A kind of non-heavy metal friction material and brake pad
A friction material and heavy metal technology, applied in the field of automobile brake pads, can solve the problems of brake discs prone to fatigue cracks, unstable friction coefficient, and reduced service life, and achieve the effects of improving the dual state, low wear rate, and reduced wear Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] The heavy metal-free automobile brake pad friction material of the present invention, in parts by weight (1 part by weight is 1g), comprises raw materials:
[0024] 25 parts of steel fiber, 7 parts of mineral fiber, 12 parts of modified phenolic resin, 10 parts of nitrile rubber, 15 parts of styrene-butadiene rubber, 3 parts of graphite, 4 parts of molybdenum disulfide, 8 parts of barium sulfate, 3 parts of aramid, weight 3 parts of high-quality calcium carbonate, 3 parts of heavy magnesium oxide, 2 parts of white corundum, and 3 parts of silicon carbide.
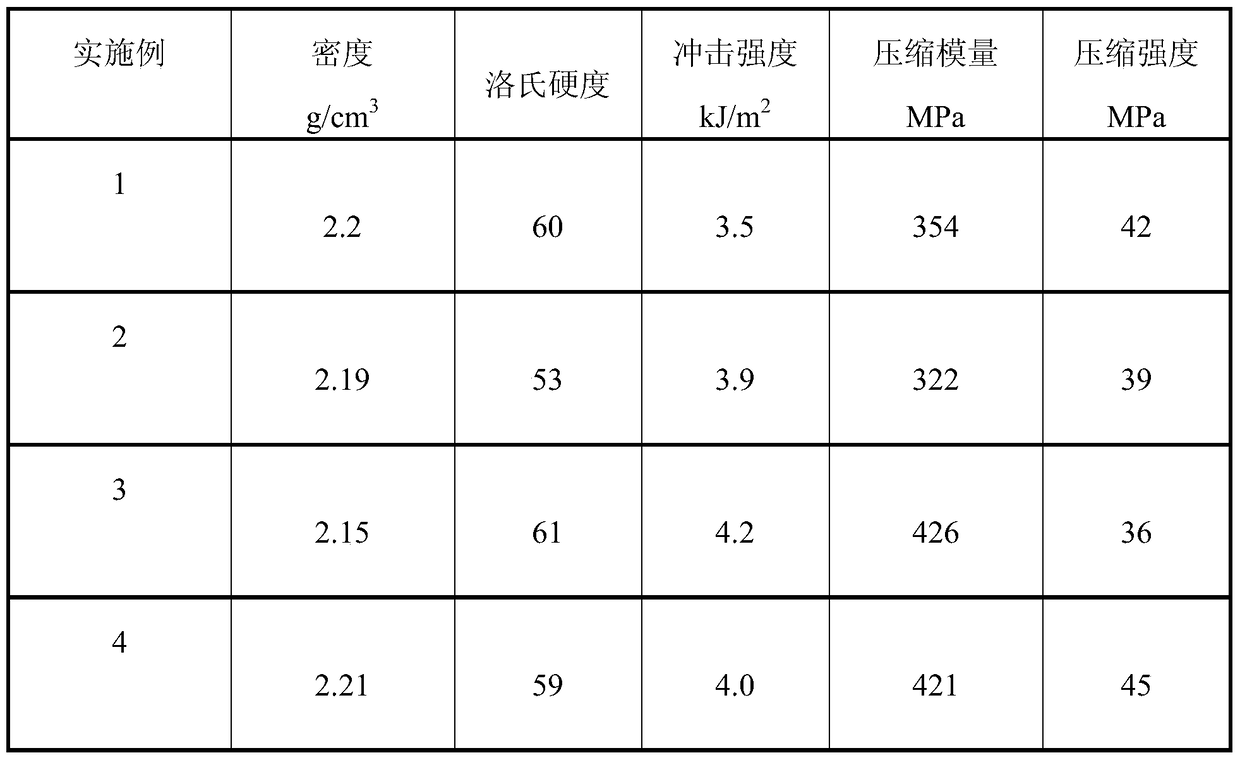
[0025] Mix the components uniformly according to the above ratio to obtain a mixture, place the mixture in a mold and press it, set the pressing pressure to 10Mpa, and the pressing time to 150s, then cure the pressed blank at a temperature of 180°C for 20 hours, Automobile brake pads are prepared. The performance of the automobile brake pads prepared above is shown in Table 1.
Embodiment 2
[0027] The heavy metal-free automobile brake pad friction material of the present invention, in parts by weight (1 part by weight is 1g), comprises raw materials:
[0028] 30 parts of steel fiber, 9 parts of mineral fiber, 10 parts of modified phenolic resin, 10 parts of nitrile rubber, 12 parts of styrene-butadiene rubber, 3 parts of graphite, 3 parts of molybdenum disulfide, 5 parts of barium sulfate, 4 parts of aramid, weight 5 parts of high-quality calcium carbonate, 1 part of heavy magnesium oxide, 2 parts of white corundum, and 4 parts of silicon carbide.
[0029] Mix the components uniformly according to the above ratio to obtain a mixture, place the mixture in a mold and press it, set the pressing pressure to 15Mpa, and the pressing time to 100s, then cure the pressed blank at a temperature of 150°C for 24 hours, Automobile brake pads are prepared. The performance of the automobile brake pads prepared above is shown in Table 1.
Embodiment 3
[0031] The heavy metal-free automobile brake pad friction material of the present invention, in parts by weight (1 part by weight is 1g), comprises raw materials:
[0032] 20 parts of steel fiber, 15 parts of mineral fiber, 10 parts of modified phenolic resin, 15 parts of nitrile rubber, 10 parts of styrene-butadiene rubber, 2 parts of graphite, 4 parts of molybdenum disulfide, 8 parts of barium sulfate, 1 part of aramid, weight 5 parts of high-quality calcium carbonate, 1 part of heavy magnesium oxide, 1 part of white corundum, and 4 parts of silicon carbide.
[0033] Mix the components uniformly according to the above ratio to obtain a mixture, place the mixture in a mold and press it, set the pressing pressure to 12Mpa, and the pressing time to 120s, then cure the pressed blank at a temperature of 160°C for 22 hours, Automobile brake pads are prepared. The performance of the automobile brake pads prepared above is shown in Table 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com