An efficient method for separating mortar based on temperature sensitivity
A sensitive and mortar-based technology, applied in the field of mortar separation, can solve the problems of low efficiency of mortar separation methods, and achieve the effects of improving cutting ability, improving the quality of silicon carbide, and improving the purity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
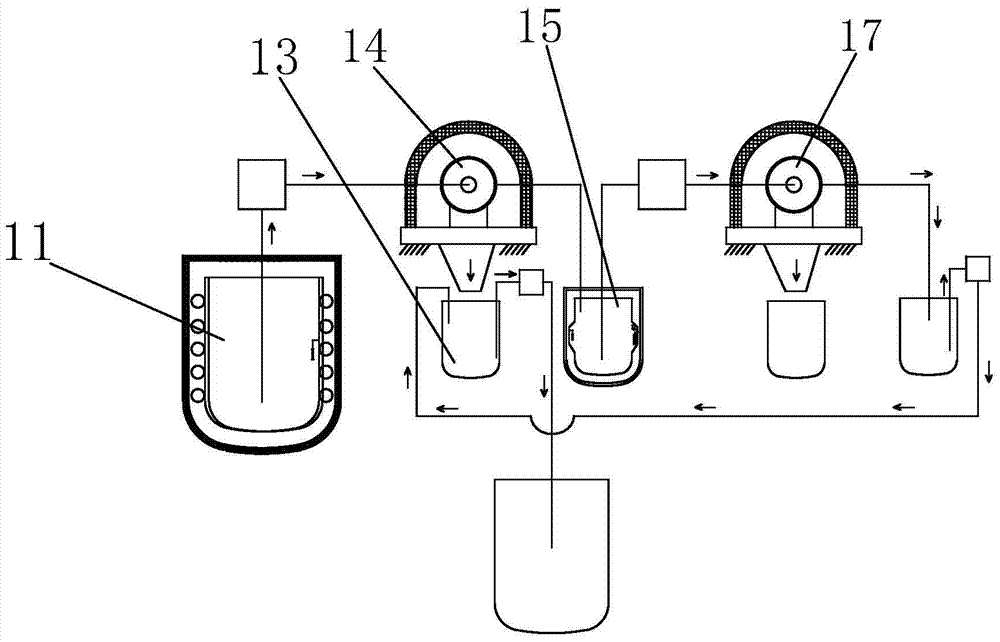
[0023] Such as figure 1 As shown, it includes a cooling cylinder 11, the cooling cylinder 11 is connected to the raw material input port of the first centrifuge 14 through a pipeline, and the raw material output port of the first centrifuge 14 is connected to the heating cylinder 15 through a pipeline, and the first centrifuge 14 The centrifuge product port is aligned to the recovery cylinder 13, and the heating cylinder 15 is connected to the raw material input port of the second centrifuge 17 through a pipeline, and the raw material output port of the second centrifuge 17 is connected to the recovery cylinder 13 through a pipeline.
[0024] The periphery of the cooling cylinder 11 is surrounded by cooling water pipes, and a temperature sensor is arranged inside the cooling cylinder 11. The cooling cylinder 11 is also sealed with a thermal insulation cover, and the cooling cylinder 11 is wrapped with a heat insulating material to prevent the external environment from affecting...
Embodiment 2
[0029] The concrete steps of a kind of processing method based on temperature sensitivity high-efficiency separation mortar are:
[0030] S1: Transport the waste mortar liquid generated during the operation of the multi-wire cutting machine to the cooling cylinder 11, and the cooling cylinder 11 starts to stir and cool down according to the temperature set by the external control equipment, and the waste mortar is cooled to 6 in the cooling cylinder 11. °C to obtain a low-temperature waste mortar liquid at 6 °C.
[0031] S2: Transport the 6°C low-temperature waste mortar liquid to the first centrifuge 14 via the extraction pump, and the first centrifuge 14 performs solid-liquid separation treatment on the 6°C low-temperature waste mortar liquid obtained in step S1. The waste mortar liquid still maintains a certain viscosity, but the sedimentation speed of silicon carbide micropowder with different particle sizes is different. The centrifuge preferentially separates large parti...
Embodiment 3
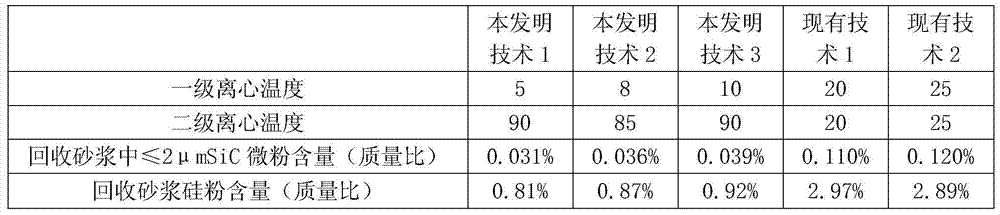
[0036] Embodiment 3 describes the realization mechanism of the present invention in combination with data.
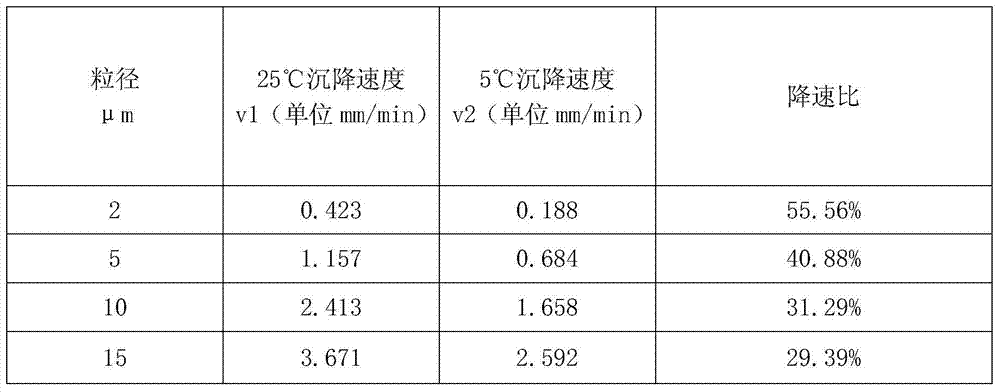
[0037] Table 1: The effect of temperature on the sedimentation velocity of different particle sizes.
[0038]
[0039] Table 2: Effect of Temperature on Viscosity
[0040] temperature °C
Viscosity mPa.s
5
332
25
288
90
116
[0041] It can be seen from Table 1 that in the same temperature range (5°C-25°C), the speed reduction ratio of silicon carbide particles with a particle size of 2 μm is 55.56%, and the speed reduction ratio of silicon carbide particles with a particle size of 15 μm is 29.39%, the more obvious the speed reduction, the more difficult it is for small particles of silicon carbide to be centrifuged. It can be seen that lowering the temperature can reduce the recovery of small particle size silicon carbide micropowder.
[0042] It can be seen from Table 2 that the lower the temperature, the greater the vis...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com