Solimonas capable of efficiently degrading aflatoxin B1 and application thereof
A kind of technology of aflatoxin and monas, which is applied in the field of microbiology and biodegradation, can solve the problems of no substantive detoxification significance and rare reports, and achieve the effect of efficient degradation and detoxification ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
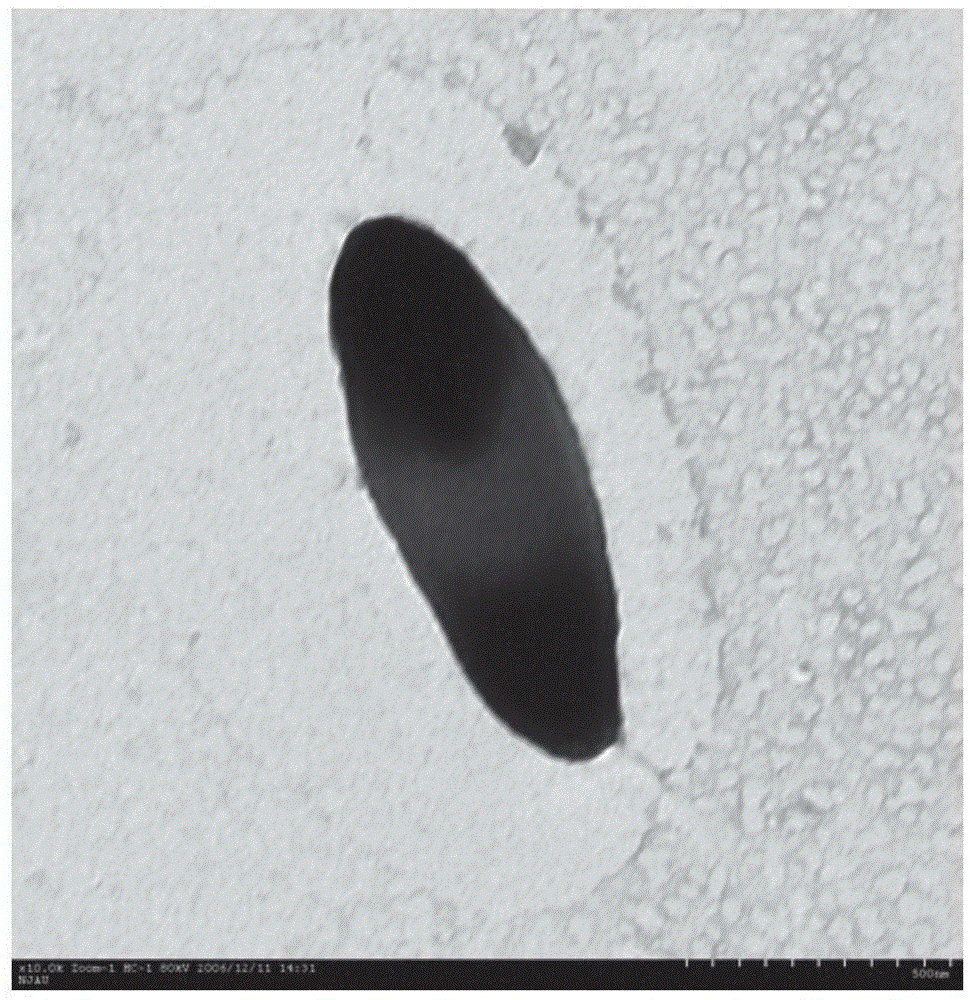
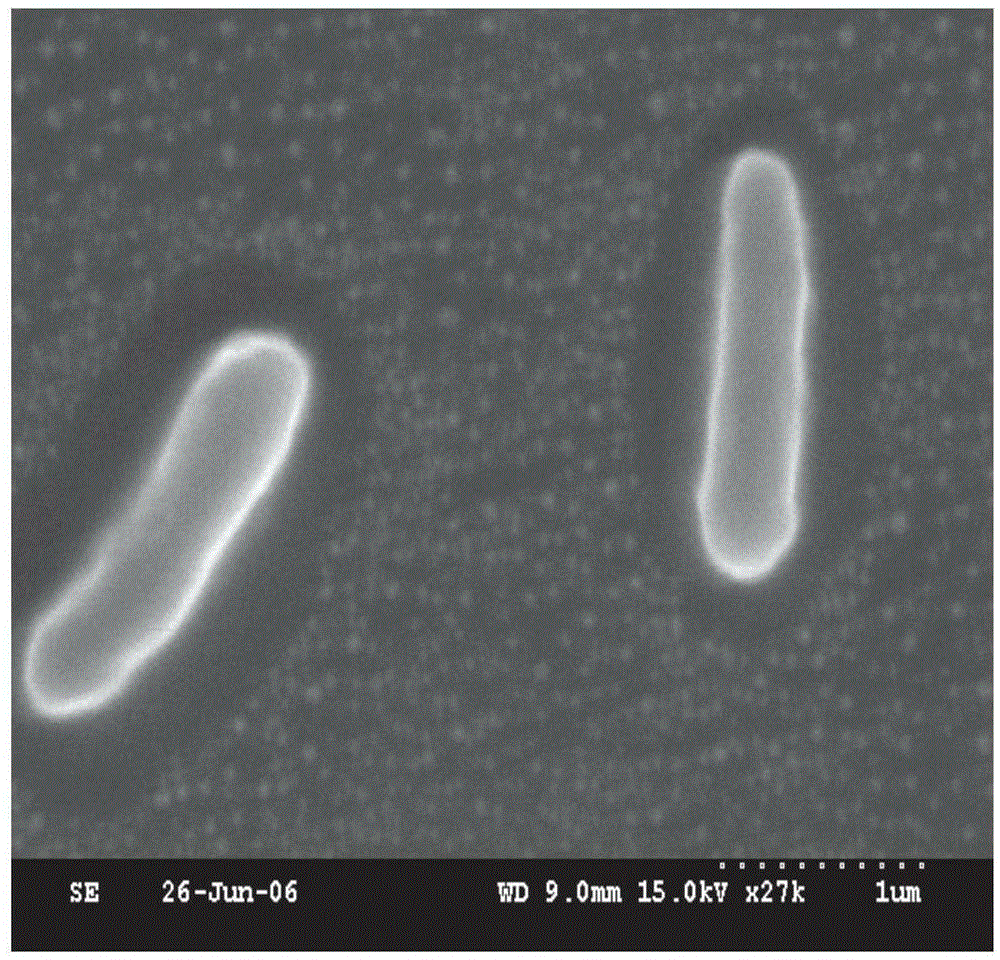
[0021] Screening, identification and cultivation of embodiment 1 aflatoxin B1 degrading bacteria
[0022] 1. Screening of bacterial strains
[0023] The samples were collected from soil heavily polluted by PAHs (near oil refineries, auto repair shops) and moldy food heavily polluted by mycotoxins. Take 0.5 g of the collected sample and add it to 150 mL of enrichment medium (AFB1 content is about 20 μg / L), and enrich and culture it in a constant temperature incubator at 30°C for 7 days. After the first enrichment culture, 5 mL of enrichment culture solution was inoculated into 150 mL of fresh AFB1 enrichment medium, the concentration of AFB1 was increased to 30 μg / L, and enrichment culture was continued for 7 days under the same conditions. Complete the third enrichment culture experiment with the same enrichment method, increasing the concentration of AFB1 to 50μg / L. After the enrichment culture was completed, the enriched culture solution was serially diluted with sterile w...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Example 2 Degradation characteristics of bacterial strain CW980 detected by high performance liquid chromatography
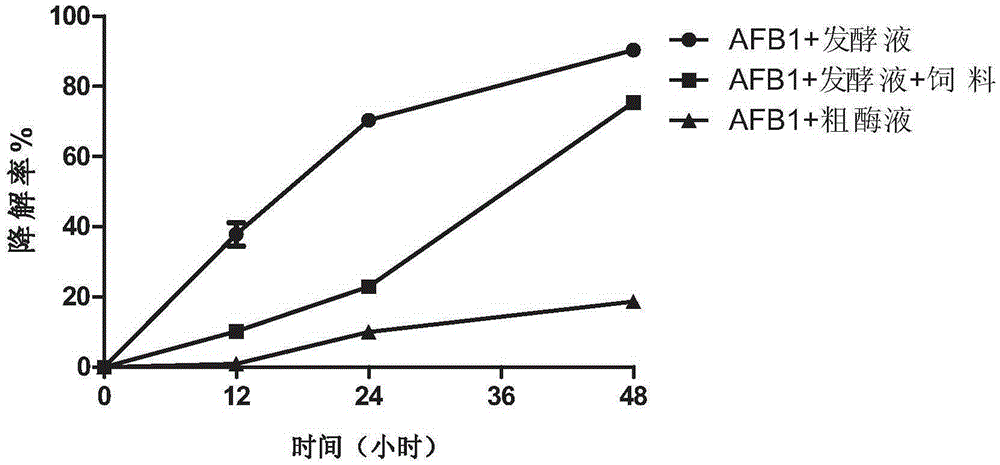
[0034] Degradation dynamic detection of degrading strains: The degrading strain CW980 was continuously activated for 2 generations on the most suitable solid medium, inoculated in 4mL liquid medium for overnight culture, and fresh bacterial liquid was obtained. 50 μL of fresh bacterial liquid was inoculated into 4 mL of AFB1 test medium (containing 20.0 μg / LAFB1), and the inoculated test tubes were shaken for 0 h, 12 h, 24 h and 48 h, and each degradation experiment was set in triplicate. Escherichia coli K12 (E.coliK12) was used as a negative control strain. After the culture was completed, mix well, centrifuge at 8000r / min for 10min, and collect the supernatant and bacterial precipitate respectively.
[0035] The degraded supernatant was passed through the AFB1 immunoaffinity column, eluted with methanol, and the eluate was collected in a glass sample ...
Embodiment 3
[0040] Example 3 Application of bacterial strain CW980 in detoxification treatment of corn soybean meal type feed
[0041] 1. Experimental materials
[0042] Strain activation medium Ⅰ: tryptone 17.0g / L, soytone 3.0g / L, glucose 2.5g / L, NaCl 5.0g / L, K 2 HPO 4 2.5g / L, agar 20.0g / L.
[0043] Strain activation medium II: peptone 5.0g / L, beef extract 30.0g / L, NaCl 5.0g / L, pH7.0-7.2.
[0044] The above-mentioned medium was autoclaved at 120°C for 15 minutes, and the experimental feed was a corn-soybean meal-based diet.
[0045] 2. Experimental method
[0046] Add an appropriate amount of AFB1 standard stock solution to 50mL of phosphate buffer solution, mix well and immediately pour into 100g of crushed feed samples, stir evenly, so that the final concentration of AFB1 reaches 40.0μg / kg respectively, and dry the feed in a cool and ventilated place Dry and set aside. Continuously activate the strains to be tested for 2 generations on the solid activation medium I, inoculate the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com