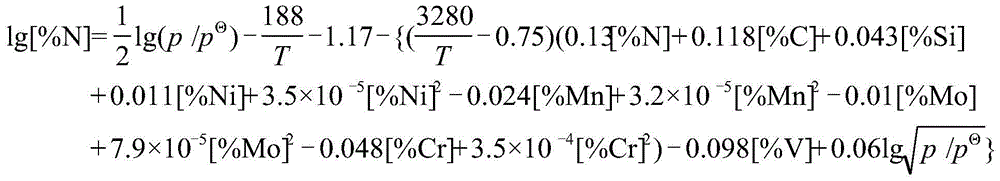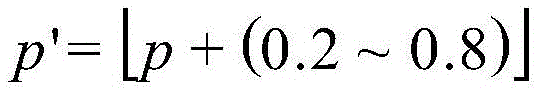Method for smelting low-aluminum high-nitrogen martensitic stainless steel in pressurization and induction manner
A martensitic stainless steel, pressure induction technology, applied in the field of pressure induction smelting low aluminum high nitrogen martensitic stainless steel, can solve the problems of slag boiling, silicon increase, cost increase, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] 21.0kg target steel grade 30Cr15MoN0.4 was smelted by pressure induction, and its composition range is shown in Table 2.
[0034] Table 2 Steel Type 30Cr15MoN0.4 Composition Range and Target Composition / wt.%
[0035]
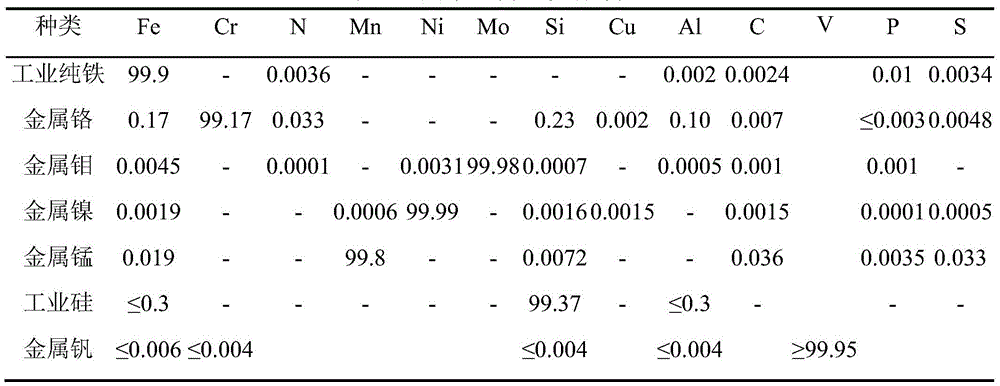
[0036] (1) Determining the smelting and casting pressure and batching: According to the target composition of the steel grade in Table 2 and the smelting temperature of about 1550°C, it is calculated according to formula ① and formula ②: the smelting pressure p is 0.37MPa, and the casting pressure p' is 1.0MPa. The smelting raw materials and their quality are as follows: industrial pure iron 17250g, metal chromium 3240g, metal molybdenum 210g, metal manganese 90g, industrial silicon 101g, graphite 67g. Among them, graphite and industrial silicon are added 6.8% and 3.1% respectively on the basis of the target components for deoxidation. In addition, 21.0g of nickel-magnesium alloy containing 20% magnesium was added for deep deoxidation, and 10.5g of ...
Embodiment 2
[0046] 20.0kg target steel grade 50Cr18MoVN0.36 was smelted by pressure induction, and its composition range is shown in Table 4.
[0047] Table 4 Steel Type 50Cr18MoVN0.36 Composition Range and Target Composition / wt.%
[0048]
[0049] (1) Determining the smelting and casting pressure and batching: According to the target composition of the steel grade in Table 4 and the smelting temperature of about 1550°C, it is calculated according to formula ① and formula ②: the smelting pressure p is 0.22MPa, and the casting pressure p' is 1.0MPa. The smelting raw materials and their quality are as follows: industrial pure iron 15950g, metal chromium 3529g, metal molybdenum 220g, metal manganese 64g, industrial silicon 97g, metal vanadium 40g, graphite 110g. Among them, graphite and industrial silicon are added 5.7% and 4.8% respectively on the basis of the target components for deoxidation. In addition, 25.0g of nickel-magnesium alloy containing 20% magnesium was added for deep de...
Embodiment 3
[0059] 20.5kg of target steel grade 12Cr16MoNiVN0.5 was melted by pressure induction, and its composition range is shown in Table 6.
[0060] Table 6 Steel Type 12Cr16MoNiVN0.5 Composition Range and Target Composition / wt.%
[0061]
[0062] (1) Determining the smelting and casting pressure and batching: According to the target composition of the steel grade in Table 6 and the smelting temperature of about 1550°C, it is calculated according to formula ① and formula ②: the smelting pressure p is 0.46MPa, and the casting pressure p' is 1.2MPa. The smelting raw materials and their quality are as follows: industrial pure iron 16470g, metal chromium 3349g, metal molybdenum 205g, metal nickel 205g, metal manganese 110g, industrial silicon 77g, metal vanadium 61.5g, graphite 26g. Among them, graphite and industrial silicon are added 7.0% and 3.0% respectively on the basis of the target components for deoxidation. In addition, 20.5g of nickel-magnesium alloy containing 20% magnes...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com