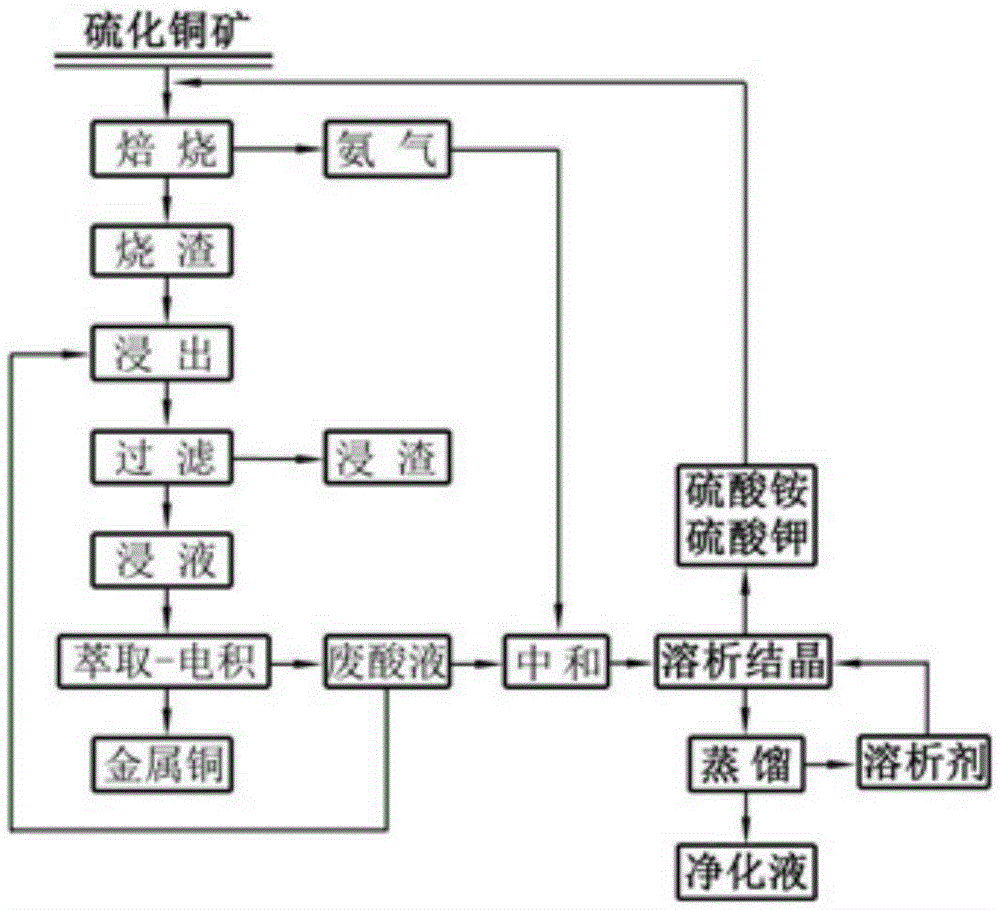
Technique for recycling ammonium sulfate to extract copper from copper sulphide minerals through wet process
A technology of copper sulfide ore and process method, which is applied in the direction of improving process efficiency, etc., can solve problems such as secondary pollution, difficulty in large-scale application, and increased production costs, so as to reduce energy consumption and production costs, reduce use costs, and solve The effect of dealing with problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] In this embodiment, the copper sulfide concentrate of Hubei Daye Nonferrous Metals Co., Ltd. is selected. After analysis, the main chemical components are: Cu20.27%, Fe28.36%, S29.21%, SiO 2 12.43%, Zn0.65%, Pb0.13%, MgO0.39%, As0.53%, CaO3.42%, Ni0.018%, Al 2 o 33.16%. Among them, copper minerals are mostly primary copper sulfide, which is difficult to be leached, with a ratio of 82.54%, and secondary copper sulfide and copper oxide, which are easy to be leached, only account for 15.54%, and contain alkaline gangue minerals, which will consume more acid when leaching with sulfuric acid , and at the same time bring difficulties to the selective leaching of copper.
[0042] The process method of recycling ammonium sulfate used in the present embodiment to extract copper by wet method from copper sulfide ore is characterized in that it comprises the following steps:
[0043] (1) Mix 50g copper sulfide ore with 30% ammonium sulfate, place it in a porcelain ark, put it i...
Embodiment 2
[0048] The copper sulfide concentrate that this implementation selects is the same as embodiment 1, and the operating steps of the processing method of the wet extraction copper from copper sulfide ore by recycling ammonium sulfate are roughly the same as embodiment 1, and the difference is that: 50g of this copper concentrate Mix with 28.5g of ammonium sulfate, and add 1g of potassium sulfate as catalyst.
[0049] The leaching rate of copper in this embodiment can reach 98.73%, and the NH decomposed by roasting 3 , 97.11% can be absorbed and neutralized by waste acid liquid to generate ammonium sulfate.
Embodiment 3
[0051] This embodiment selects the copper sulfide concentrate of Jiangxi Dexing Copper Mine, and the main chemical components after analysis are: Cu24.35%, Fe29.79%, S31.42%, SiO 2 10.11%, Al 2 o 3 4.06%, Zn0.06%, Pb0.16%, MgO0.85%, As0.09%, CaO0.83%, Mo0.05%. Among them, chalcopyrite is the main copper mineral, followed by tetrahedrite, arsenite, chalcocite, bornite, malachite, azurite and copper blue. Other metallic minerals mainly include pyrite, hematite, magnetite and a small amount of molybdenite, and non-metallic minerals mainly include quartz, sericite and chlorite.
[0052] The process method of recycling ammonium sulfate used in the present embodiment to extract copper by wet method from copper sulfide ore is characterized in that it comprises the following steps:
[0053] (1) Mix 50g copper sulfide ore with 36 ammonium sulfate, place it in a porcelain ark, put it into a tubular roaster and roast it at 500°C for 100min, and obtain calcined sand and ammonia gas aft...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com