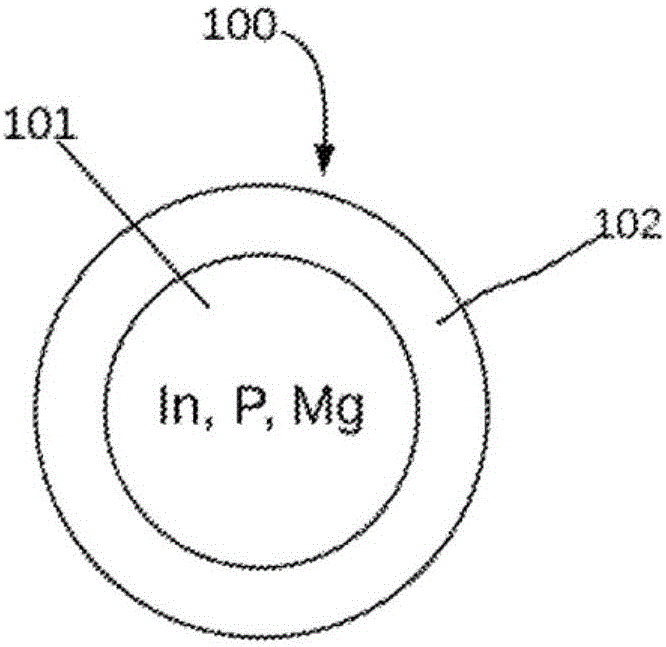
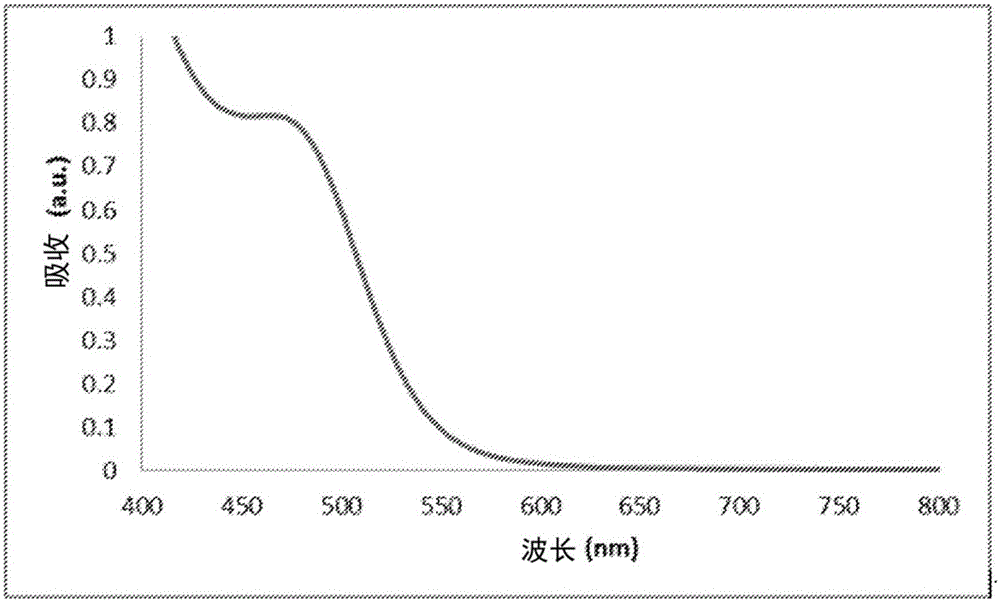
Cadmium-free quantum dot nanoparticles
A technology of nanoparticles and quantum dots, applied in the field of quantum dot nanoparticles, can solve problems such as difficulty in obtaining
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] Example 1: Magnesium-containing core.
[0043] Magnesium myristate was prepared by heating magnesium acetate tetrahydrate (2.92 g) and myristic acid (12.4 g) to 110° C. under vacuum until the solution became clear and no more liquid was produced. This freshly prepared magnesium myristate was used in the following synthesis: Indium myristate (4.55 g), magnesium myristate (2.33 mL), myristic acid (0.76 g) and Therminol 66 (50 mL) were placed in an apparatus In a dry 250 mL round bottom flask with air condenser, nitrogen inlet, suba seal, thermocouple and stir bar, and degas under vacuum at 100 °C for 1 hour. The reaction was then placed under a nitrogen atmosphere and zinc sulfide clusters (1.35 g, prepared as described in US Pat. No. 8,062,703) were added. The reaction was then degassed under vacuum for another 1 / 2 hour, and then placed under a nitrogen atmosphere. A solution of tris(trimethylsilyl)phosphine (1 M in diphenyl ether) was added dropwise while increasing...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Example 2: Cores containing zinc and magnesium
[0047] Indium myristate (11.74 g), zinc acetate (0.734 g), magnesium stearate (0.591 g) and myristic acid (1.507 g) were stirred in 100 mL of Therminol 66 and heated to 100°C. Zinc sulfide clusters (2.7 g, prepared as described in US Pat. No. 8,062,703) were added. Trimethylsilylphosphine (18.5 mmol) was added at a rate of 7.2 mL / hour, and the reaction mixture was heated to 195° C. and allowed to anneal for 140 hours.
Embodiment 3
[0048] Example 3: Cores Containing Zinc and Aluminum
[0049] Indium myristate (11.74 g), zinc acetate (0.734 g), aluminum stearate (0.877 g) and myristic acid (1.507 g) were stirred in 100 mL of Therminol 66 and heated to 100°C. Zinc sulfide clusters (2.7 g, prepared as described in US Pat. No. 8,062,703) were added. Trimethylsilylphosphine (18.5 mmol) was added at a rate of 7.2 mL / hour, and the reaction mixture was heated to 195° C. and allowed to anneal for 140 hours.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com