Low-temperature brazing method for ceramics
A brazing method and ceramic technology, applied in the field of brazing, can solve problems such as poor interface bonding performance, low temperature of ceramic materials, and difficulty in realizing high-strength connections, so as to improve mechanical properties, improve microstructure and mechanical properties, reduce The effect of the difference in coefficient of thermal expansion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] A low-temperature brazing method, the ceramic base material selected is alumina ceramics, and the brazing filler metal is pure Sn brazing filler metal, and the specific steps are as follows:
[0033] 1) Take two cylindrical ceramic base materials 1 with a size of Ф5mm×5mm×5mm, and plate a layer of Ni layer with a thickness of 2 μm on the surfaces to be welded of the two ceramic base materials 1 by physical vapor deposition method;
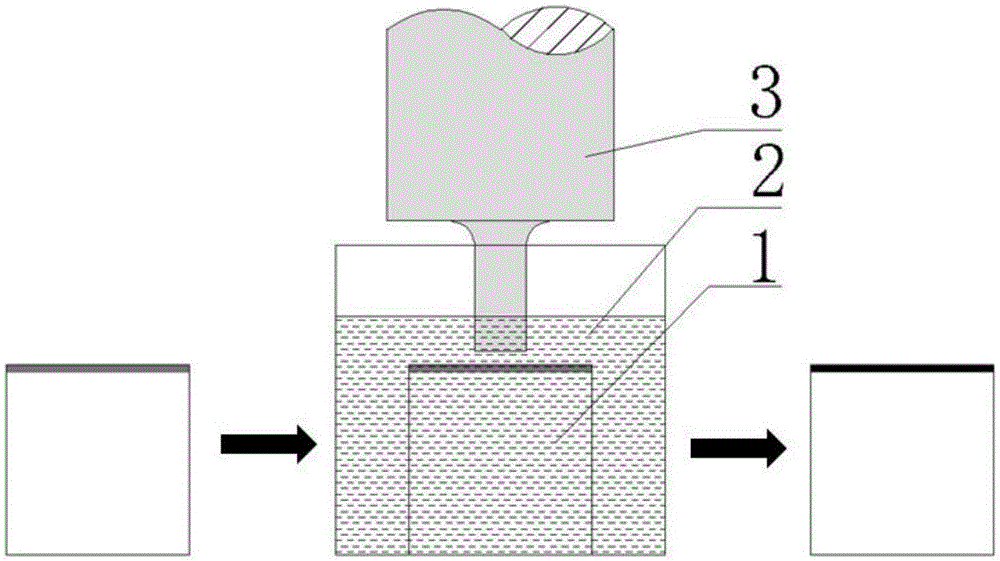
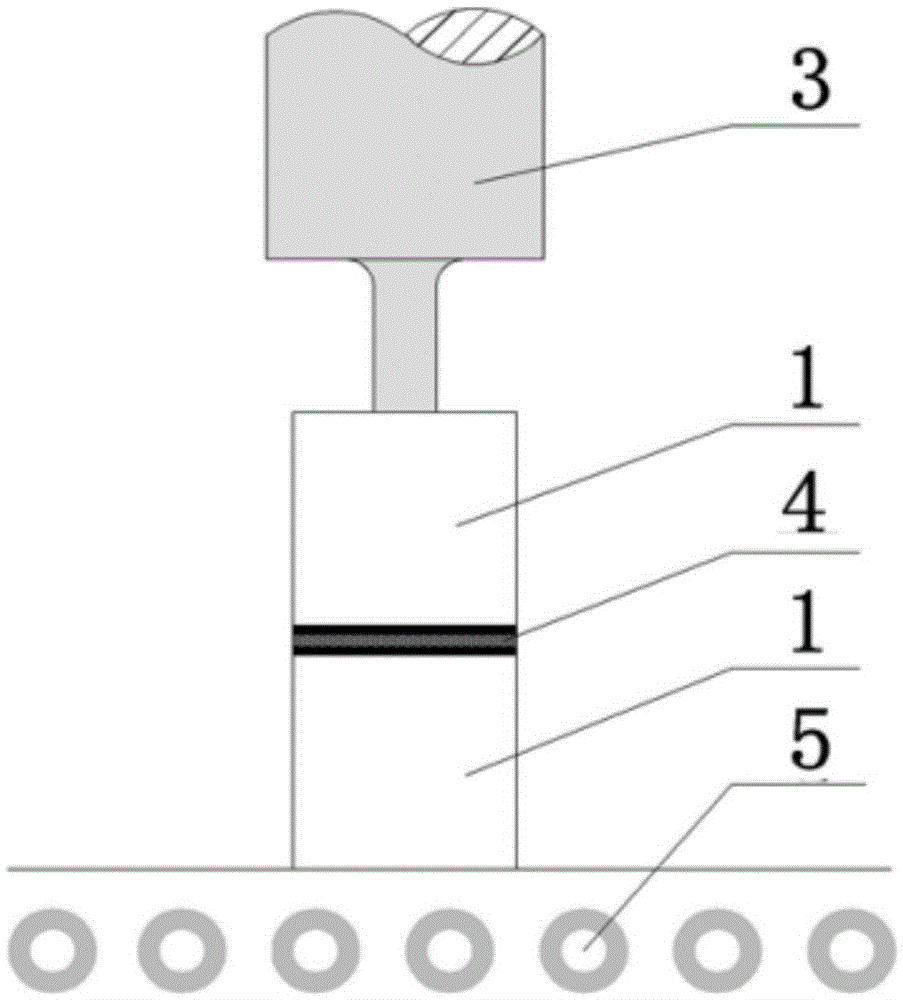
[0034] 2) if figure 1 As shown, the Ni layer of the two ceramic base materials 1 is immersed in the molten Sn pool 2 respectively, and the ultrasonic probe 3 is placed 1000 μm above the Ni coating, and the ultrasonic vibration is turned on. The vibration frequency, power, time and amplitude used 30kHz, 100W, 1min and 5μm respectively, the vibration direction is perpendicular to the upper surface of the ceramic base material 1, remove the ultrasonic probe 3 after the vibration is over, and take out the obtained base material to be welded (wit...
Embodiment 2
[0038] A low-temperature brazing method, the ceramic base material selected is zirconia ceramics, and the solder is Sn-Bi solder, and the specific steps are as follows:
[0039] 1) Take two cylindrical ceramic base materials 1 (zirconia ceramics) whose dimensions are both Ф5mm×5mm×5mm, and plate a layer of 2 μm thick on the surface to be welded of the two ceramic base materials 1 by electroless plating process. Ni layer;
[0040] 2) if figure 1 As shown, the Ni layer of the two ceramic base materials 1 is immersed in the molten Sn pool 2 respectively, and the ultrasonic probe 3 is placed 100 μm above the Ni coating layer, and the ultrasonic vibration is turned on. The vibration frequency, power, time and amplitude used 30kHz, 100W, 5min and 5μm respectively, the vibration direction is perpendicular to the upper surface of the ceramic base material 1, after the vibration is over, remove the ultrasonic probe 3, and take out the obtained base material to be welded (with Sn metal...
Embodiment 3
[0044] A low-temperature brazing method, the ceramic base material selected is alumina ceramics, and the brazing filler metal is pure Sn-based brazing filler metal, and the specific steps are as follows:
[0045] 1) Take two cuboid ceramic base materials 1 whose dimensions are 4mm×4mm×3mm, and plate a layer of Ni layer with a thickness of 2 μm on the surfaces to be welded of the two ceramic base materials 1 respectively by electroplating process;
[0046] 2) if figure 1 As shown, the Ni layer of the two ceramic base materials 1 is immersed in the molten Sn pool 2 respectively, and the ultrasonic probe 3 is placed 100 μm above the Ni coating layer, and the ultrasonic vibration is turned on. The vibration frequency, power, time and amplitude used 30kHz, 100W, 2min and 5μm respectively, the vibration direction is perpendicular to the upper surface of the ceramic base material 1, remove the ultrasonic probe 3 after the vibration is over, and take out the obtained base material to ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com