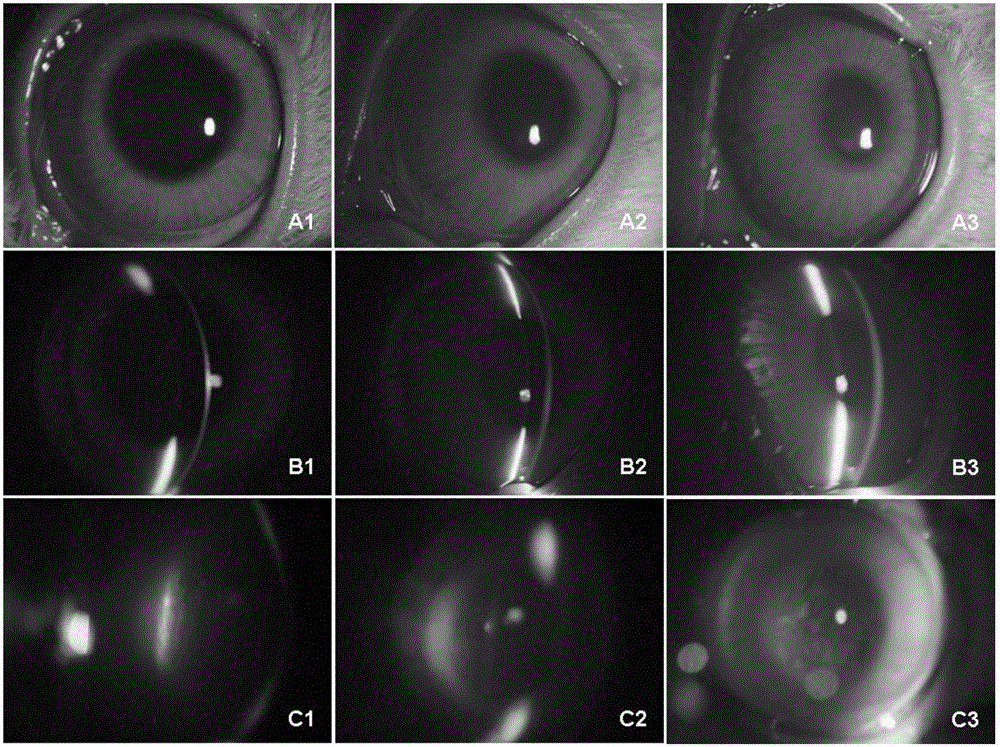
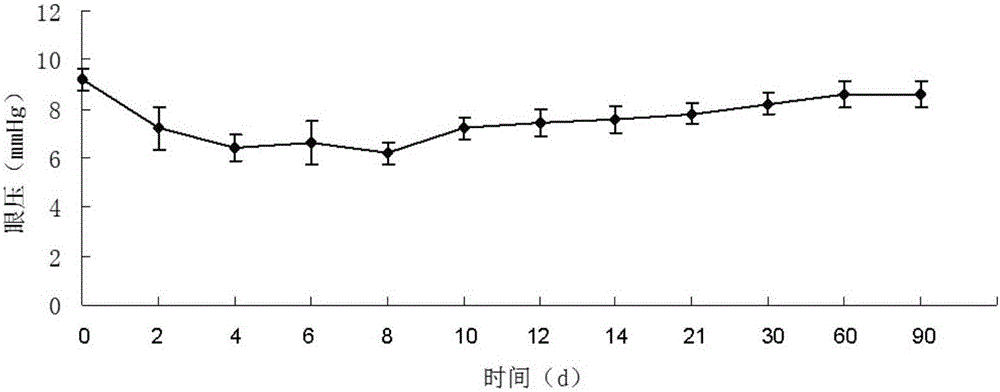
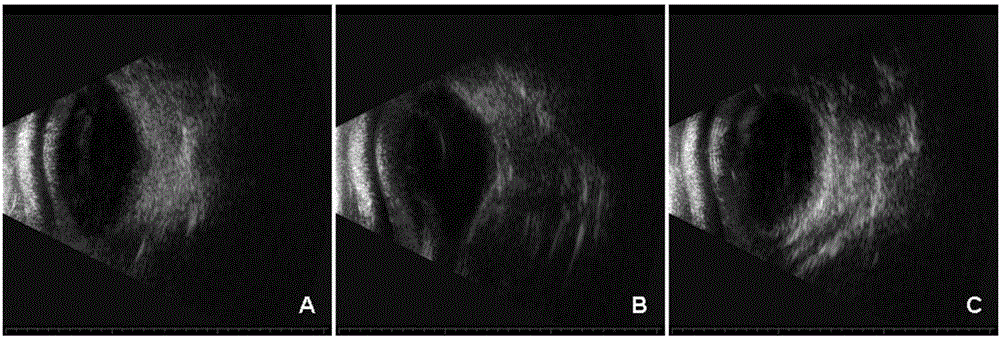
Application of injectable hydrogel in preparing intraocular filling materials
A technology for injecting water and fillers, which is applied in medical preparations with non-active ingredients, medical science, prostheses, etc., and can solve problems such as lack of vitreous fillers, small molecule cross-linking agents that cannot be removed, side effects of eye tissue cells, etc. Achieve good biocompatibility and biosafety in the eye, reduce the number of medications, and have no toxic and side effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] Example 1: Preparation of oxidized chondroitin sulfate
[0021] Weigh 12.0g of chondroitin sulfate, add it to a 500ml glass Erlenmeyer flask, add 200ml of water, stir to dissolve, adjust the pH value to pH5.0 with 1mol / L hydrochloric acid aqueous solution, add the oxidant NaIO 4 1g, sealed, stirred and oxidized for 18h at 4°C in the dark. After the reaction, the reaction solution was put into a dialysis bag with a molecular weight cut-off of 3000 Daltons, and the solution was dialyzed against light and distilled water at 4° C. for 24 hours, and the distilled water was replaced every 6 hours. After the dialysis, the liquid in the dialysis bag was freeze-dried in a freeze dryer for 48 hours to obtain 11.3 g of oxychondroitin sulfate containing dialdehyde groups, with a dialdehyde group percentage of 2.5% (dialdehyde group percentage is Refers to the percentage of sugar units containing dialdehyde groups in the polysaccharide molecule to the total sugar units of the polysacc...
Embodiment 2
[0022] Example 2: Preparation of oxidized starch
[0023] Weigh 15g starch, add it to a 500ml glass Erlenmeyer flask, add 200ml water, heat and stir to dissolve, adjust the pH value to pH 5.5 with 5% (weight percentage, the same below) aqueous acetic acid solution, add the oxidant NaIO 4 3.5g, sealed, stirred and oxidized at room temperature for 24h in the dark. After the reaction, the reaction solution was put into a dialysis bag with a molecular weight cut-off of 3000 Daltons, and the solution was dialyzed against light and distilled water at 4° C. for 24 hours, and the distilled water was replaced every 6 hours. After the dialysis, the liquid in the dialysis bag was freeze-dried in a freeze dryer for 48 hours to obtain 13.5 g of oxidized starch containing dialdehyde groups, with a dialdehyde group percentage of 12.5%.
Embodiment 3
[0024] Example 3: Preparation of oxidized hyaluronic acid
[0025] Weigh 5g of hyaluronic acid, add it to a 1000ml glass Erlenmeyer flask, add 500ml of water, stir to dissolve, adjust the pH value to pH 5.5 with 5% (weight percentage, the same below) aqueous acetic acid solution, add the oxidant NaIO 4 2.5g, sealed, stirred and oxidized at room temperature in the dark for 24h. After the reaction, the reaction solution was put into a dialysis bag with a molecular weight cut-off of 3000 Daltons, and the solution was dialyzed against light and distilled water at 4° C. for 24 hours, and the distilled water was replaced every 6 hours. After the dialysis, the liquid in the dialysis bag was freeze-dried in a freeze dryer for 48 hours to obtain 3.9 g of oxidized hyaluronic acid containing dialdehyde groups, with a dialdehyde group percentage of 30.8%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com