Photo-crosslinking bionic hydrogel and preparation and application thereof
A hydrogel and photo-crosslinking technology, applied in medical science, absorbent pads, prostheses, etc., can solve problems such as poor antibacterial properties and non-specific protein adsorption, and achieve improved hydrophilicity, rapid molding conditions, and inhibition The effect of protein adsorption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] A preparation method of glycidyl methacrylate-phosphoric acid dicholine chitosan hydrochloride hydrogel, comprising the steps of:
[0043] Step (1): Synthesis of Phosphodicholine Chitosan Hydrochloride (PDCCs)
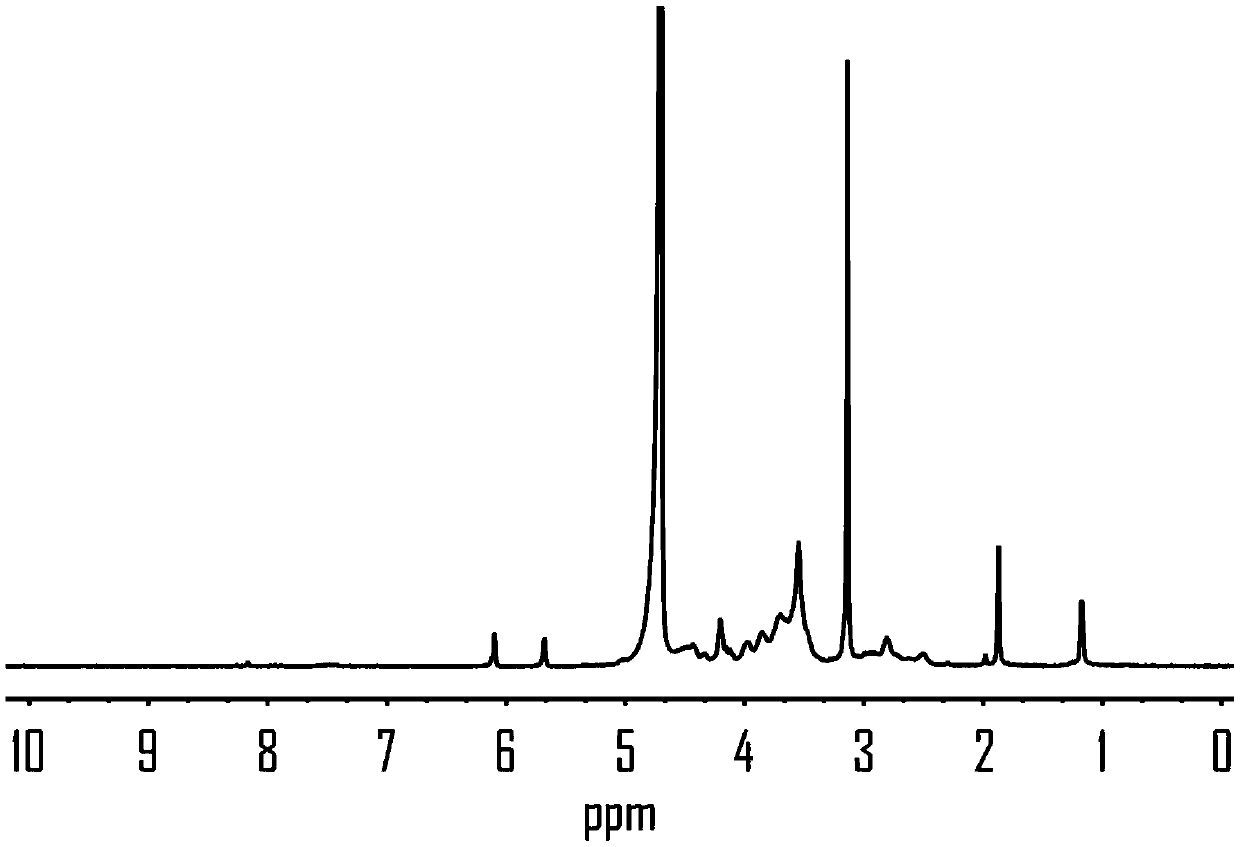
[0044] Get 200mg of 6-O-triphenyl methyl etherified chitosan (Cs-Tr) obtained by modification of chitosan (x / n=0) and dissolve it in 10mL of anhydrous N, N-dimethylacetamide, Add 1.05mL of triethylamine and 0.475mL of carbon tetrachloride at the same time; slowly add 10mL of isopropanol to dissolve 0.475mL of disubstituted choline phosphonate The molar ratio is 1:5, stirred at room temperature for 12 hours; spin-dried the solvent, added formic acid, and stirred at room temperature for 2 hours; spin-dried formic acid, dialyzed with normal saline and deionized water, freeze-dried to obtain phosphoric acid dicholine chitosan Sugar hydrochloride in which the degree of substitution of phosphoricholine groups is 42%.
[0045] Step (2): Synthesis of glycidyl methacry...
Embodiment 2
[0050] A preparation method of glycidyl methacrylate-phosphoric acid dicholine chitosan hydrochloride hydrogel, comprising the steps of:
[0051] Step (1): Synthesis of Phosphodicholine Chitosan Hydrochloride (PDCCs)
[0052] Get 200mg of 6-O-triphenyl methyl etherified chitosan (Cs-Tr) obtained by modification of chitosan (x / n=0) and dissolve it in 10mL of anhydrous N, N-dimethylacetamide, Add 1.05mL of triethylamine and 0.475mL of carbon tetrachloride at the same time; slowly add 10mL of isopropanol to dissolve 0.285mL of disubstituted choline phosphonate The molar ratio of the solution was 1:3, and the reaction was stirred at room temperature for 12 hours; the solvent was spin-dried, and formic acid was added, and stirred at room temperature for 4 hours; Sugar hydrochloride with a degree of substitution of 25% phosphodicholine groups.
[0053] Step (2): Synthesis of glycidyl methacrylate-phosphodicholine chitosan hydrochloride (PDCCs-GMA)
[0054] Dissolve 0.5 g of phosp...
Embodiment 3
[0057] Example 3: Evaluation of antibacterial properties of glycidyl methacrylate-phosphodicholined chitosan hydrochloride hydrogel.
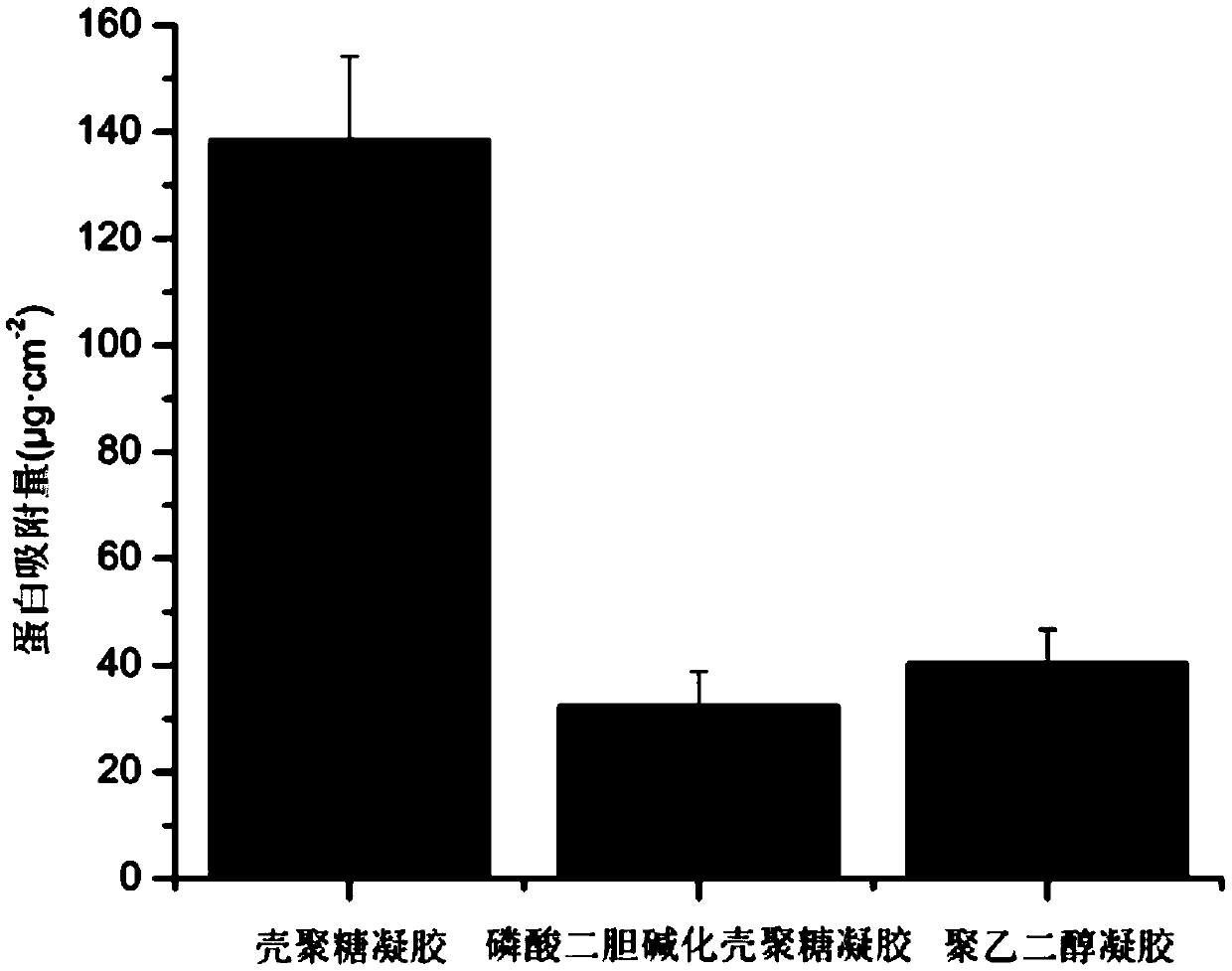
[0058] Taking Escherichia coli (Escherichia coli) (commercially available) (Gram-negative bacterium) as bacterial model, measure the glycidyl methacrylate-phosphodicholine chitosan hydrochloride hydrogel prepared in Example 1 at 37°C, Bacteriostasis at pH=7. Escherichia coli bacterial liquid OD598=0.1 (10 6 ~10 8 CFU / mL) 100 μL was added dropwise on the surface of glycidyl methacrylate-phosphate dicholine chitosan hydrogel hydrogel (1cm 2 ), cultured in a constant temperature and humidity shaker at 37°C with a humidity greater than 90% for 3 hours, then put it into sterile water and sonicate it for 10 minutes to elute surface bacteria. Take 50 μL of the eluate and evenly spread it on LB solid medium for 18 hours to observe the growth of bacteria. The results show that the antibacterial rate of glycidyl methacrylate-phosphodicholined chitosan...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com