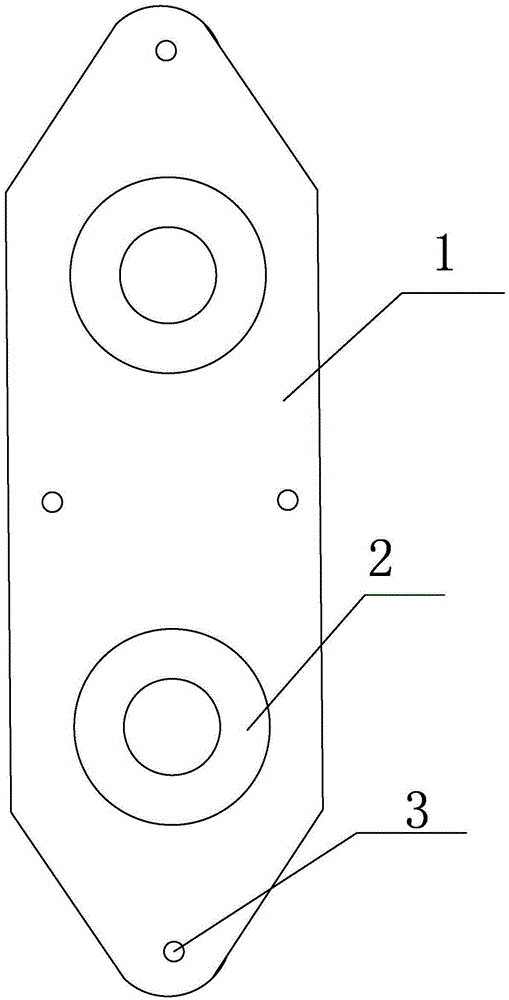
Nut plate
A nut plate, main body technology, applied in the direction of nuts, threaded fasteners, connecting components, etc., can solve the problems of the nut not meeting the required peeling torque, difficult to weld, etc., to save the high temperature reheating process, easy welding, high The effect of low temperature impact toughness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
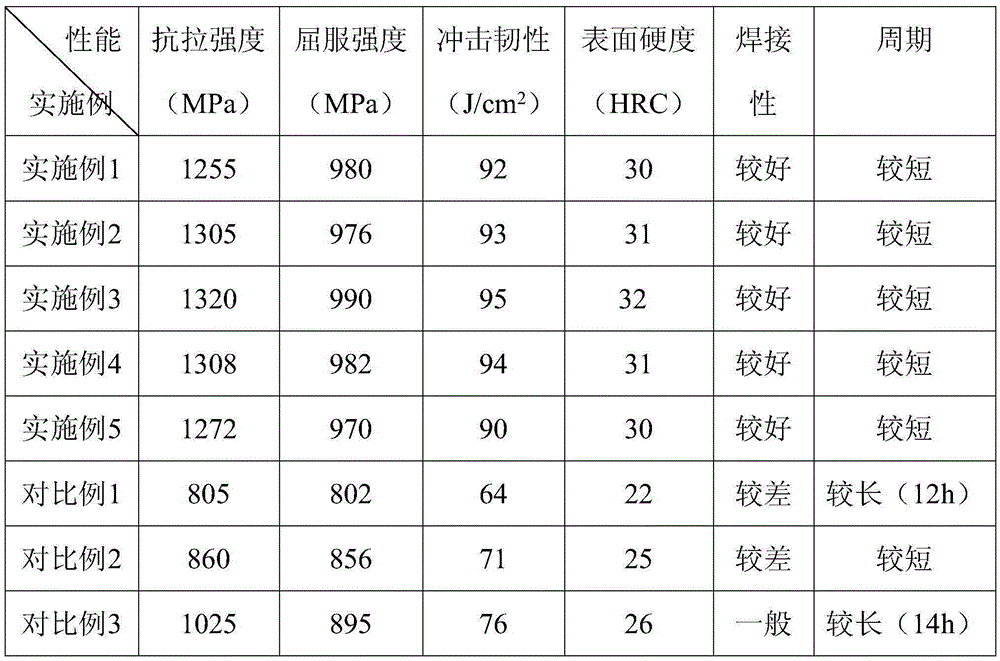
Embodiment 1
[0034] Pretreatment: high-strength alloy steel (high-strength alloy steel is composed of the following mass percentages: C: 0.10%, Si: 0.05%, Mn: 0.50%, Al: 0.15%, Cr: 1.20%, V: 0.003% , B: 0.20%, Ti: 0.01%-0.03%, S ≤ 0.035%, P ≤ 0.035%, and the rest is Fe) quenching and tempering treatment at 880°C, heat preservation for 2h;
[0035] Heat treatment: Forge the quenched and tempered high-strength alloy steel at 1220°C, hold it for 0.3h, and then use the residual heat of forging for quenching treatment. When the temperature is cooled to 900°C, it is immediately water-cooled to room temperature at a rate of 25°C / min. Then heat it to 520°C for tempering treatment for 2 hours, and finally cool it to room temperature with oil at a rate of 22°C / min to obtain a semi-finished nut plate;
[0036] Surface treatment: degrease and derust the semi-finished nut plate in turn (the temperature of degreasing and derusting treatment is 30°C, the treatment time is 10min, and the treatment liquid ...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Pretreatment: high-strength alloy steel (high-strength alloy steel is composed of the following mass percentages: C: 0.04%, Si: 0.25%, Mn: 0.25%, Al: 1.00%, Cr: 0.60%, V: 0.01% , B: 0.10%, Ti: 0.025%, S ≤ 0.035%, P ≤ 0.035%, the rest is Fe) quenching and tempering treatment at 820 ° C, heat preservation 2h;
[0039] Heat treatment: Forge the quenched and tempered high-strength alloy steel at 1200°C, keep it warm for 0.5h, and then quench it with forging waste heat. When the temperature is cooled to 900°C, it is immediately water-cooled to room temperature at a rate of 22°C / min. Then heat it to 500°C for tempering treatment for 2 hours, and finally cool it to room temperature with oil at a rate of 20°C / min to obtain a semi-finished nut plate;
[0040] Surface treatment: degrease and derust the semi-finished nut plate in turn (the temperature of degreasing and derusting treatment is 35°C, the treatment time is 8min, and the treatment liquid used is: thiourea 2.2g / L, sodiu...
Embodiment 3
[0042] Pretreatment: high-strength alloy steel (high-strength alloy steel is composed of the following mass percentages: C: 0.06%, Si: 0.15%, Mn: 0.35%, Al: 0.60%, Cr: 0.70%, V: 0.009% , B: 0.12%, Ti: 0.022%, S ≤ 0.035%, P ≤ 0.035%, the rest is Fe) quenching and tempering treatment at 900 ° C, heat preservation 2h;
[0043] Heat treatment: Forge the quenched and tempered high-strength alloy steel at 1190°C, keep it warm for 0.4h, and then quench it with forging waste heat. When the temperature cools to 900°C, it is immediately water-cooled to room temperature at a rate of 20°C / min. Then heat it to 480°C for tempering treatment for 2 hours, and finally cool it to room temperature at a speed of 18°C / min to obtain a semi-finished nut plate;
[0044] Surface treatment: The semi-finished nut plate is degreased and derusted in turn ((The temperature of degreasing and derusting treatment is 40°C, the treatment time is 8min, the treatment liquid used is: thiourea 3.0g / L, sodium dihydr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com