Nano-particle material, and light-emitting device
一种纳米粒子、发光器件的技术,应用在发光器件领域,能够解决材料制约大、成本提高、制造工序工序增加等问题,达到阻挡性能提高、注入效率提高、驱动电压低的效果
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach 〕
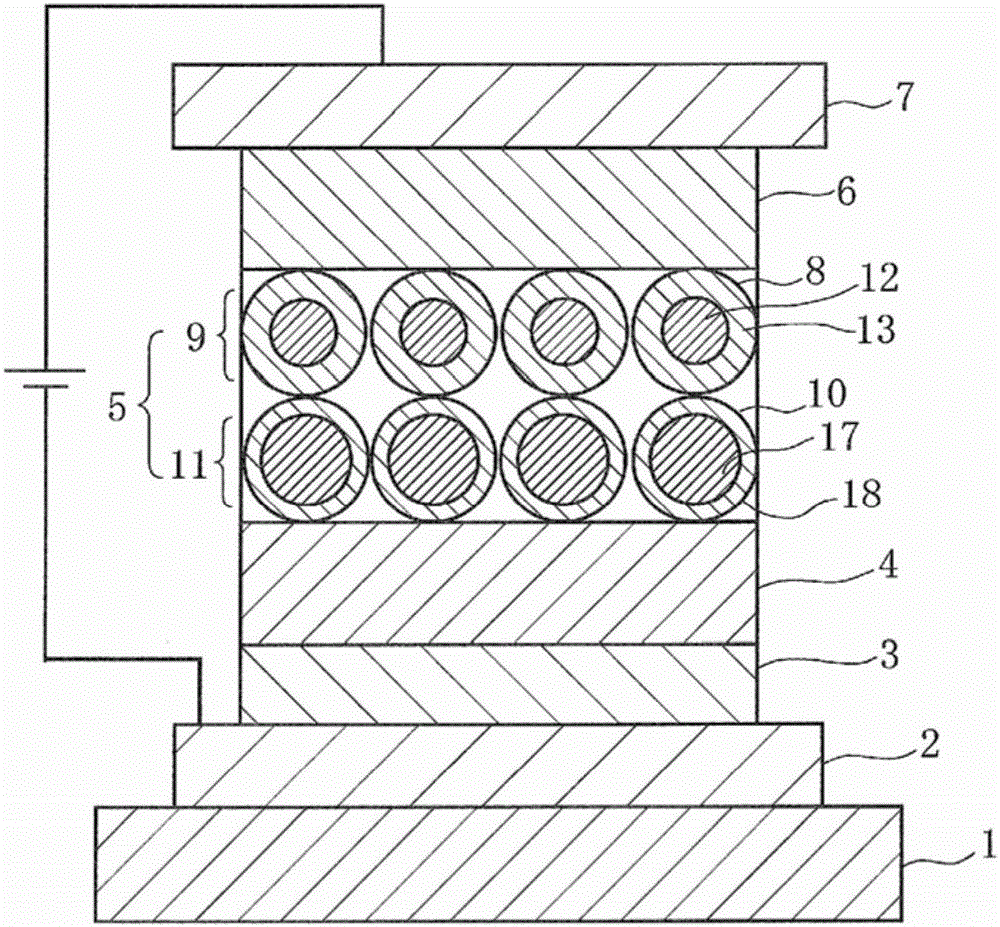
[0098] figure 1 It is a cross-sectional view schematically showing a first embodiment of an EL element as a light-emitting device according to the present invention, and the light-emitting layer is formed of the nanoparticle material according to the present invention.
[0099] In this EL element, an anode 2 is formed on a transparent substrate 1 such as a glass substrate, and a hole injection layer 3 and a hole transport layer 4 formed of a hole transport material are sequentially formed on the surface of the anode 2. The surface of the layer 4 is formed with a light emitting layer 5 . In addition, an electron transport layer 6 made of an electron transport material is formed on the surface of the light emitting layer 5 , and a cathode 7 is formed on the surface of the electron transport layer 6 .
[0100] The light-emitting layer 5 becomes a first light-emitting layer 9 having first quantum dots 8 arranged vertically and horizontally as the nanoparticle material of the pre...
no. 2 approach 〕
[0184] Figure 8 It is a cross-sectional view schematically showing a second embodiment of an EL element as a light emitting device according to the present invention.
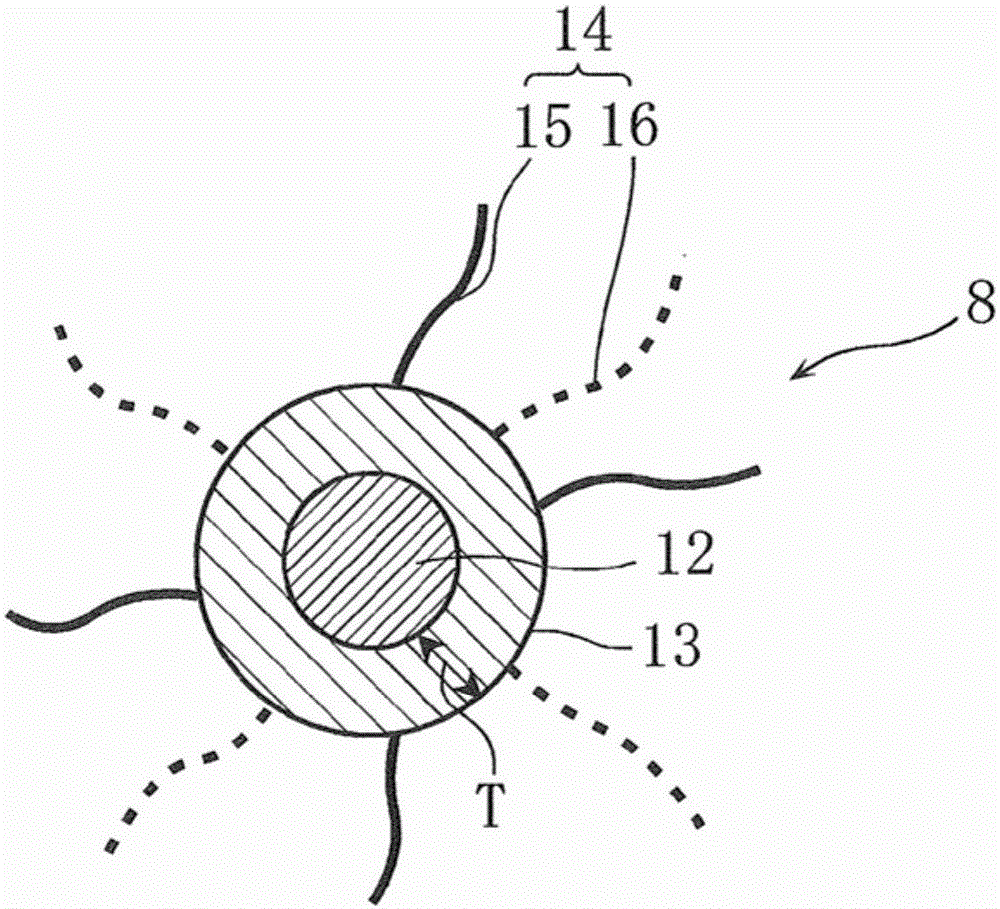
[0185] In this EL element, the light-emitting layer 24 has a laminated structure of a first light-emitting layer 25 formed of first quantum dots 27 and a second light-emitting layer 26 formed of second quantum dots 10 . Furthermore, in the second quantum dot 10, the shell portion 18 is covered with the respective surfactants having hole-transporting and electron-transporting properties, while in the first quantum dot 27, the shell portion 13 is only transported by electrons. Active surfactant coverage.
[0186] That is, in this second embodiment, the first quantum dot 27 such as Figure 9 As shown, it has a core-shell structure including a core part 12 and a shell part 13. The surface of the shell part 13 is covered only by the second surfactant 16 having electron transport properties. The thickness T of the...
no. 3 approach 〕
[0204] Figure 12 It is a cross-sectional view schematically showing a third embodiment of an EL element as a light emitting device according to the present invention.
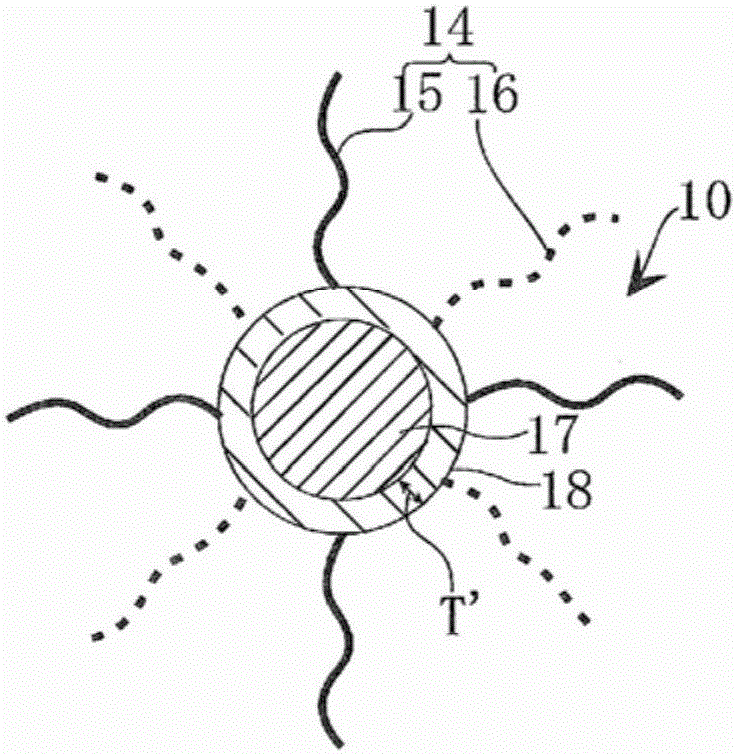
[0205] In this EL element, the light-emitting layer 30 has a laminated structure of a first light-emitting layer 31 formed of first quantum dots 33 and a second light-emitting layer 32 formed of second quantum dots 10 . Furthermore, the second quantum dots 10 are covered with the respective surfactants having hole-transporting properties and electron-transporting properties, while the first quantum dots 33 are covered with insulating surfactants.
[0206] That is, in this third embodiment, the first quantum dot 33 such as Figure 13 As shown, it has a core-shell structure including a core part 12 and a shell part 13. The surface of the shell part 13 is covered with an insulating third surfactant 34. The thickness T of the shell part 13 is determined by the constituent molecules of the shell part 13. Benchmar...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com