Preparation recipe and preparation method of low-temperature anti-sulfur SCR (Selective Catalytic Reduction) catalyst
An SCR catalyst and catalyst technology, applied in the field of catalytic chemistry, can solve the problems of reducing the life of the catalyst, the efficiency of the catalyst, and energy consumption, and achieve the effects of increasing the service life, shortening the drying process, and reducing energy consumption.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
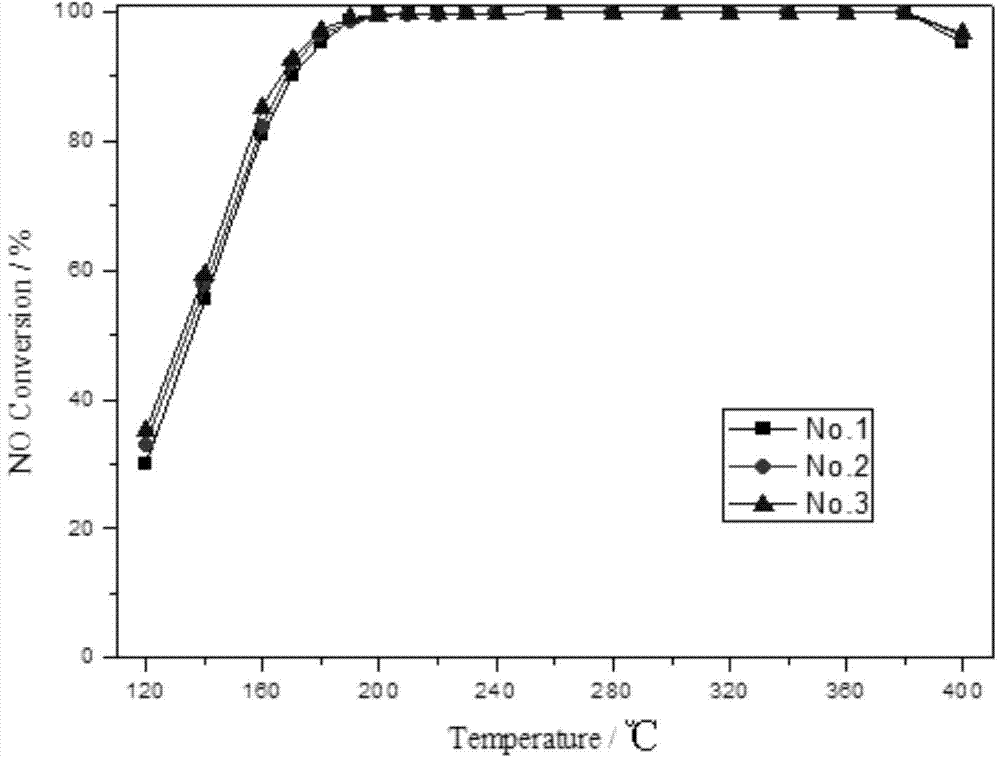
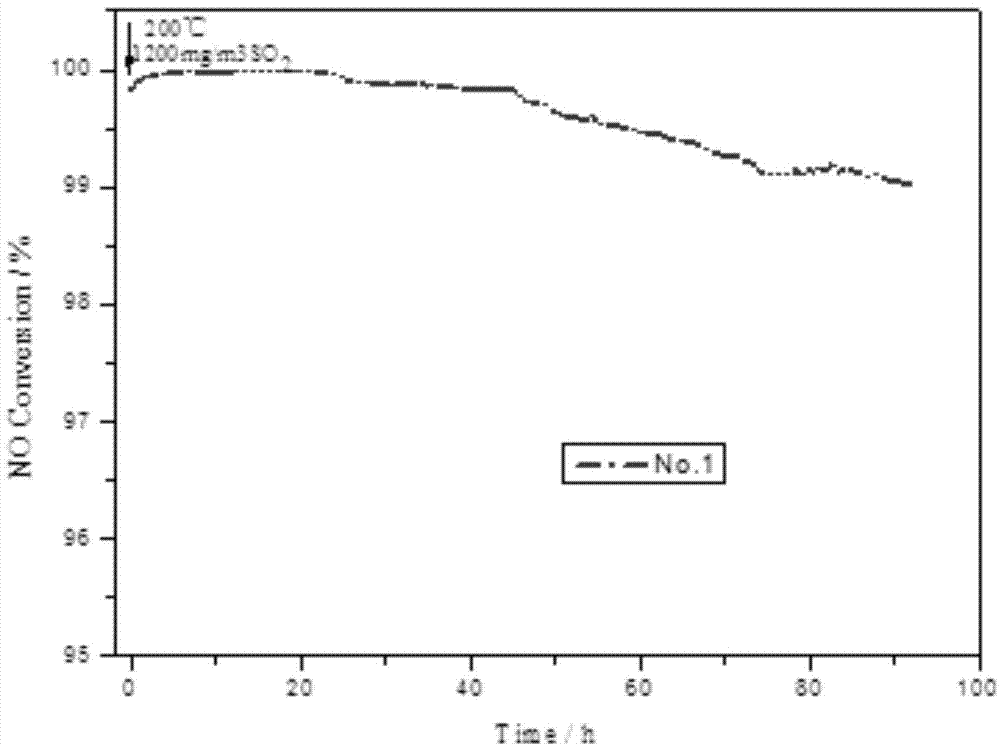
[0027] Dissolve 2g of oxalic acid in 50g of deionized water and stir to dissolve at 50℃. Add 1g of ammonium metavanadate and continue to stir until it becomes a blue clear solution; 0.3g of triammonium phosphate and 1.5g of ammonium tungstate And 0.15g of ammonium bromide were sequentially added to the resulting solution, and continued to stir at 50℃, all dissolved until it became a black solution; add 20g of TiO 2 The carrier was slowly added to the above solution and stirred at 40°C until it became viscous; the obtained viscous solid was placed in a muffle furnace without drying and calcined at 250°C for 2 hours. Then it is calcined at 450°C for 5 hours, naturally cooled to room temperature, and sieved to 20-120 meshes for use to obtain 1# catalyst.
example 2
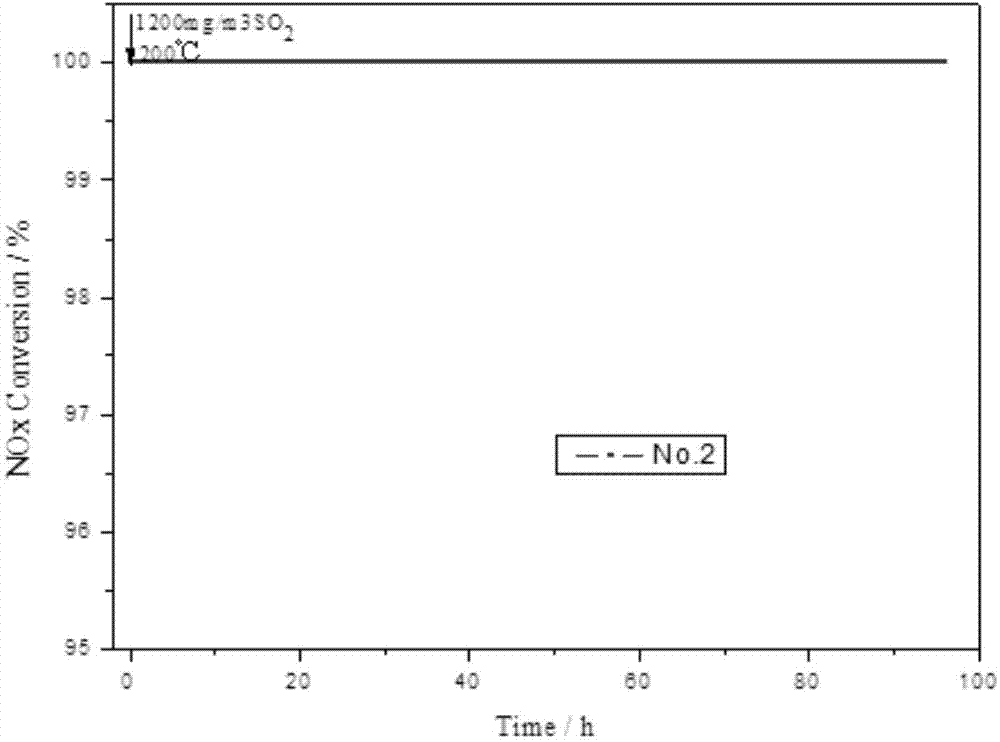
[0029] Dissolve 4g of oxalic acid in 100g of deionized water and stir to dissolve at 50℃. Add 2g of ammonium metavanadate and continue to stir until it becomes a blue clear solution; add 0.6g of triammonium phosphate, 3g of ammonium tungstate and 0.3g of ammonium bromide was added to the resulting solution one by one, and stirring was continued at 50°C, all dissolved until it became a black solution; 40g of TiO 2 The carrier was slowly added to the above solution and stirred at 40°C until it became viscous; the obtained viscous solid was placed in a muffle furnace without drying and calcined at 250°C for 2 hours. Then it is calcined at 480°C for 5 hours, naturally cooled to room temperature, and sieved to 20-120 meshes for later use to obtain 2# catalyst.
example 3
[0031] Dissolve 4g of oxalic acid in 100g of deionized water and stir to dissolve at 50℃. Add 2g of ammonium metavanadate and continue to stir until it becomes a blue clear solution; add 0.6g of triammonium phosphate, 3g of ammonium tungstate and 0.35g of ammonium bromide was added to the resulting solution in sequence, and stirring was continued at 50°C, all dissolved until it became a black solution; 40g of TiO 2 The carrier was slowly added to the above solution and stirred at 40°C until it became viscous; the obtained viscous solid was placed in a muffle furnace without drying, and calcined at 250°C for 2 hours. Then it is calcined at 450°C for 5 hours, naturally cooled to room temperature, and sieved to 20-120 meshes for use to obtain 3# catalyst.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com