Soybean phosphate-starvation negative regulatory gene GmSPX1, and coding protein and application thereof
A technology of phosphorus starvation and negative regulation, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of increased plant total phosphorus content, increased PSI gene expression, and low affinity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
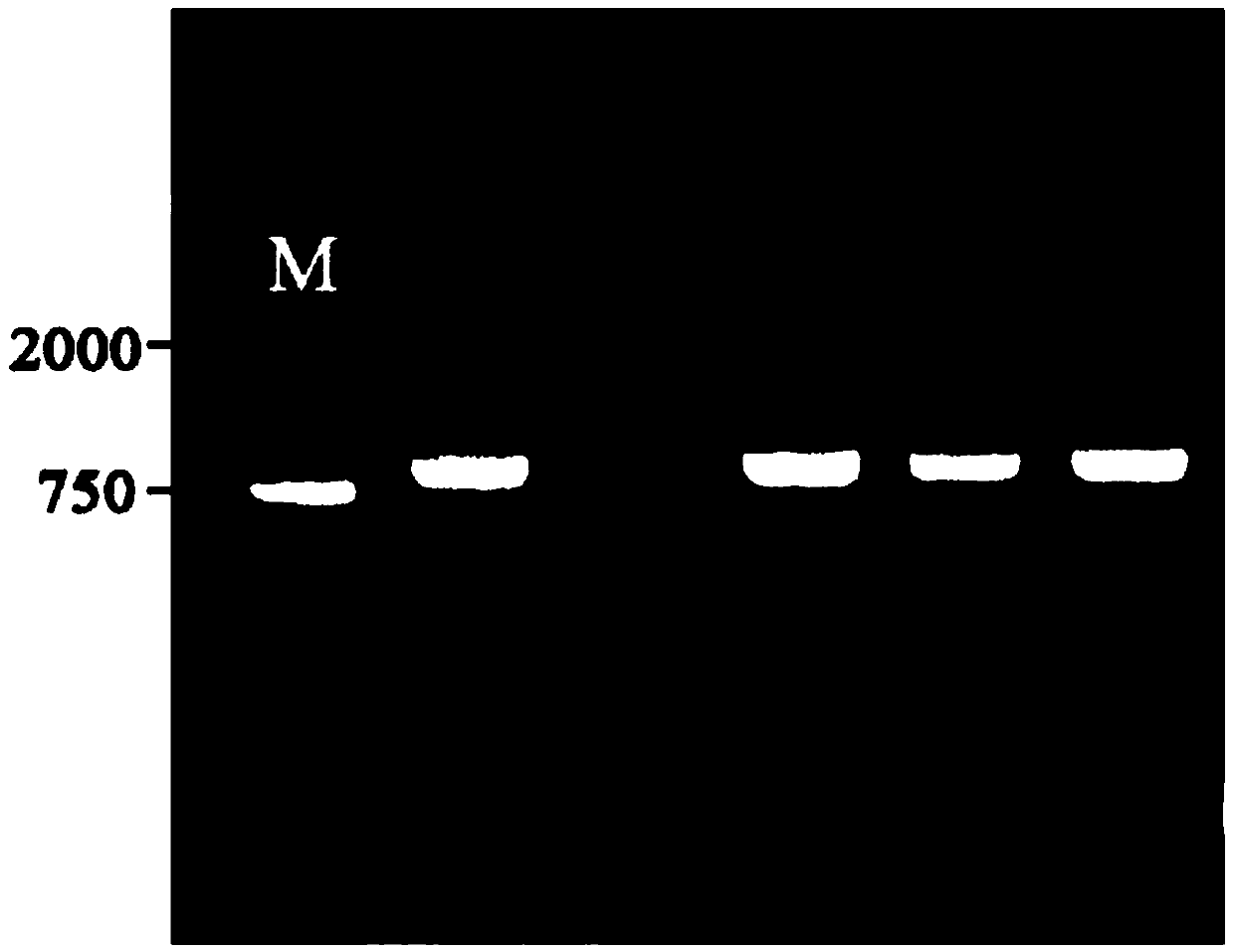
[0041] Example 1: Cloning of Soybean Phosphorus Starvation Negative Regulatory Gene GmSPX1
[0042] (1) Design primers, extract RNA, reverse cDNA:
[0043] RNAisoReagent (purchased from TaKaRa) was used to extract total RNA from the roots of soybean variety Williams82 treated with low phosphorus for 5 days, and the integrity of the RNA was detected by 1% agarose electrophoresis; The primer sequence of the amplified gene GmSPX1 is:
[0044] Seq ID NO.3: GmSPX1-F5'-ATGAAGTTTGGGAAGAGACT-3';
[0045] Seq ID NO.4: GmSPX1-R5'-ACAATAGGAACTGCAGCATTG-3'.
[0046] (2) PCR amplification, the specific steps are as follows:
[0047] Step 1: Prepare PCR reaction solution (50 μL system) according to the following components: ExTaq enzyme mix (25 μL), GmSPX1-F (1 μL), GmSPX1-R (1 μL), cDNA (1 μL), ddH 2 O (22 μL);
[0048] Step 2: Set the reaction program as follows: 95°C, 5min; (94°C, 30sec; 58°C, 30sec; 72°C, 60sec; 30 cycles); 72°C, 10min; store at 4°C;
[0049] Step 3: PCR products ...
Embodiment 2
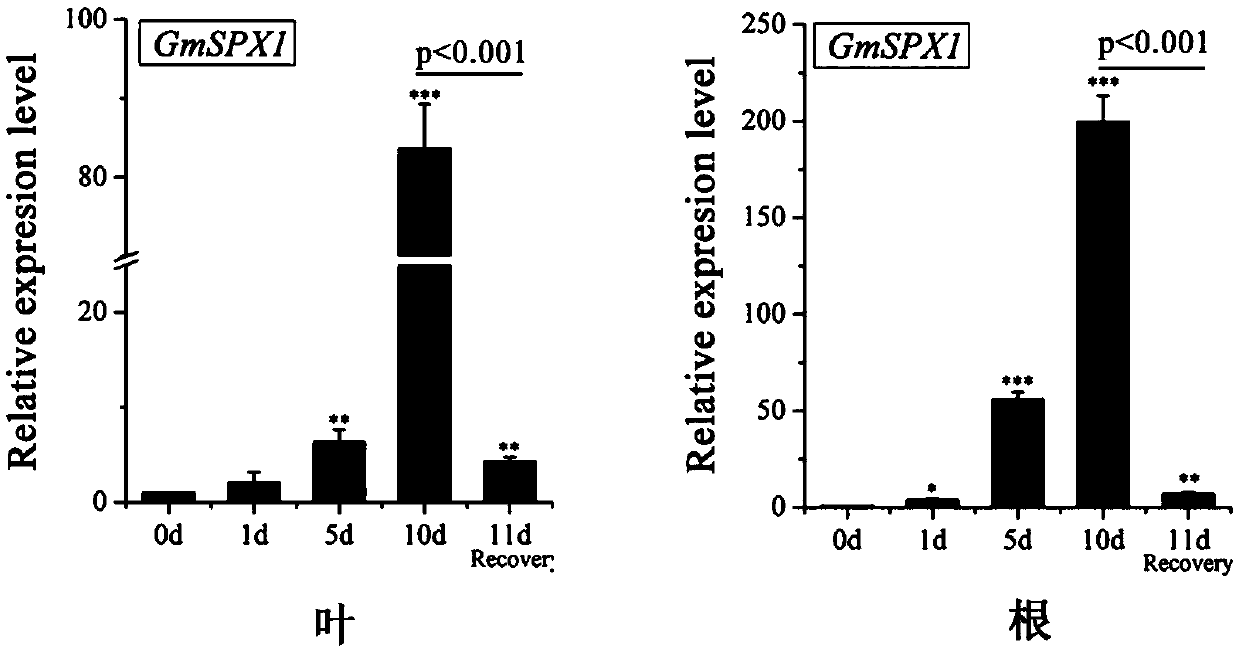
[0050] Example 2: Fluorescent quantitative analysis of soybean phosphorus starvation negative regulator gene GmSPX1
[0051] (1) The cDNA samples of soybean roots and leaves with treatment times of 0d, 1d, 5d, 10d and R-11d (recovery treatment 1 day) were selected as materials, and the fluorescent quantitative PCR (qRT-PCR) kit selected was IQSYBRGreen (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA);
[0052] (2) Design primers
[0053] The fluorescent quantitative specific primers designed for the GmSPX1 gene sequence are:
[0054] SeqID NO.5: Upstream primer 5'-TGAATGATCCTGCTCCAGTTT-3';
[0055] Seq ID NO.6: Downstream primer 5'-TATCTTCAACGGTGGCAATG-3'.
[0056] The internal reference gene was Tubulin, and the primer sequences were as follows:
[0057] SeqID NO.7: Upstream primer 5'-GGAGTTCACAGAGGCAGAG-3';
[0058] Seq ID NO.8: Downstream primer 5'-CACTTACGCATCACATAGCA-3'.
[0059] (3) Fluorescent quantitative PCR amplification, the specific steps are as follows:
[0060] Step 1: Prepar...
Embodiment 3
[0064] Example 3: Expression analysis of soybean GmSPX1 gene in Arabidopsis
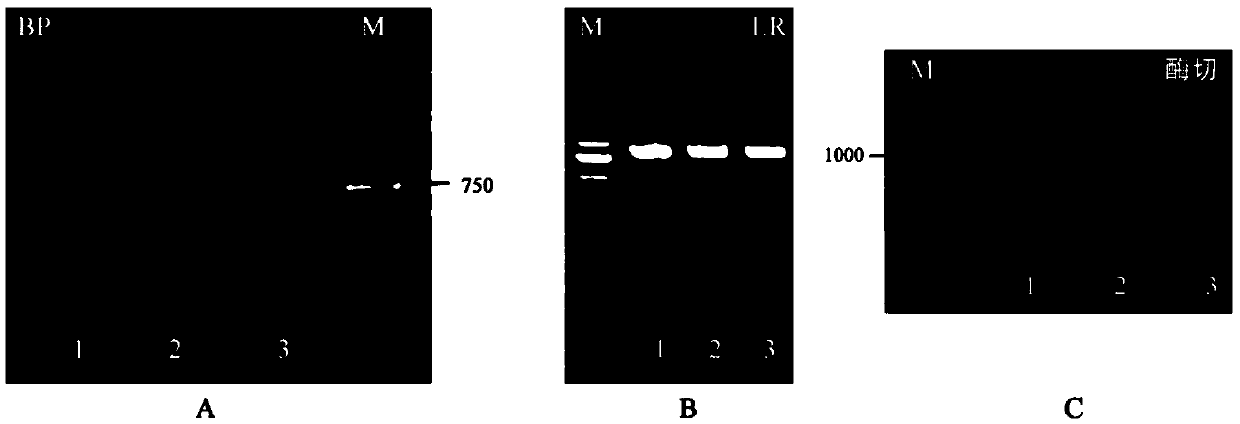
[0065] (1) Utilize Gateway technology to construct plant expression vector pEarleygate103-GmSPX1 (such as image 3 A, B shown). Design specific primers according to the instructions of Gateway;
[0066] SeqIDNO.9: The upstream primer is as follows
[0067] 5'-GGGGACAAGTTTGTACAAAAAAGCAGGCTTCATGAAGTTTGGGAAGAGACT-3'
[0068] SeqIDNO.10: Downstream primers are as follows
[0069] 5'-GGGGACCACTTTGTACAAGAAAGCTGGGTCACAATAGGAACTGCAGCATTG-3';
[0070] (2) Using the PCR amplification product obtained in Example 1 as a template, carry out PCR amplification, and the specific operation is the same as in Example 1, and then carry out BP reaction and LR reaction successively;
[0071] BP reaction: Prepare the reaction solution according to the following components and add it to a 200 μL EP tube: GmSPX1 (3 μL), pDONR221 (1 μL), ddH 2 O (4 μL); quickly vortex BPClonase enzyme once, add 2 μL to the above reactio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com