Preparation method for papermaking dry-strength agent with temporary wet-strength improving effect
A temporary, dry strength agent technology, applied in the field of polymer chemistry, can solve the problems of reduced aldehyde group reactivity and product storage stability, and achieve easy retention and adsorption, resistance to anion garbage interference, and improved dry strength Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
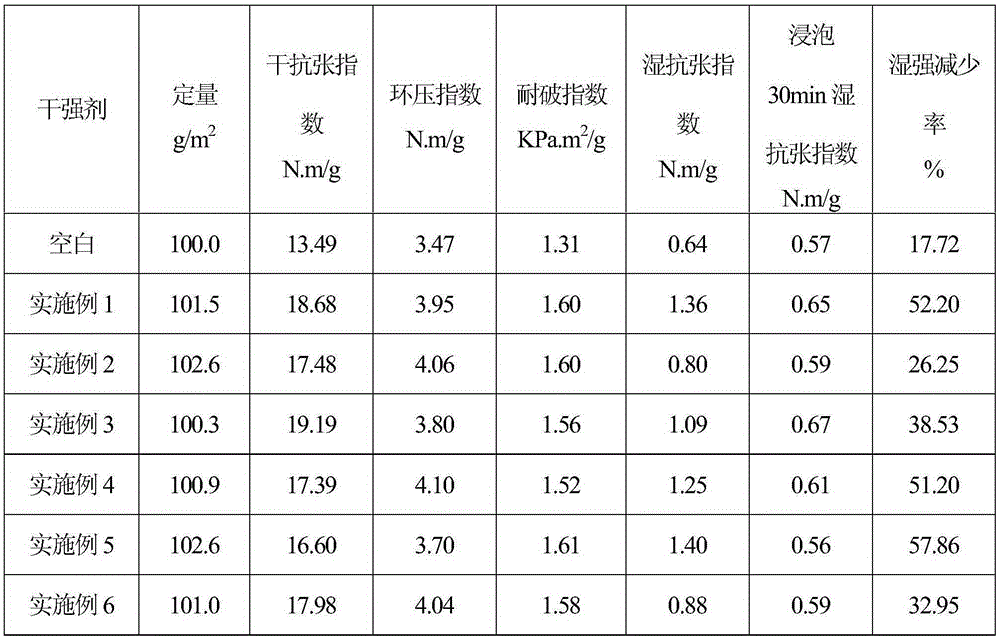
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] ①Acrylamide 1.78g (0.025mol), N-methylolacrylamide 42.93g (0.425mol), diallyl dimethyl ammonium chloride 7.48g (solid content 65%, 0.03mol), methyl Dimethylaminoethyl acrylate 2.36g (0.015mol), methacrylic acid 0.43g (0.005mol), diethylene glycol diacrylate 0.0054g (0.25×10 -4 mol), 80 g of deionized water were mixed evenly to obtain monomer solution I, and an appropriate amount of dilute sulfuric acid was added to adjust the pH value of monomer solution I to 3;
[0023] ②Mix 1.05g of azobisisobutylimidazoline hydrochloride VA-044 with 90g of deionized water to obtain initiator solution II;
[0024] ③Put 1 / 3 of the monomer solution I and 130g of deionized water into a four-necked flask equipped with a reflux condenser, an air guide tube, and a thermometer, and heat up to 55°C after blowing nitrogen gas, and add 1 / 3 of the initiator into the system Solution II, heat preservation reaction for 1h, then drop the remaining 2 / 3 monomer solution I and 2 / 3 initiator solution I...
Embodiment 2
[0026] ①Acrylamide 10.65g (0.15mol), N-methylolacrylamide 20.2g (0.2mol), acryloyloxyethyltrimethylammonium chloride 29.94g (solid content 81%, 0.125mol), acrylic acid 1.08g (0.015mol), 2-acrylamido-2-methylpropanesulfonic acid 1.04g (0.005mol), glycidyl methacrylate 0.0071g (0.5×10 -4 mol), 0.215g (0.0025mol) of methyl acrylate, 0.285g (0.0025mol) of ethyl methacrylate, and 120g of deionized water were mixed evenly to obtain monomer solution I, and an appropriate amount of dilute sulfuric acid was added to adjust the pH value of monomer solution I is 4;
[0027] ②Mix 1.43g of ammonium persulfate and 85g of deionized water evenly to obtain initiator solution II;
[0028] ③Put 1 / 3 of the monomer solution I and 199g of deionized water into a four-necked flask equipped with a reflux condenser, an air guide tube, and a thermometer, and heat up to 70°C after passing through nitrogen, and add 1 / 3 of the initiator into the system Solution II, keep warm for 1.5h, then add the remain...
Embodiment 3
[0030] ① 7.1g (0.1mol) of acrylamide, 30.3g (0.3mol) of N-methylolacrylamide, 5.57g (solid content 84%, 0.0225mol) of methacryloyloxyethyltrimethylammonium chloride , Dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate 3.53g (0.0225mol), diallyldimethylammonium chloride 11.22g (solid content 65%, 0.045mol), itaconic acid 0.975g (0.0075mol), Methylenebisacrylamide 0.019g (1.25×10 -4 mol), 0.11g (0.00083mol) of butyl acrylate, 0.17g (0.00167mol) of methyl methacrylate, and 45g of deionized water were mixed evenly to obtain monomer solution I, and an appropriate amount of dilute sulfuric acid was added to adjust the pH value of monomer solution I is 3.5;
[0031] ②Mix 0.54g potassium persulfate and 60g deionized water evenly to obtain initiator solution II;
[0032] ③Put 1 / 3 of the monomer solution I and 109g of deionized water into a four-necked flask equipped with a reflux condenser, an air guide tube, and a thermometer, and heat up to 75°C after passing through nitrogen, and add 1 / 3 of the init...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com