Method for purifying mulberry phytoplasma genome
A purification method and genome technology, applied in the field of purification of mulberry phytoplasma DNA, can solve the problems of increased purification difficulty, inapplicability, and high genome content requirements
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0024] The present invention is further described below in conjunction with the examples, but the present invention is not limited to the following examples.
[0025] A kind of purification method for mulberry phytoplasma genome, comprising the following steps:
[0026] Step 1, sample processing, because the phloem sieve tube cells of plants do not have nuclei, the genome content of mulberry is low, and the content of phytoplasma is high. Use a scalpel to take 1 g of the phloem of the branches of the diseased plant infected with phytoplasma of mulberry, put it into a clean mortar, add liquid nitrogen to freeze and grind it evenly;
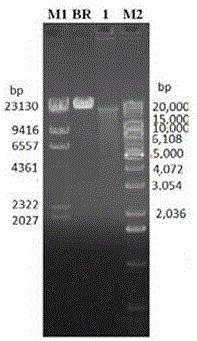
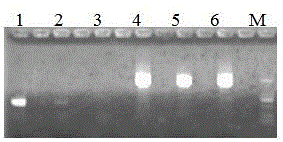
[0027] Step 2: Extract genomic DNA. Compare the three genomic extraction methods of spin column, magnetic beads and ethanol precipitation. The magnetic bead method can extract the longest fragment, which can reach more than 50kbp. In order to improve the removal efficiency of the host protein in the next step, magnetic The genome of the sample was...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com