Method and device for degrading nitrobenzene waste water through reinforced iron-carbon micro-electrolysis-ozonation method
A technology for iron-carbon micro-electrolysis and nitrobenzene wastewater, which is applied in chemical instruments and methods, oxidized water/sewage treatment, water pollutants, etc., and can solve the problems of passivation and deactivation of fillers, limited efficiency improvement, and blocked electrolysis reactions. problem, to achieve high reaction rate, reduce ozone consumption, reduce the effect of loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
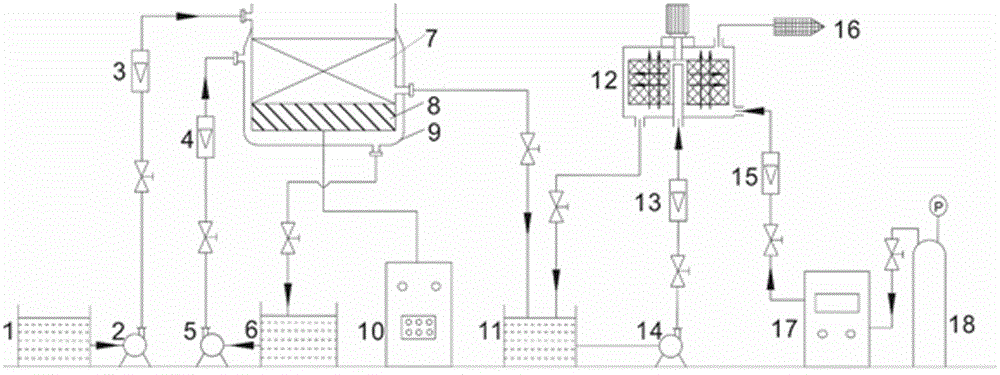
[0033] Example 1: Using figure 1 The flow chart of the device shown is for the treatment of wastewater containing nitrobenzene. The initial concentration of nitrobenzene in the wastewater was 300 mg / L, and the pH value was 2. In the micro-electrolyzer, the concentration of scrap iron chips is 20g / L, the mass ratio of iron to carbon is 3:1, the ultrasonic output power is 8kW, the frequency is 40 KHz, and the cooling water flow rate in the jacket and external circulation is 60L / h. will be 1m 3 After the nitrobenzene wastewater was injected into the micro-electrolyzer for 30 minutes, 99% of the nitrobenzene was reduced to aniline, and the reaction rate was 7 times higher than that of the traditional iron-carbon micro-electrolysis method, and the free Fe in the wastewater 2+ Concentration increased by 6.2 times. After the micro-electrolysis is completed, the wastewater is subjected to high-gravity-ozone oxidation for deep degradation. The rotation speed of the rotating packed b...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Example 2: Using figure 1 The flow chart of the device shown is for the treatment of wastewater containing nitrobenzene. The initial concentration of nitrobenzene in the wastewater was 500 mg / L, and the pH value was 2.5. In the micro-electrolyzer, the concentration of scrap iron chips is 30 g / L, the mass ratio of iron to carbon is 1:3, the ultrasonic output power is 6 kW, the frequency is 20 KHz, and the flow rate of cooling water in the jacket and external circulation is 45 L / h. will be 1m 3 After the nitrobenzene wastewater was injected into the micro-electrolyzer and reacted for 45 minutes, 96% of the nitrobenzene was reduced to aniline, and the reaction rate was 10 times higher than that of the traditional iron-carbon micro-electrolysis method, and the free Fe in the wastewater 2+ Concentration increased by 8 times. After the micro-electrolysis is completed, the wastewater is subjected to high-gravity-ozone oxidation for deep degradation. The rotation speed of th...
Embodiment 3
[0035] Example 3: Using figure 1 The flow chart of the device shown is for the treatment of wastewater containing nitrobenzene. The initial concentration of nitrobenzene in the wastewater was 100 mg / L, and the pH value was 4. In the micro-electrolyzer, the concentration of scrap iron chips is 10 g / L, the mass ratio of iron to carbon is 1:1, the ultrasonic output power is 4 kW, the frequency is 30 KHz, and the flow rate of cooling water in the jacket and external circulation is 30 L / h. will be 1m 3 After the nitrobenzene wastewater was injected into the micro-electrolyzer for 40 minutes, 99% of the nitrobenzene was reduced to aniline, the reaction rate was 6 times higher than that of the traditional iron-carbon micro-electrolysis method, and the free Fe in the wastewater 2+ Concentration increased by 5 times. After the micro-electrolysis is completed, the wastewater is subjected to high-gravity-ozone oxidation deep degradation, the rotary packed bed speed is 600 rpm, the liq...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com