Anti-ferroelectric ceramic material which is sintered at low temperatures and has high energy storage density and method for preparing anti-ferroelectric ceramic material
A technology of high energy storage density and ceramic material, applied in the field of high energy storage density antiferroelectric ceramic material and preparation thereof, can solve the problems of increasing the production cost of multilayer ceramic capacitors, high sintering temperature, and high electrode Pd content, and achieves good Application prospect, high energy storage density, low sintering temperature effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0037] The antiferroelectric ceramic material provided by the invention can be prepared by adopting the traditional solid-state powder making and air sintering techniques. In one example, its preparation method comprises the following steps:
[0038] 1) with Pb 3 o 4 , La 2 o 3 , ZrO 2 , SnO 2 、TiO 2 As starting material, according to Pb 0.97 La 0.02 (Zr x sn y Ti 1-x-y )O 3 The stoichiometric ratio of ingredients, mixed by wet ball milling, drying and calcination to get Pb 0.97 La 0.02 (Zr x sn y Ti 1-x-y )O 3 Powder, wherein, 0.4≤x≤0.6, 0.4≤y≤0.6, x and y are the number of moles;
[0039] 2) Add the sintering aid CuO to the powder synthesized in step 1) at a mass ratio of 0.2-1 wt%. After fine grinding, add a binder to granulate, and press to form a green body;
[0040] 3) removing the organic matter in the green body from the green body obtained in step 2) at a certain temperature;
[0041] 4) Sintering the mold-expelled green body obtained in step 3) a...
Embodiment 1
[0050] Antiferroelectric ceramic materials consist of:
[0051] Pb 0.97 La 0.02 (Zr 0.45 sn 0.45 Ti 0.10 )O 3 +0.5wt.%CuO
[0052] (1) Calculate the required Pb according to the composition of the above chemical formula 3 o 4 , La 2 o 3 , ZrO 2 , SnO 2 、TiO 2 Quality, mixed by wet ball milling method, according to the mass ratio of raw materials: balls: deionized water = 1:1.5:0.8, mixed for 6-8 hours, so that all components are mixed evenly. After drying, pass through a 30-mesh sieve, briquette in an air atmosphere, raise the temperature to 850°C at a rate of 2°C / min, and keep it warm for 3 hours. The synthetic composition is Pb 0.97 La 0.02 (Zr 0.45 sn 0.45 Ti 0.10 )O 3 of powder;
[0053] (2) Add the sintering aid CuO to the powder synthesized in step (1) according to the stoichiometric ratio. According to the ratio of material: ball: deionized water = 1:2:0.6, the wet method is finely ground for 24 hours, then the material is dried, passed through a 40-...
Embodiment 2
[0062] Antiferroelectric ceramic materials consist of:
[0063] Pb 0.97 La 0.02 (Zr 0.45 sn 0.45 Ti 0.10 )O 3 +0.4wt.%CuO
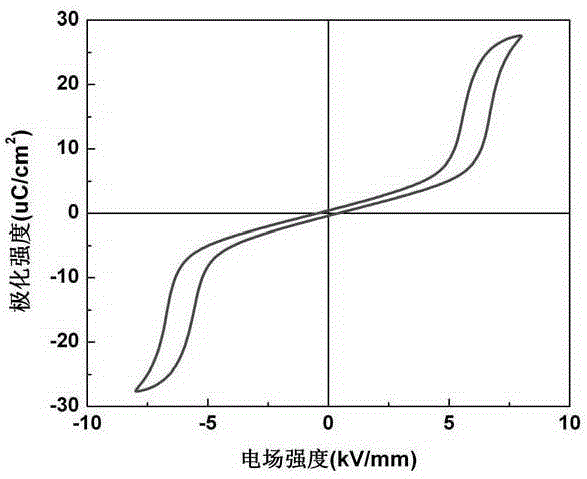
[0064] (1) Repeat the preparation method of Example 1 according to the above formula, and sinter the green body obtained at 1000° C. and keep it warm for 2 hours. The dielectric properties and energy storage characteristics of the ceramic samples were tested. At room temperature, the relative permittivity is 648, the dielectric loss is 0.005, and the AFE-FE phase transition electric field is 6.8kV / mm. Under the working electric field of 8.4kV / mm, the releasable energy storage density is 1.18J / cm 3 , the energy storage efficiency is 75%, see Table 1 for details;
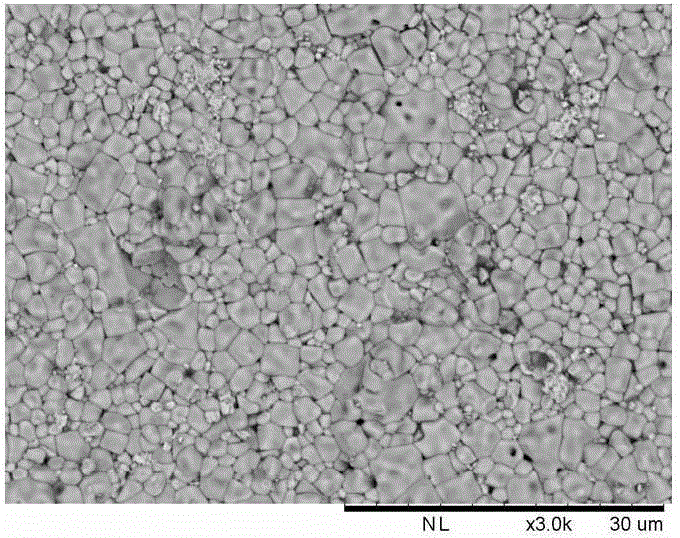
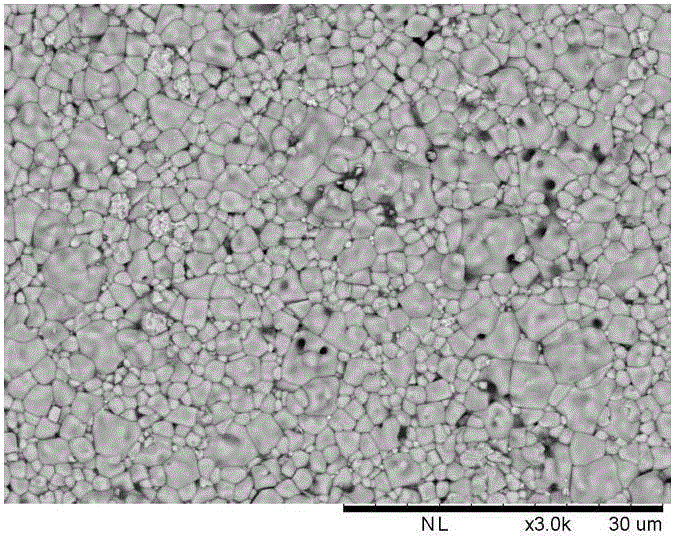
[0065] (2) Surface SEM observations were carried out on ceramic samples, figure 2 The surface topography structure diagram of the ceramic sample of the present embodiment is provided;
[0066](3) The hysteresis loop was measured at room temperature for the ceramic sample of this embod...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Energy storage density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Energy storage density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com