Deafness gene screening chip
A deafness gene and chip technology, applied in the field of deafness gene screening chip, can solve the problems of narrow detection range, complicated operation process, and small screening coverage, and achieve the effect of wide application field, wide coverage, and simple interpretation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0044] The present invention will be described in detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings and in combination with embodiments.
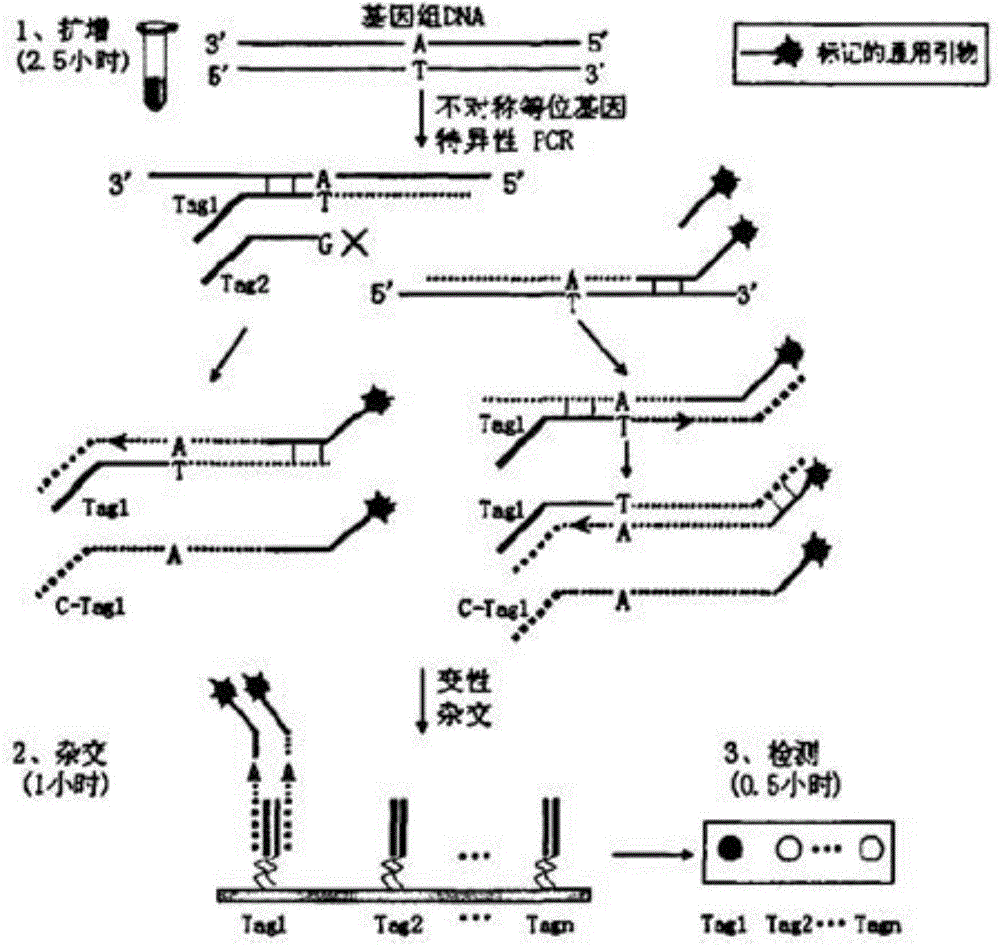
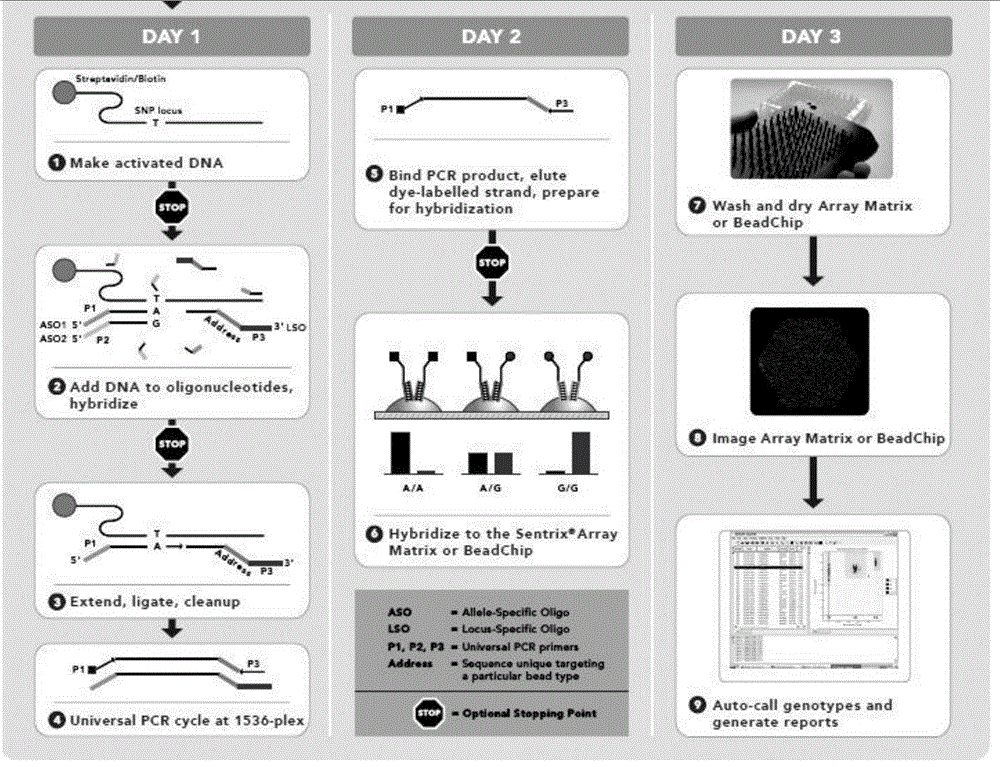
[0045] 1. Principle of Illumina GoldenGate chip technology
[0046] Illumina GoldenGate chip technology principle ( image 3 ) is based on the design of upstream and downstream primers based on the known DNA sequences on both sides of the SNP. Three oligonucleotide primers are required to detect each SNP: two upstream primers, P1′ and P2′, cover the same site, representing the dimorphic SNP respectively. One allelic type of ; one downstream primer, P3'. These three oligonucleotides all include regions complementary to genomic DNA and sequences paired with universal PCR primers. The downstream probe also contains a specific tag sequence, which can be complementary to the probe on a specific type of bead in the BeadArray. When the three oligonucleotide primers hybridize with a small amount of genomic DNA samples, the 3' terminal bas...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com