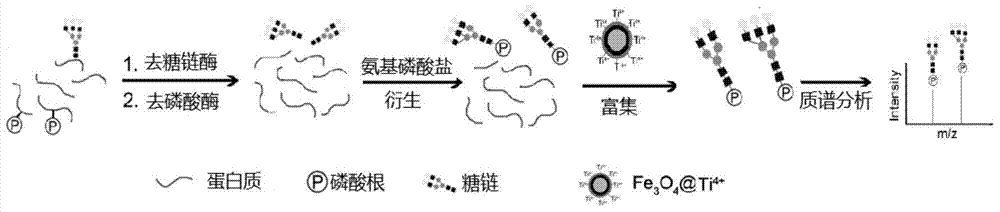
A method for solid-phase enrichment and mass spectrometry analysis of n-sugar chains
A mass spectrometry, sugar chain technology, applied in the field of glycoproteomics and glycomic analysis, can solve the problems of low ionization efficiency, difficult identification by mass spectrometry, lack of hydrophobic groups, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
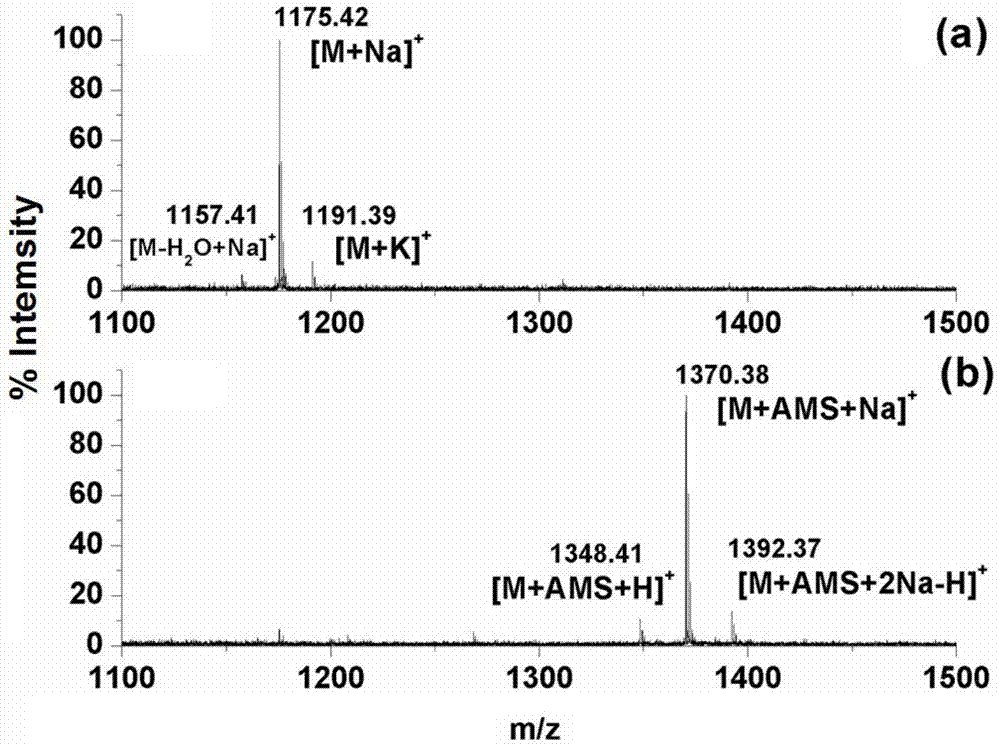
[0037] N-glycan derivatization experiments
[0038] Prepare 100 μL of 100ng / μL standard sugar chain maltoheptaose (DP7) with methanol, add 0.5-2.5 mg / mL of aminophosphonate 4-aminophenylphosphate sodium salt (AMS), and incubate at 60-90 degrees Celsius for 1-3 hours ; freeze-dry the above sample, and add 50μL-1mL 50% ACN aqueous solution (containing 1-5% TFA) to mix for 0.5-2 hours; separate the magnetic nanomaterials from the solution under the action of an external magnetic field; discard the supernatant Then take 50μL-1mL 50% ACN aqueous solution (containing 1-5% TFA) to wash the material 1-3 times, and collect the solid phase material each time; then use 5-10μL NH 3 ·H 2O solution to re-mix the material; under the action of an external magnetic field, the magnetic nanomaterials were separated from the solution, and 1 μL of the supernatant (the final solution containing N-glycan chains) was spotted on the MALDI target plate, and then dried. Spot an equal volume of DHB mat...
Embodiment 2
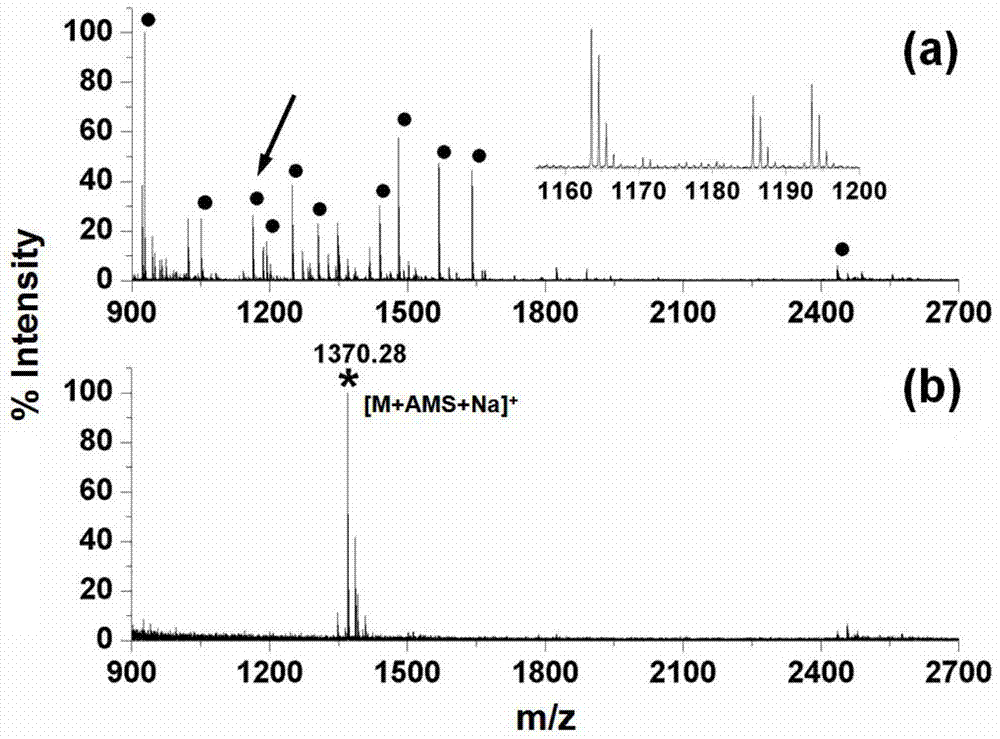
[0040] Fe 3 o 4 @Ti 4+ Experiments on the ability to selectively enrich N-glycan chains
[0041] Prepare 100 μL of 10ng / μL standard sugar chain maltoheptaose (DP7) and 1 μg / μL bovine serum albumin (BSA) enzymatic peptide with methanol to obtain a mixture of sugar chains and peptides, add 0.5-2.5mg / mL Aminophosphonate 4-aminophenylphosphate sodium salt (AMS), incubated at 60-90 degrees Celsius for 1-3 hours; freeze-dried the above sample, and added 50μL-1mL50% ACN aqueous solution (containing 1-5% TFA) to mix 0.5-2 hours; separate the magnetic nanomaterials from the solution under the action of an external magnetic field; discard the supernatant, and then take 50μL-1mL 50% ACN aqueous solution (containing 1-5% TFA) to wash the material 1-3 times, Collect the solid phase material each time; re-mix the material with 5-10 μL ammonia solution; separate the magnetic nanomaterials from the solution under the action of an external magnetic field, and take 1 μL of the supernatant (f...
Embodiment 3
[0043] Fe 3 o 4 @Ti 4+ Experiments on the selective ability of N-glycan derivatization and solid-phase enrichment in complex samples of human serum
[0044] Use 10-50mM ammonium bicarbonate aqueous solution to prepare 10μL of 100ng / μL human serum enzymatic peptide mixture, add 1μL of PNGase F enzyme, incubate at 37 degrees Celsius for 12-16 hours, then add 1μL of alkaline phosphatase CIP in Incubate at 37°C for 12-16 hours; lyophilize the above sample, re-dissolve the sample with methanol to a final concentration of 100ng / μL, add 0.5-2.5mg / mL of aminophosphonate 4-aminophenylphosphate sodium salt (AMS), in Incubate at 60-90 degrees Celsius for 1-3 hours; freeze-dry the above samples, and add 50 μL-1mL 50% ACN aqueous solution (containing 1-5% TFA) to mix for 0.5-2 hours; Discard the supernatant, then take 50μL-1mL 50% ACN aqueous solution (containing 1-5% TFA) to wash the material 1-3 times, and collect the solid phase material each time; then re-mix with 5-10μL ammonia sol...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com