Immunofluorescence reagent for detecting E-type enterovirus and detection kit thereof
An enterovirus and immunofluorescence technology, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of endangering the healthy development of the cattle industry, lack of research on diagnosis and prevention, and achieve the effect of ensuring sensitivity, high sensitivity, and high sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] The construction of embodiment 1E enterovirus structural protein VP1 prokaryotic expression recombinant plasmid
[0023] 1. Primer design
[0024] According to the base composition of the target sequence, primers were designed to amplify the VP1 gene, and the upstream and downstream contained BamHI and EcoRI restriction sites respectively. The primer sequences are as follows:
[0025] E-VP1-FCGC GGATCC GAAACAAGCGTGGAGA (BamHI)
[0026] E-VP1-RCCG GAATTC GTACGAGGTGAGGCT (EcoRI)
[0027] 2. Gene amplification
[0028] Genomic RNA of enterovirus E was extracted by the conventional Trizol method, and cDNA was obtained by using a commercially available conventional reverse transcription kit according to the instructions, and the VP1 gene was amplified using it as a template, and its base sequence is shown in the sequence table SEQ ID NO. As shown in 1, the amino acid sequence of expressed protein VP1 is shown in SEQ ID NO.2; PCR reaction system:
[0029]
[0030]...
Embodiment 2V
[0033] Expression and purification of embodiment 2VP1 recombinant protein
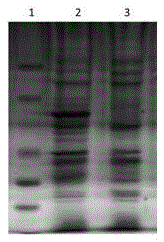
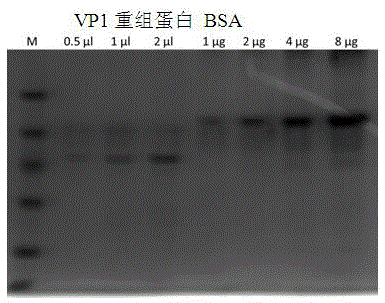
[0034] After the identified positive recombinant plasmid pGEX-4T-1-VP1 was transformed into BL21(DE3) competent cells, a single colony was picked and inoculated into 3 mL of LB liquid medium containing 100 μg / mL ampicillin for overnight culture, and then 1 mL of the above The culture was inoculated into 200 mL LB liquid medium containing 100 μg / mL ampicillin and cultured with shaking at 37 °C until the logarithmic growth phase (OD 600 =0.6~0.8), adding IPTG to a final concentration of 1mmol / L, inducing culture at 20°C for 3h, and detecting by SDS-PAGE, the recombinant target protein VP1 was obtained, as shown in figure 2 shown. Centrifuge and precipitate the bacteria, and after sonication, use urea to purify inclusion bodies to obtain high-purity recombinant proteins, such as image 3 shown.
Embodiment 3
[0035] Example 3 Preparation of anti-E enterovirus VP1 protein monoclonal antibody
[0036] 1. Animal immunization: select healthy BALB / c mice aged 6-8 weeks, emulsify the purified VP1 protein with Freund's complete adjuvant, inject about 100 μg intraperitoneally into each mouse, and emulsify the protein with Freund's incomplete adjuvant 14 days later Inject 100 μg intraperitoneally, and inject 100 μg purified protein directly intraperitoneally during the last booster immunization, and inject 50 μg purified protein into the tail vein 3 to 4 days before fusion;
[0037] 2. Cell fusion: Take splenocytes from immunized mice and mix them with SP2 / 0 in a fusion tube, centrifuge at 300g for 10 minutes, discard the supernatant, shake the cells to mix the two cells as evenly as possible, and then slowly drop and preheat within 60 seconds PEG-4000 solution, then slowly add serum-free 1640 medium to terminate the fusion, let it stand still and then centrifuge at 1000r / min for 10min, dis...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com