution in Example 1 was changed to GO N, N-dimethylformamide solution, and the average size of GO sheets was changed from 1000 nm to 50 nm; ionic surface activity The agent cetyltrimethylammonium bromide was changed to isocyanate modifier phenyl isocyanate, the mass of lipophilic modifier was changed to 200% of 6% of the mass of GO, and the stirring time was changed from 1 h to 24 h.
[0032]2. The experimental device and operation are the same as in Example 1, except that the mass of water in Example 1 is 500 times that of GO; the monomer acrylic acid is changed to N-vinylpyrrolidone, and its mass is 25 times that of GO ; The crosslinking agent N, N'-methylenebisacrylamide was changed to polyethylene glycol dimethacrylate, and its mass was twice that of GO; the initiator potassium persulfate was changed to azobisisobutyramidine salt Acid, its mass is 1 times the mass of ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Aperture | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Aperture | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com