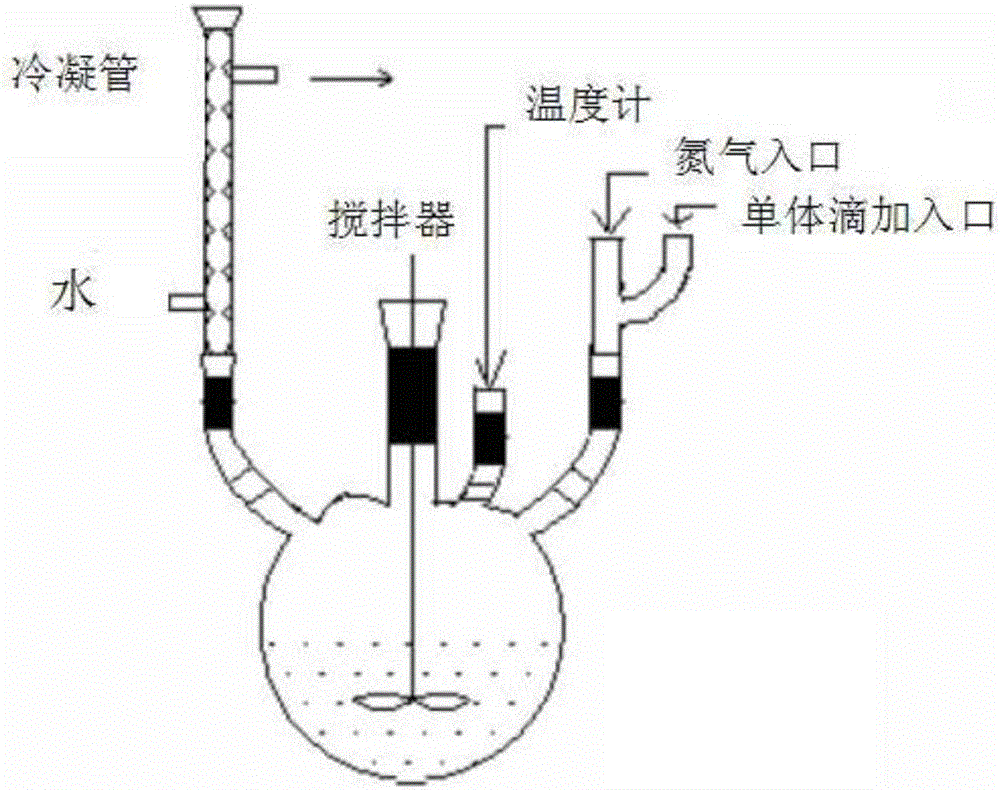
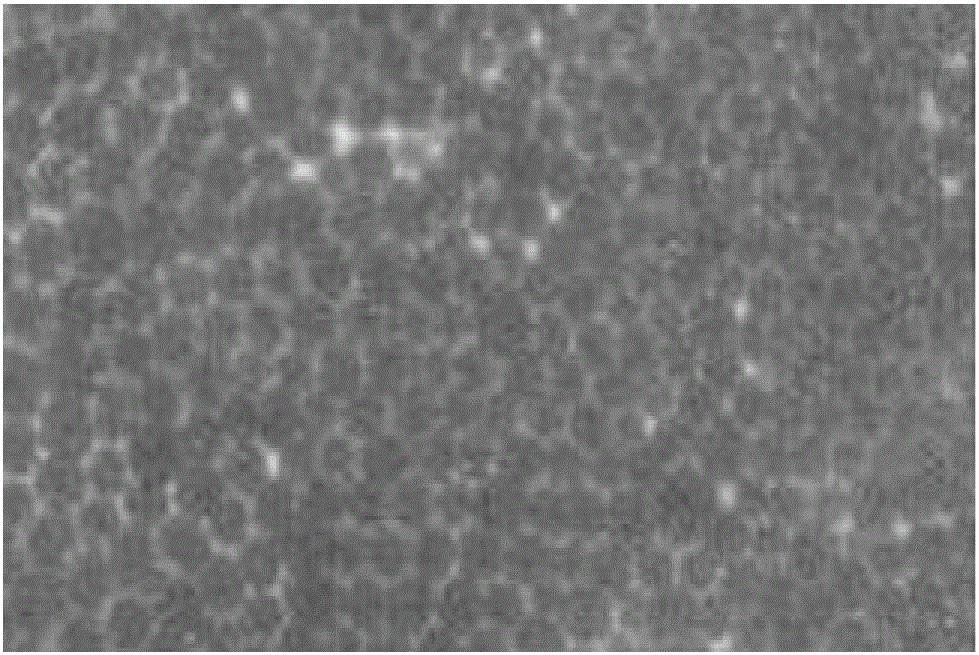
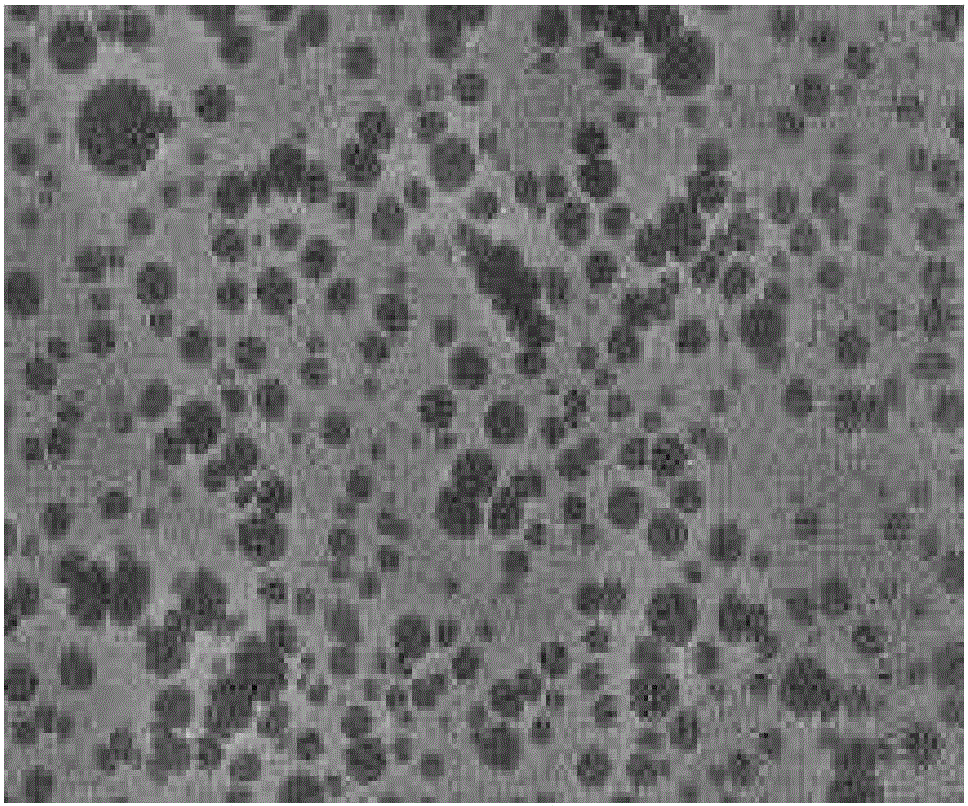
Modified superabsorbent polymer, preparation method thereof and application thereof to cement-based material
A superabsorbent and polymer technology, applied in the field of cement-based materials, can solve the problems of reduced water absorption rate, interface damage, irregular and uniform particle shape, etc., and achieve the goal of improving early hydration degree, regular and uniform particle shape, and excellent water retention performance Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Embodiment 1: In a four-necked bottle, with deionized water as the dispersed phase, add 2 parts by weight of phenethylphenol polyoxyethylene ether, 2 parts by weight of sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate, 1 part by weight of n- Butanol, 0.5 parts by weight (NH 4 ) 2 S 2 o 8 The initiator and 0.5 parts by weight of N,N'-methylenebisacrylamide are stirred and mixed to form a homogeneous soap liquid. In a four-necked flask with a water bath temperature of 60°C, under the protection of nitrogen, 100 parts by weight of mixed monomers were added dropwise within half an hour. In the mixed monomers, the content of acrylic acid neutralized by NaOH was 68%, and the content of acrylamide 12%, sodium styrene sulfonate content 10%, 2-acrylamido-2-methylpropanesulfonic acid content 10%, turn on the ultrasonic wave, react for 1 hour, and prepare SAP microemulsion. After finishing the reaction, the product was dried to obtain a crude product. The obtained crude product was put into di...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Embodiment 2: In a four-necked bottle, with deionized water as the dispersed phase, add 1 weight part of phenethylphenol polyoxyethylene ether, 2 weight parts of sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate, 1 weight part of n- Butanol, 0.7 parts by weight (NH 4 ) 2 S 2 o 8The initiator and 0.3 parts by weight of N,N'-methylenebisacrylamide are stirred and mixed to form a homogeneous soap liquid. In a four-necked flask with a water bath temperature of 50°C, under the protection of nitrogen, 100 parts by weight of mixed monomers were added dropwise within half an hour. In the mixed monomers, the content of acrylic acid neutralized by NaOH was 80%, and the content of acrylamide 10%, sodium styrene sulfonate content 5%, 2-acrylamido-2-methylpropanesulfonic acid content 5%, turn on the ultrasonic wave, react for 1.5h, and prepare SAP microemulsion. After finishing the reaction, the product was dried to obtain a crude product. The obtained crude product was put into distilled water, ...
Embodiment 3
[0035] Embodiment 3: In a four-necked bottle, with deionized water as the dispersed phase, add 2 parts by weight of phenethylphenol polyoxyethylene ether, 3 parts by weight of sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate, 2 parts by weight of n- Butanol, 0.5 parts by weight (NH 4 ) 2 S 2 o 8 The initiator and 0.5 parts by weight of N,N'-methylenebisacrylamide are stirred and mixed to form a homogeneous soap liquid. In a four-necked flask with a water bath temperature of 50°C, under the protection of nitrogen, 100 parts by weight of mixed monomers were added dropwise within half an hour. In the mixed monomers, the content of acrylic acid neutralized by NaOH was 75%, and the content of acrylamide 10%, 7% sodium styrene sulfonate, and 8% 2-acrylamido-2-methylpropanesulfonic acid, turned on the ultrasonic wave, and reacted for 1.2 hours to prepare the SAP microemulsion. After finishing the reaction, the product was dried to obtain a crude product. The obtained crude product was put into di...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com