Packaging laminate, method for producing same, and packaging container produced from the packaging laminate
A packaging laminate, technology for lamination, applied in the field of packaging laminates, for manufacturing packaging laminates and packaging containers made from packaging laminates, capable of solving loss of required capabilities, loss of mechanical strength And other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0094] The packaging laminate 10 was produced using the ingredients shown in the table below:
[0095]
[0096]
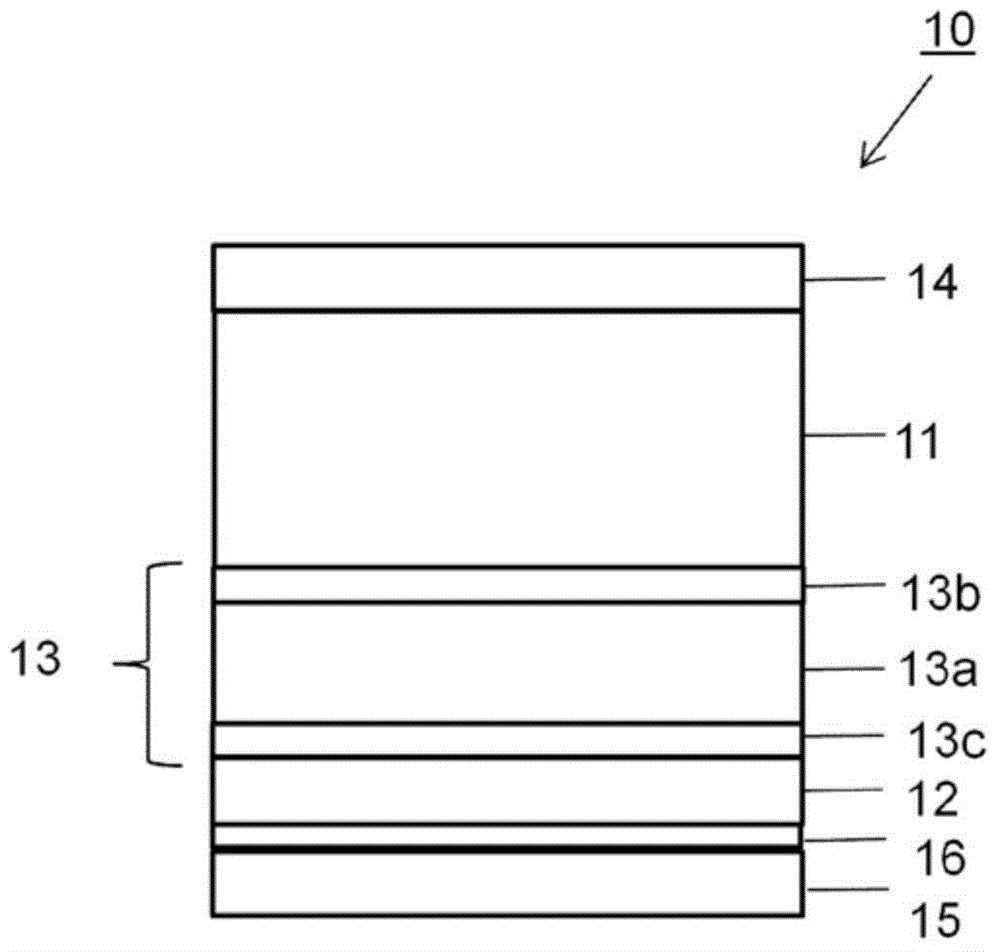
[0097] The packaging laminate 10 in Example 1 according to the invention was produced by coextruding material layers 13a-13c as a three-layer structure, with the sequence of material layers being 13b / 13a / 13c. Coextrusion can typically be performed at extrusion speeds of 200m / min and extrusion temperatures below 310°C, and without the use of ozone or other additional chemicals to obtain and maintain a permanent bond of the aluminum foil 12 acting as a gas barrier to the packaging layer Press material on paper or cardboard 11. The cardboard material used throughout was a CLC / C material with a bending force of 260 mN. The three layers can be coextruded at a temperature of 290-310-290°C and a web speed of 650m / min with excellent (not measured, above detection limit) adhesion to the paperboard layer or barrier layer.
[0098] The known packaging laminate constit...
Embodiment 2
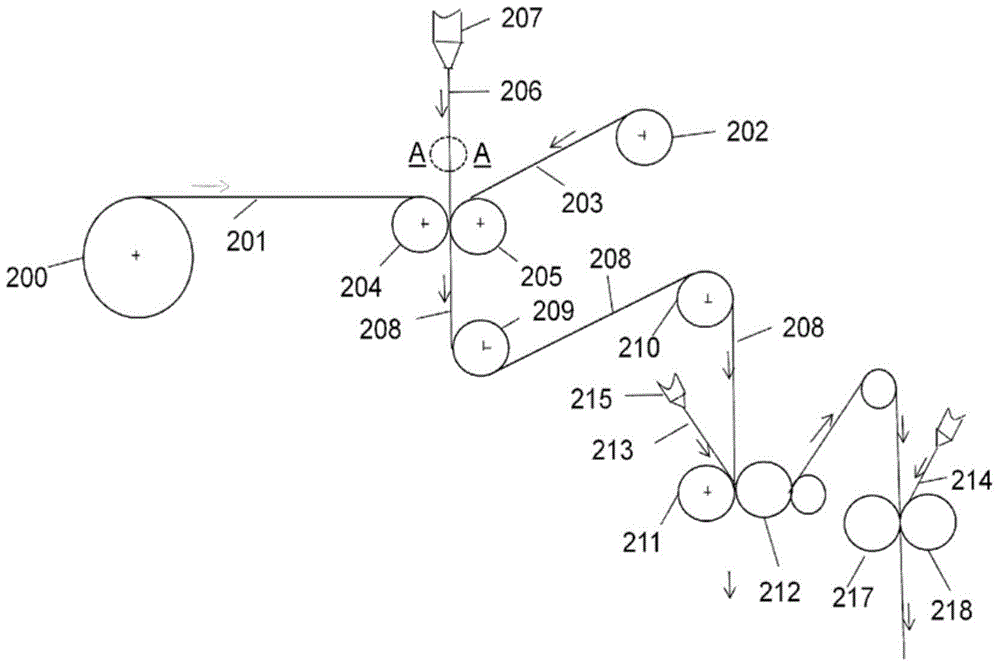
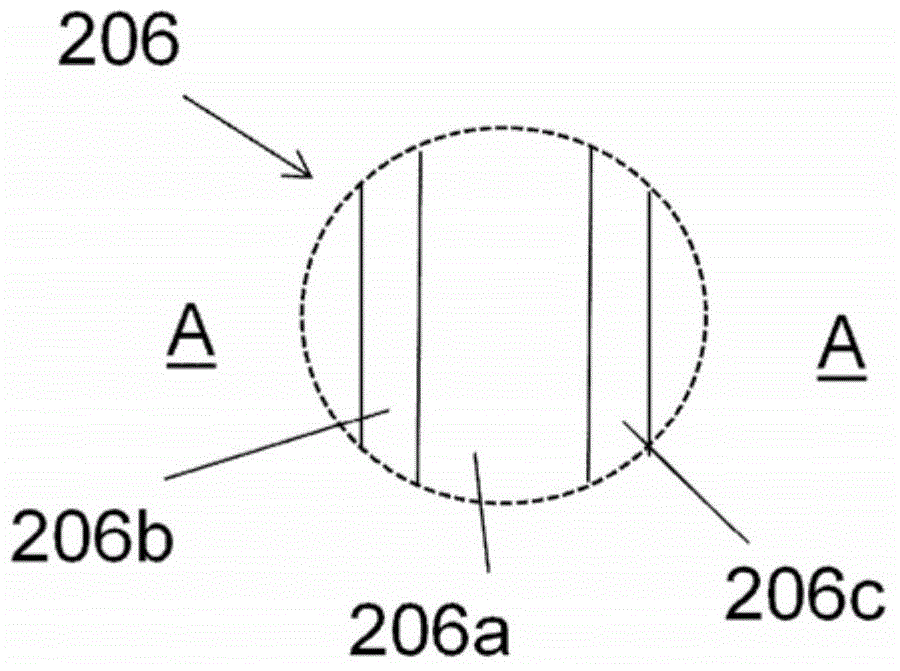
[0102] Example 1 and Reference Example 1 were repeated at a web speed of 200 m / min, and the two gaps between the exit of the extrusion die and the point of contact of the melt curtain with the web surface were different, ie the air gaps were 195 mm and 310 mm. In addition, the example was repeated with the only difference that the laminate in Reference Example 1 was replaced by a test polymer of LDPE2 produced by polymerization in a tubular reactor which, when extruded as a monolayer laminate, had Poor extrusion performance is expected in the form of high neck-in.
[0103] In Example 2, the laminate was coextruded with a central layer of the same LDPE2 and an external additive layer of the same polymer and layer thickness as Example 1 .
[0104] Equivalent packaging properties (barrier properties and cohesion) to Example 1 were obtained and also a significantly improved extrusion process (reduced neck-in ). The neck-in values expressed in Table 3 are the combined widths (m...
example 3
[0107] Reference Example 2 was repeated with the only difference that the laminate was replaced by the polymer LDPE3 (Dow750E), which was produced by polymerization in a tubular reactor and was not suitable for extrusion according to all available data and recommended practices. Coated and used instead for injection molding and has an MFI as high as 20 g / 10 min at 2.16 g, 190°C. As expected, conventional extrusion lamination could not be performed with this polymer because the neck-in was too large. In Example 3, the laminate was instead coextruded with the same central layer of LDPE3 and an outer additive layer of the same polymer and layer thickness as Example 2.
[0108] Equivalent adhesive properties were obtained, as well as a significantly improved extrusion process (reduced neck-in), including better than expected and equivalent lamination with the single layer autoclave polymerized LDPE in Example 1 . Furthermore, in all examples 1-3, according to the invention it was...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com