Bacillus siamensis strain for preventing and treating pear ring rot and soft rot and application thereof
A technology for bacillus and soft rot, applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve problems such as increasing the residual amount of toxic chemicals, polluting the ecological environment, and drug resistance of pathogenic bacteria, achieving good control effects, huge application potential, and convenient operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
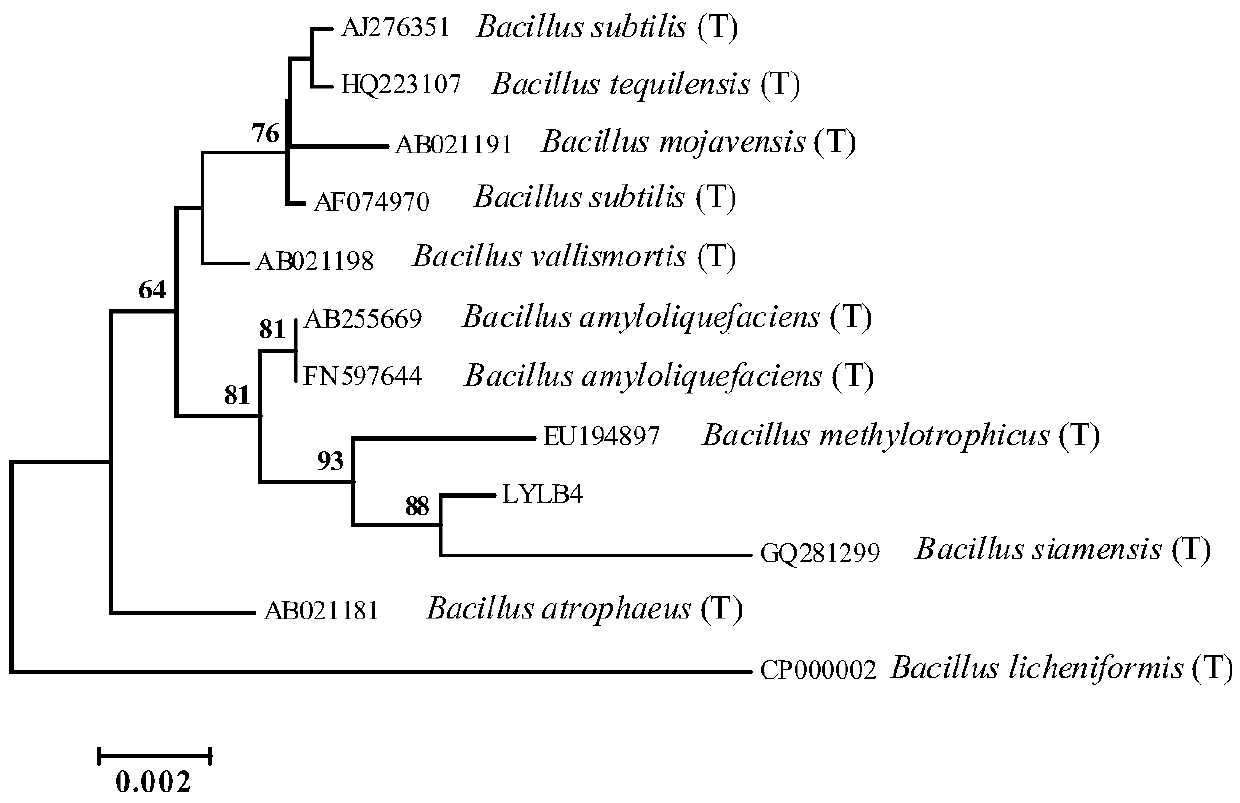
[0040] Example 1. Isolation and identification of Bacillus siamese strains
[0041] 1. Isolation and purification of strains
[0042] 1. Rinse Hongxiao pears from Beijing, Laiyang pears from Shandong, Xuehua pears from Hebei, and Dangshan pears from Anhui with tap water, rinse with distilled water, peel off the peels after drying, and disinfect the peels. The disinfection method is as follows: 70% alcohol treatment for 40s, rinsed with sterile water, then treated with 2.5% sodium hypochlorite solution for 2min, rinsed 3-4 times with sterile water.
[0043] 2. Under aseptic conditions, take 100 μL of sterile water produced by the last rinse and spread it on the beef extract medium, incubate at 30°C for 24-72 hours, and observe the formation of no colonies. Verify whether this disinfection method kills or not. microorganisms on the surface of the test material.
[0044] 3. In aseptic state, cut the peel into 0.2cm 2 The fragments were placed in plates containing beef extract ...
Embodiment 2
[0062] Embodiment 2, the application of bacterial strain LYLB4 in antibacterial or antibacterial
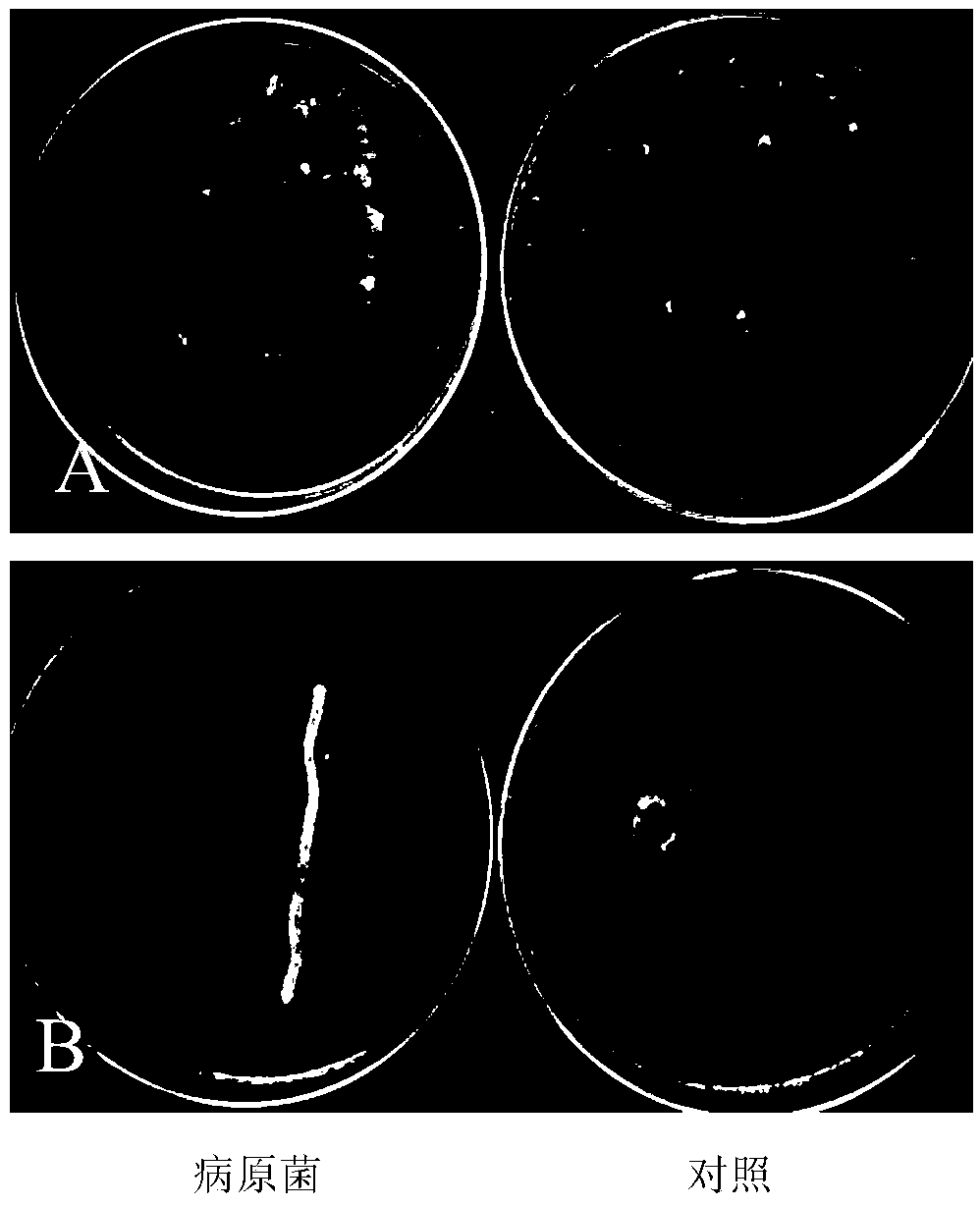
[0063] 1. Antagonistic activity of strain LYLB4 against Pear rot and soft rot
[0064] The pathogenic strains Botryosphaeria dothidea and Rhizopus stolonifer were respectively activated on PDA medium and punched with a 6 mm hole punch to obtain Botryosphaeria dothidea and Rhizopus stolonifer respectively. Using the confrontation culture method, respectively inoculate the pear rot disease cake and soft rot bacteria cake on one side of a PDA plate with a diameter of 9 cm, and streak the opposite side to inoculate the strain LYLB4, and the two inoculation points are separated by 3-4 cm. The pathogenic strains of Verticillium pear and Pseudomonas soft rot on the PDA plate were used as controls. Three replicates were set up and cultivated at 25°C. When the control was covered with the whole dish, the diameter of the treated colony and the width of the inhibition zone were measured, a...
Embodiment 3
[0077] Example 3. Application of strain LYLB4 in the prevention and treatment of pear fruit ring disease
[0078] 1. The control effect of strain LYLB4 on pear fruit ring disease
[0079] 1. Pear pretreatment
[0080] Select fruits with neat appearance, no pests and diseases, and no trauma, rinse them with tap water first, then spray and disinfect with 75% alcohol, and dry the surface with sterile filter paper after 2 minutes for use.
[0081] 2. LYLB4 bacterial suspension treatment
[0082] Two wounds with the same depth as possible were symmetrically punched on the fruit surface with a sterile hole punch (diameter 6mm), and 50 μL of 5×10 wounds were inoculated into the wounds. 7 CFU / ml of LYLB4 bacterial suspension (LYLB4 treatment group) and the same amount of sterile water (control group), 8 fruits per treatment, repeated 3 times, and placed at room temperature for one day.
[0083] 3. Inoculation with pathogenic bacteria
[0084]The wounds of the LYLB4 treatment group...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com