Single-crystal film bonding body and manufacturing method thereof
A technology of single crystal thin film and bonding body, which is applied in semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, crystal growth, single crystal growth, etc. It can solve the problems of unfavorable direct bonding at the bonding interface and failure of direct bonding, etc., and achieve the elimination of directional reflection , eliminate interference, eliminate the effect of reflection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
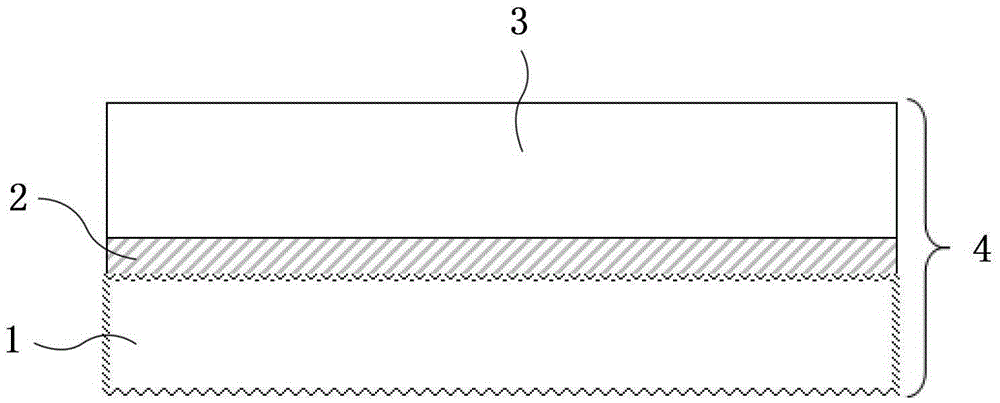
[0063] The original substrate is a lithium niobate wafer with a thickness of 200 microns and a surface roughness of micron or submicron level, such as 0.1 micron to 2 microns, which can be roughened by grinding, etching or sandblasting. Deposit a layer of silicon thin film as a transition layer on the rough surface of lithium niobate by sputtering process, the film thickness is 2 microns; anneal the deposited sheet after deposition, the annealing temperature is 300°C, and the annealing time is 5 hours. The surface of the silicon transition layer on the deposition sheet is chemically mechanically polished to make the surface roughness of the silicon transition layer less than 1 nanometer; the target substrate is a silicon substrate with a thickness of 500 microns, and the silicon substrate is chemically mechanically polished to make the surface roughness less than 1 nm. After the original substrate and the target substrate are cleaned, the polished surface of the silicon transi...
example 2
[0065] The original substrate was a lithium tantalate wafer with a thickness of 350 microns and a surface roughness of 0.2 microns. Deposit a layer of silicon film as a transition layer by evaporation process, with a thickness of 1.5 microns; anneal the deposited sheet after deposition at 200°C for 3 hours to remove defects and impurities in the silicon film. The surface of the silicon transition layer is chemically mechanically polished to make the surface roughness lower than 1 nanometer; the target substrate is a silicon substrate with a thickness of 650 microns, and the silicon substrate is chemically mechanically polished to make the surface roughness lower than 1 nanometer. After the original substrate and the target substrate are cleaned, the polished surface of the silicon transition layer and the polished surface of the silicon substrate are bonded by using a direct bonding process to form a bonded body. The bonding body is annealed at 170° C. for 2 hours to further e...
example 3
[0067] The original substrate is a lithium tantalate wafer with a thickness of 250 microns and a surface roughness of micron or submicron level. Deposit a layer of silicon dioxide as a transition layer by plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition process, the deposition thickness is 3 microns, the deposition temperature is 200°C, and the silicon dioxide deposition sheet is annealed, the annealing temperature is 300°C, and the annealing time is 3 hours , to remove defects and impurities in the transition layer. The silicon dioxide surface is chemically mechanically polished to make the surface roughness lower than 1 nanometer; the target substrate is a silicon substrate with a thickness of 500 microns, and the silicon substrate is chemically mechanically polished to make the surface roughness lower than 1 nanometer. After cleaning the original substrate and the target substrate, a direct bonding process is used to bond the polished surface of the silicon dioxide transition laye...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com