Expression of enzymes in yeast for lignocellulose derived oligomer CBP
A lignocellulose and xylanase technology, applied in the direction of enzymes, biofuels, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve the problem of expensive external enzyme addition
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
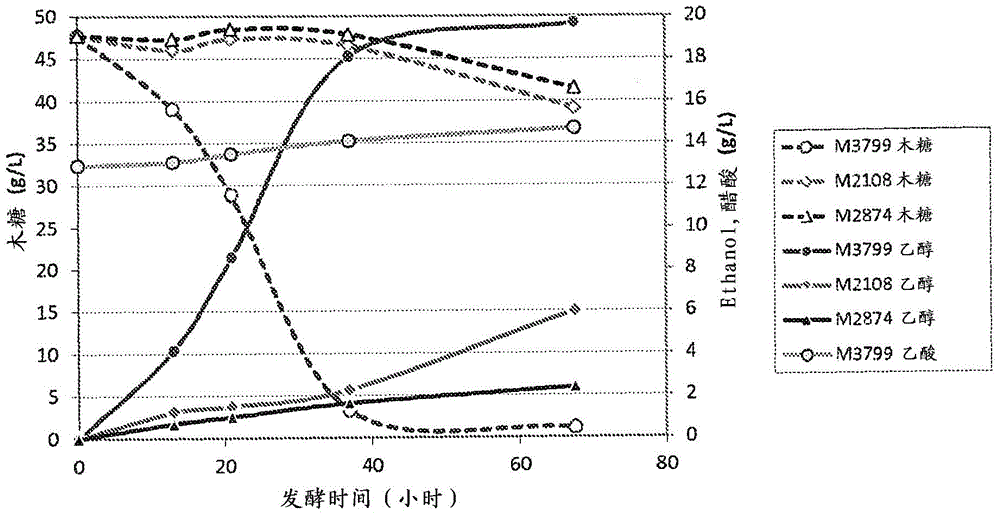
[0393] Production of M3799 and M3059, robust and efficient xylose-utilizing Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains
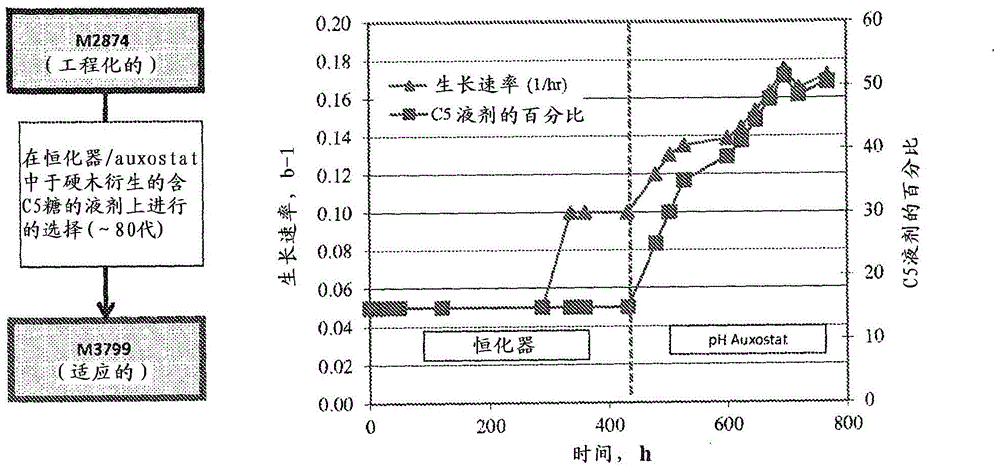
[0394] The strains described in U.S. Application No. 61 / 557,971, filed November 10, 2011, and International Application No. PCT / US2012 / 064457, filed November 9, 2012 (both of which are incorporated herein by reference) M2874, which is a xylose-utilizing derivative of the robust S. cerevisiae strain M2390, was engineered to improve its performance on concentrated C5-containing liquors derived from hardwoods. To achieve this goal, the strains were subjected to two forms of continuous culture (chemostat and pH auxostat), with the results as figure 2 described in.
[0395] The soluble sugars produced in the process were washed out of the solids by hardwood chips pretreated at a severity of 3.8, in a laboratory autoclave at 121 °C with 0.5% H 2 SO 4 Hydrolyze them for 3 hours, followed by 15M NH 4 OH to adjust the pH to 5.8 to produce a C5-containing liquor. The solu...
Embodiment 2
[0400] Characterization of accessory cellulase expression and activity
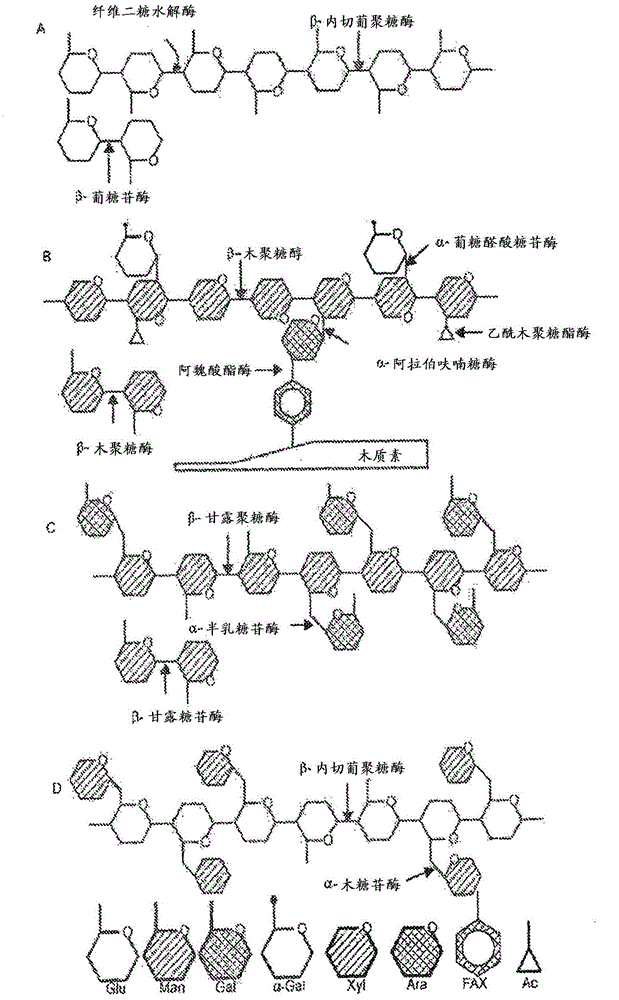
[0401] Soluble oligomers extracted from hardwood after pretreatment consist of various sugars linked in multiple ways. Linkages require different types of enzymes to hydrolyze them into their constituent monosaccharides. Figure 5 Several oligomers presumed to be present in hardwood-derived oligomers based on a review of the literature related to the composition of hardwoods are presented (e.g. Wilfor (2005) Wood Sci Tech; Teleman (2003) Carbohydrate Res; Shallom (2003) Curr Op Biotech ; Spanikova (2006) FEBS Letters; Rowell, RM. Handbook of Wood Chemistry and Composites. London: Taylor & Francis (2005)), and the general types of enzymes expected to hydrolyze these types of bonds.
[0402] Extracted forms of oligomers, especially xylooligomers, are noteworthy as potent inhibitors of cellulase during cellulose hydrolysis (Qing, Q., Yang, B., Wyman, C.E. Xylooligomers are strong inhibitors of cellulose hy...
Embodiment 3
[0508] Generation of engineered strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for enzyme expression and integrated bioprocessing of hardwood-derived soluble oligomers
[0509] As described above, a group of enzymes was discovered by screening various enzyme types and several amino acid sequences for each active type capable of hydrolyzing soluble oligomers isolated from lignocellulose with very high efficiency. The next set of enzymes selected for strain engineering was based on these data.
[0510] Table 13. Enzymes selected for CBP strain construction
[0511]
[0512] Using U.S. Application No. 61 / 557,971, filed November 10, 2011, International Application No. PCT / US2012 / 064457, and International Publication No. WO2011 / 140386, filed November 9, 2012 (these applications and publications are adopted Several strains were generated by the method described in (incorporated herein by reference) for the integration of genetic element islands into S. cerevisiae. The strains produced to ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com