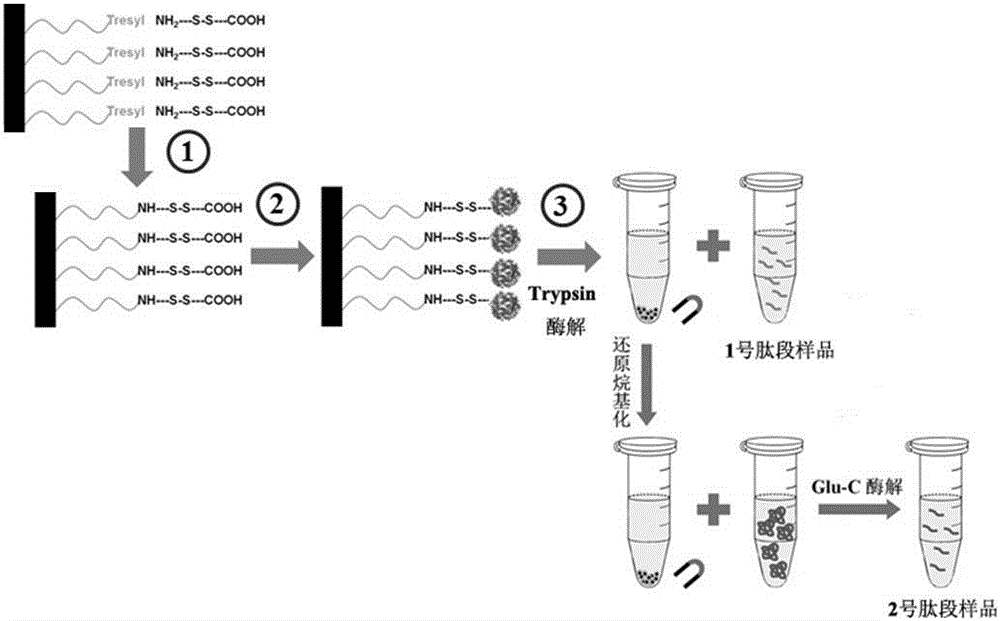
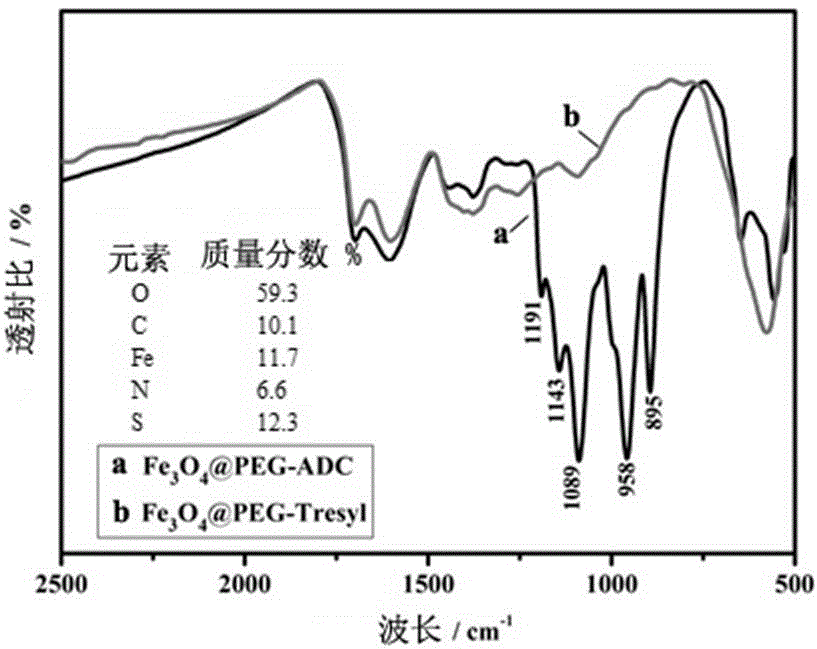
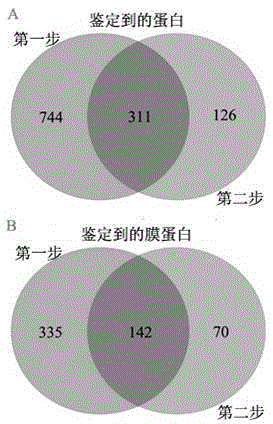
Two-step enzymolysis identification method based on protein reversible fixation
An identification method and protein technology, applied in the field of two-step enzymatic hydrolysis identification based on reversible protein immobilization, can solve problems such as protein loss, inapplicability, and DNA double-strand damage, and achieve good repeatability, high stability and broad application prospects. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Example 1: The membrane proteomics research route based on the controllable breaking characteristics of disulfide bonds investigated the enzymatic hydrolysis effect of special membrane proteins, and compared with the filter-assisted sample pretreatment method
[0026] Bacteriorhodopsin (bR) solution (concentration: 0.5-1.0 mg / mL) and Fe activated by EDC and NHS 3 o 4 After the PEGADC magnetic nanomaterials were mixed, they were shaken and reacted for 2 hours at 37°C. The resulting material was thoroughly washed and redispersed in 50 μL NH 4 HCO 3 (25mM) solution, two-step enzymatic hydrolysis. Step 1: Add 1.0-2.0 μg Trypsin, and digest overnight at 37°C. Peptide sample No. 1 was obtained after magnetic separation. Step 2: add 10-20mM MDTT solution to the material, react at 56°C for 1 hour, then add IAA to a final concentration of 25-50mM, and react at room temperature for 1 hour in the dark. After magnetic separation, the residual peptide segment of reductive alky...
Embodiment 2
[0028] Example 2: The application of the membrane proteomics research route based on the controlled breakage of disulfide bonds in the large-scale identification of Hela cell membrane proteins
[0029] 10~20mgFe 3 o 4 The PEGADC magnetic nanometer material is dispersed in the MES buffer solution containing 0.1-0.2 mmol EDC and 0.1-0.2 mmol NHS, and reacted at room temperature for 30 minutes. After removing excess EDC and NHS, add 50 μg of Hela cell membrane protein extract (MES solution containing 4% SDS, pH 5.0-6.0), and react at 37°C for 3 hours. After the material was washed with deionized water to remove SDS, it was subjected to a two-step enzymatic hydrolysis. Step 1: Material is dispersed in 50 μL NH 4 HCO 3 (25mM) solution, and add 1μg Trypsin, 37 ℃ overnight enzymatic hydrolysis. Peptide sample No. 1 was obtained after magnetic separation. Step 2: Add 10mM MDTT solution to the material, react at 56°C for 1 hour, then add IAA to a final concentration of 25mM, and ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com