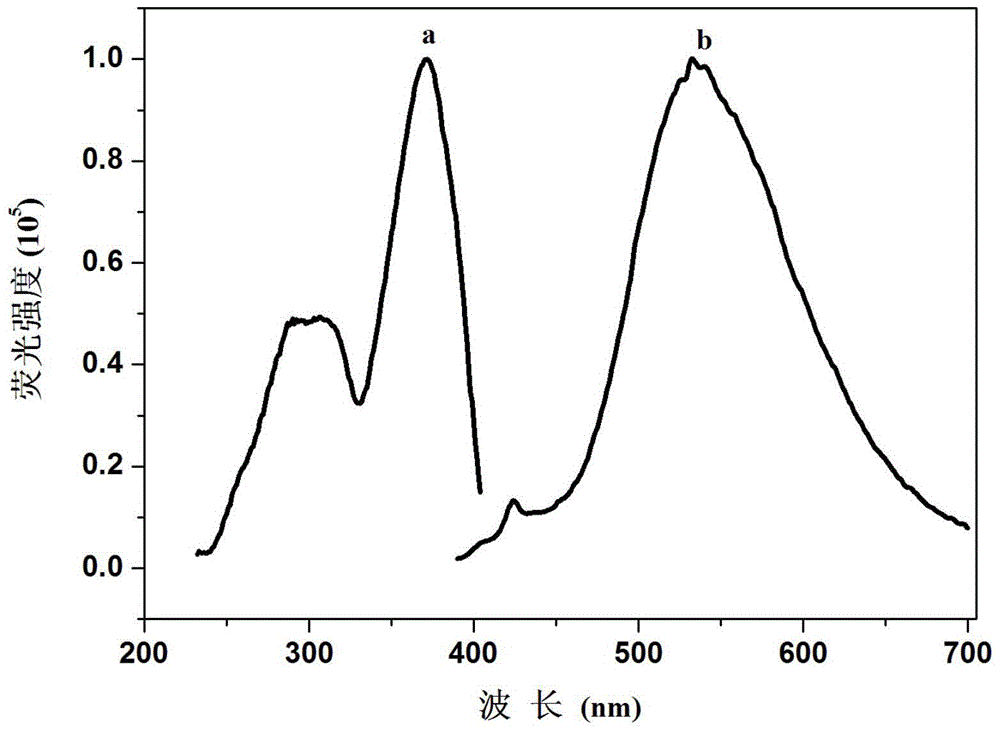
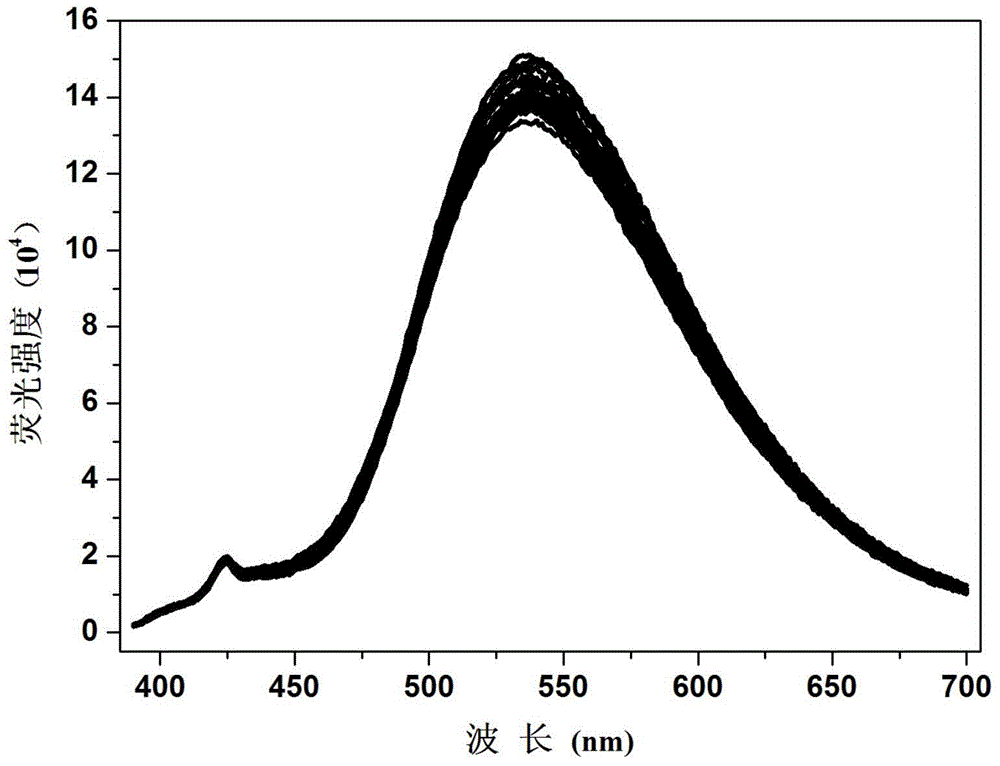
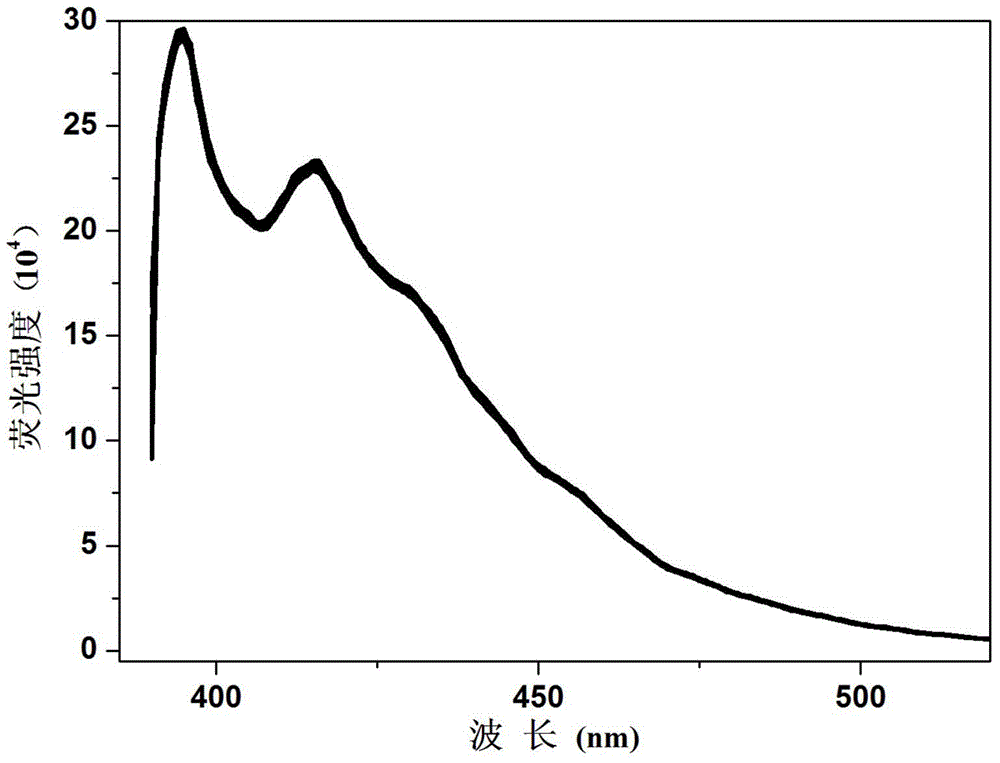
Fluorescent compound and fluorescent probe based on fluorescent compound as well as preparation method and application of visible test paper
A fluorescent compound and compound technology, applied in the field of fluorescent compounds, can solve problems such as difficulty in dissolving, affecting processing and performance, and achieve the effects of increasing solubility, good photochemical stability, and strong van der Waals stacking interaction.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0059] 1. Preparation of fluorescent compounds
[0060] 1) Preparation of compound 1
[0061] Under an argon protective atmosphere, iodine, potassium iodate and concentrated sulfuric acid aqueous solution with a mass fraction of 9%-12% are respectively added to the acetic acid solution of p-methoxybenzene. Wherein the molar ratio of p-methoxybenzene, iodine, potassium iodate, acetic acid and concentrated sulfuric acid is: 1: (0.8-1.2): (0.2-0.5): (80-100): (2-3). React at 70-80°C for 8-12 hours, transfer the reaction solution to saturated sodium thiosulfate solution and stir, filter with suction, wash with ethanol, and dry in vacuum to obtain a white solid. Its reaction equation is as follows:
[0062]
[0063] 2) Preparation of compound 2
[0064] Under the protection of argon, compound 1 was dissolved in dichloromethane, and boron tribromide was added dropwise to the solution at -78°C. After the dropwise addition, stir at room temperature for 14-18 hours. Wherein the...
Embodiment 1
[0101] 1. Preparation of fluorescent compounds
[0102] ①Synthesis of compound 1
[0103] Under an argon atmosphere, 6 g of p-methoxybenzene, 12 g of iodine, 3.66 g of potassium iodate and 45 mL of 10% sulfuric acid aqueous solution were added to 200 mL of acetic acid solution. The molar ratio of p-methoxybenzene, iodine, potassium iodate, acetic acid and concentrated sulfuric acid is 1:1.1:0.4:80:2. React at 80°C for 10 hours. After the reaction, transfer the reaction solution to sodium thiosulfate Stir in a saturated solution, filter with suction, and dry in vacuo to obtain a white solid.
[0104] ② Synthesis of Compound 2
[0105] Under an argon atmosphere, 15.6 g of compound 1 was dissolved in 100 mL of dichloromethane, and 8.18 mL of boron tribromide was added dropwise to the solution at -78°C. Wherein the molar ratio of compound 1, boron tribromide and dichloromethane is: 1:2.2:40. The reaction was stirred for 16 hours. After the reaction was completed, the reaction ...
Embodiment 2
[0124] In this example, in step ① of the synthesis of compound 1, 6 g of p-methoxybenzene, 9.6 g of iodine, 3.66 g of potassium iodate and 45 mL of 10% sulfuric acid aqueous solution were added to 200 mL of acetic acid solution. The molar ratio of p-methoxybenzene, iodine, potassium iodate, acetic acid and concentrated sulfuric acid is 1:0.88:0.4:80:2. React at 80°C for 10 hours. After the reaction, transfer the reaction solution to sodium thiosulfate Stir in a saturated solution, filter with suction, and dry in vacuo to obtain a white solid.
[0125] In the step ② of synthesizing compound 2, under the protection of argon, 15.6 g of compound 1 was dissolved in 100 mL of dichloromethane, and 7.44 mL of boron tribromide was added dropwise to the solution at -78°C. Wherein the molar ratio of compound 1, boron tribromide and methylene chloride is: 1:2:40. The reaction was stirred for 16 hours. After the reaction was completed, the reaction solution was transferred to an ice-water...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com