Nucleic acid aptamer S3 of Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin A and application thereof
A nucleic acid aptamer, staphylococcal intestinal technology, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of false negative, high cost, false positive, etc., and achieve the effect of inhibiting the proliferation of mononuclear cells, easy to synthesize and label, and small molecular weight
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Example 1: In vitro screening of nucleic acid aptamers that specifically bind to SEA
[0027] (1) Design and synthesis of random single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) library
[0028] Design and synthesize a random ssDNA library with fixed regions of 18 nucleotides at both ends and a random region of 40 nucleotides in the middle as follows: 5’-ATACCAGCTTTATTCAATT–N40–AGATAGTAAGTGCAATCT-3’, with a library capacity of 4 40 . The primer sequences used are:
[0029] P1: 5'-ATACCAGCTTATTCAATT-3';
[0030] P2: 5'-AGATTGCACTTACTATCT-3';
[0031] P3: 5'-FAM-ATACCAGCTTTATTCAATT-3';
[0032] P4: 5'-triple Biotin-AGATTGCACTTACTATCT-3'.
[0033] The above nucleic acid sequences were synthesized by a biotechnology company and purified by HPLC.
[0034] (2) Screening of nucleic acid aptamers
[0035] 1) Carboxyl magnetic beads are used as the carrier of the target molecule SEA, which is convenient for the separation operation of the binding sequence. Using a commercial EDC kit, refer t...
Embodiment 2
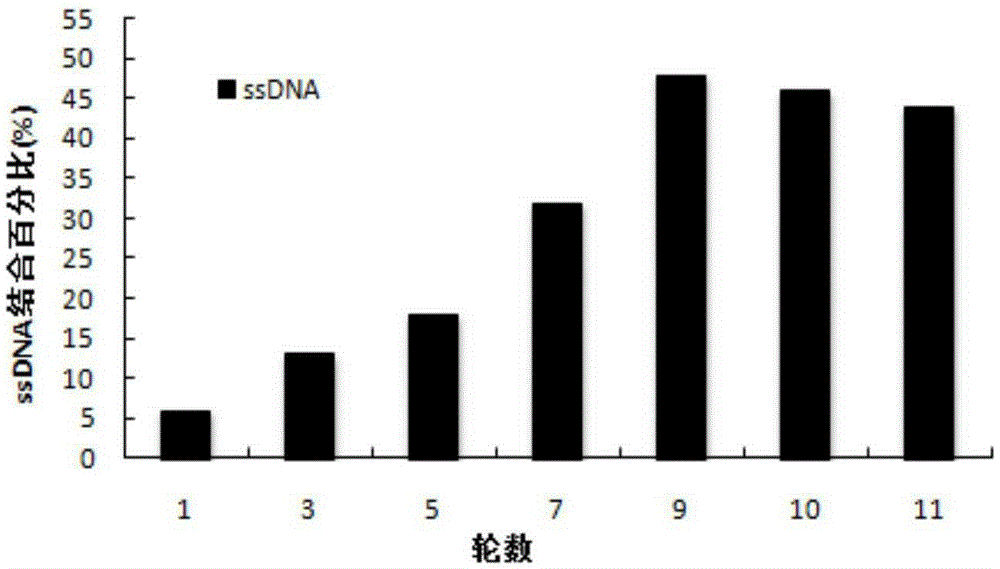
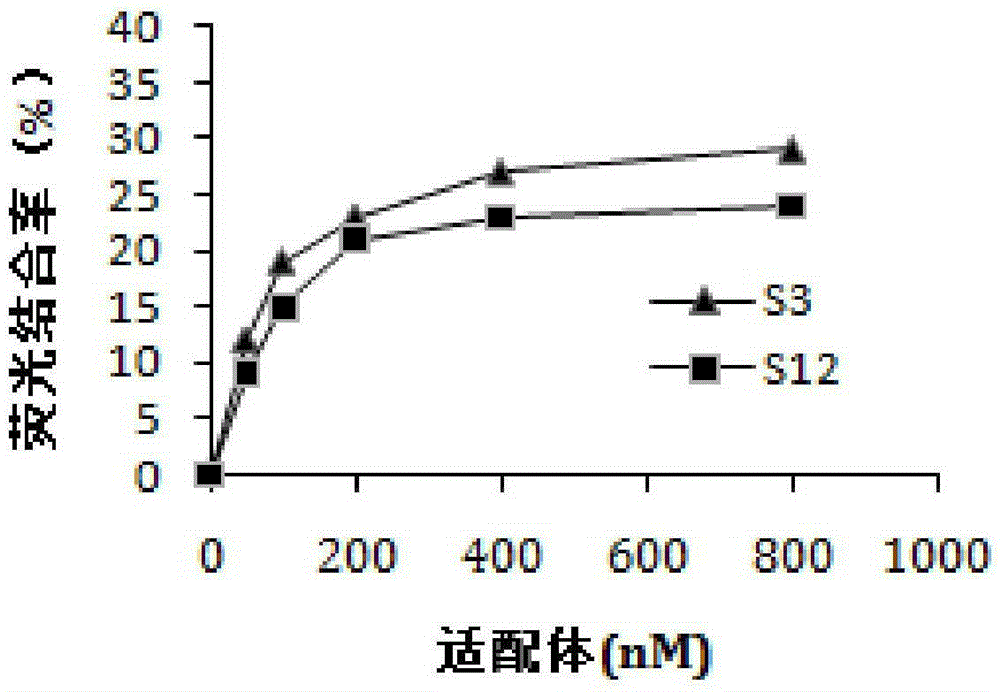
[0043] Example 2: Fluorescence binding rate experiment monitoring the enrichment of ssDNA library
[0044] (1) In Example 1, the FAM-labeled ssDNA library obtained in each round of screening was used in the fluorescence binding rate experiment;
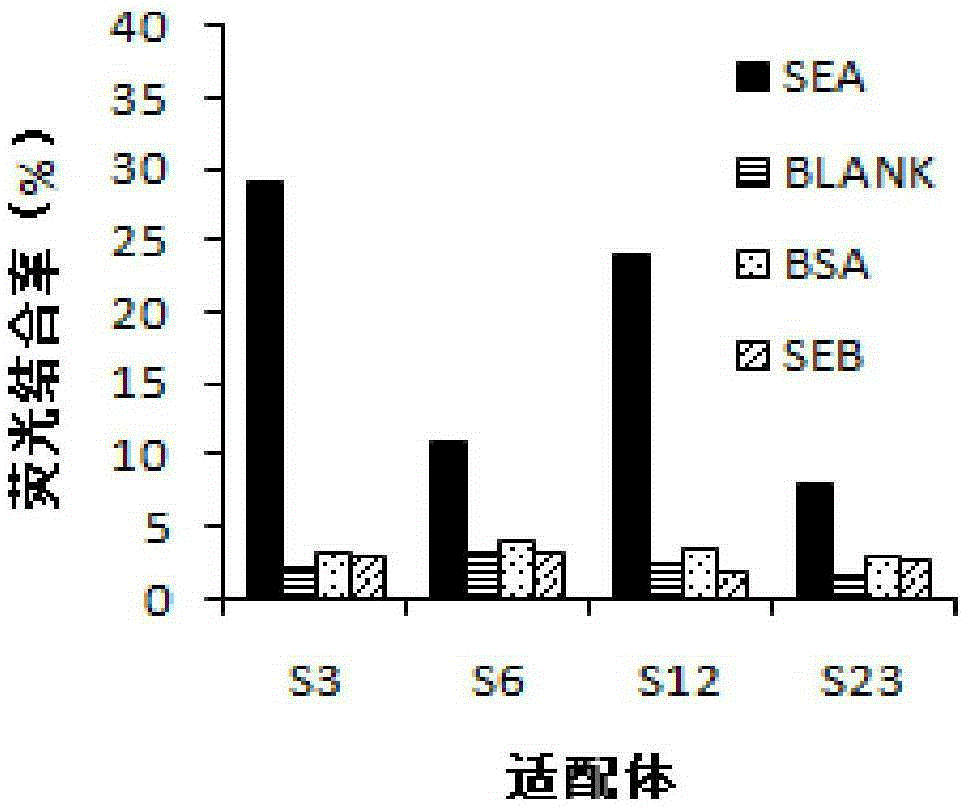
[0045] (2) Take 200 μl of ssDNA-containing library and dissolve it in selection buffer, heat denature at 95°C for about 5 minutes, put it in ice bath for 10 minutes, and place it at room temperature for 10 minutes; then mix it with SEA-beads (SEA load is 100 ng) Incubate at 37°C for 1 hour in a dark box;
[0046] (3) Collect supernatant (containing ssDNA not bound to SEA); ssDNA bound to SEA-beads was eluted with 200 μl selection buffer at 100°C for 5 min;
[0047] (4) Measure the fluorescence intensity of the initial, non-SEA-bound, and SEA-bound ssDNA libraries using a fluorescence quantitator, and calculate the fluorescence binding rate=(initial fluorescence intensity-eluent fluorescence intensity) / initial fluorescence intensity×1...
Embodiment 3
[0049] Example 3: Cloning, sequencing and biological analysis of aptamers
[0050] (1) Using the enriched ssDNA library as a template, PCR amplification is performed with primers P1 and P2;
[0051] (2) Take the purified PCR product and carry out T-A cloning;
[0052] (3) pick 50 positive clones and carry out nucleotide sequence analysis;
[0053] (4) Use ClustalXSoftware to analyze the homology of nucleic acid sequences, select the most 4 kinds of sequences as candidate aptamers, the candidate aptamers are respectively S3, S6, S12, S23; use the network tool mfold according to the lowest free energy In principle, the secondary structure of candidate aptamers is modeled.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com