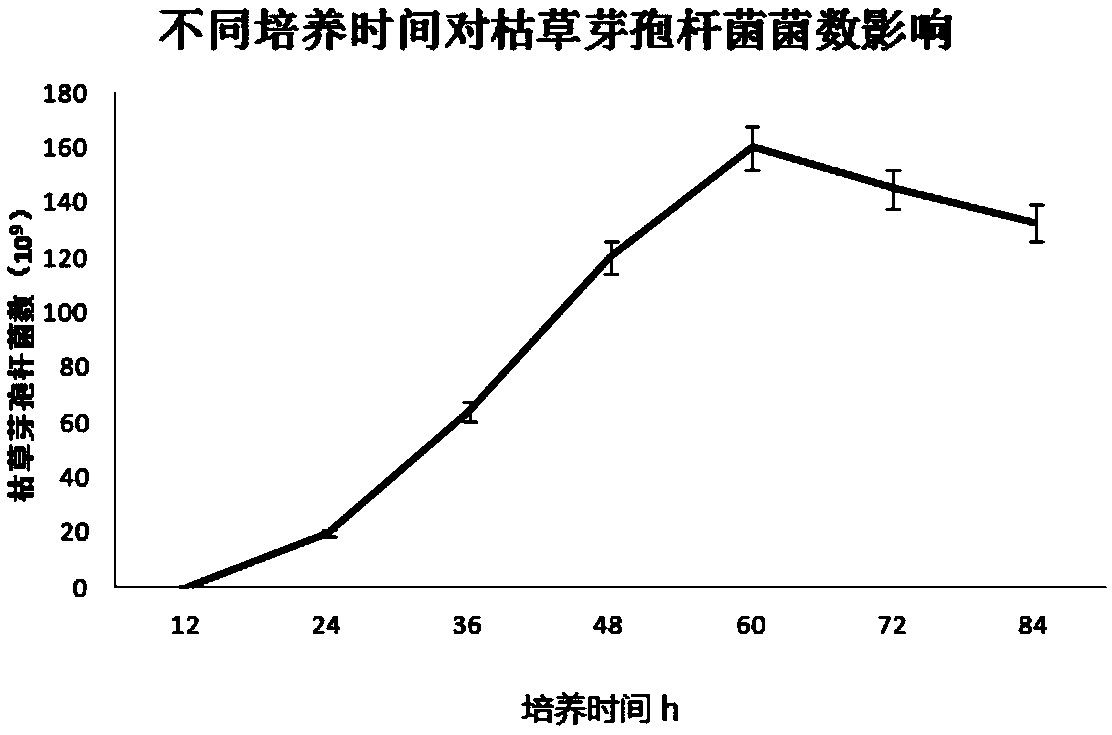
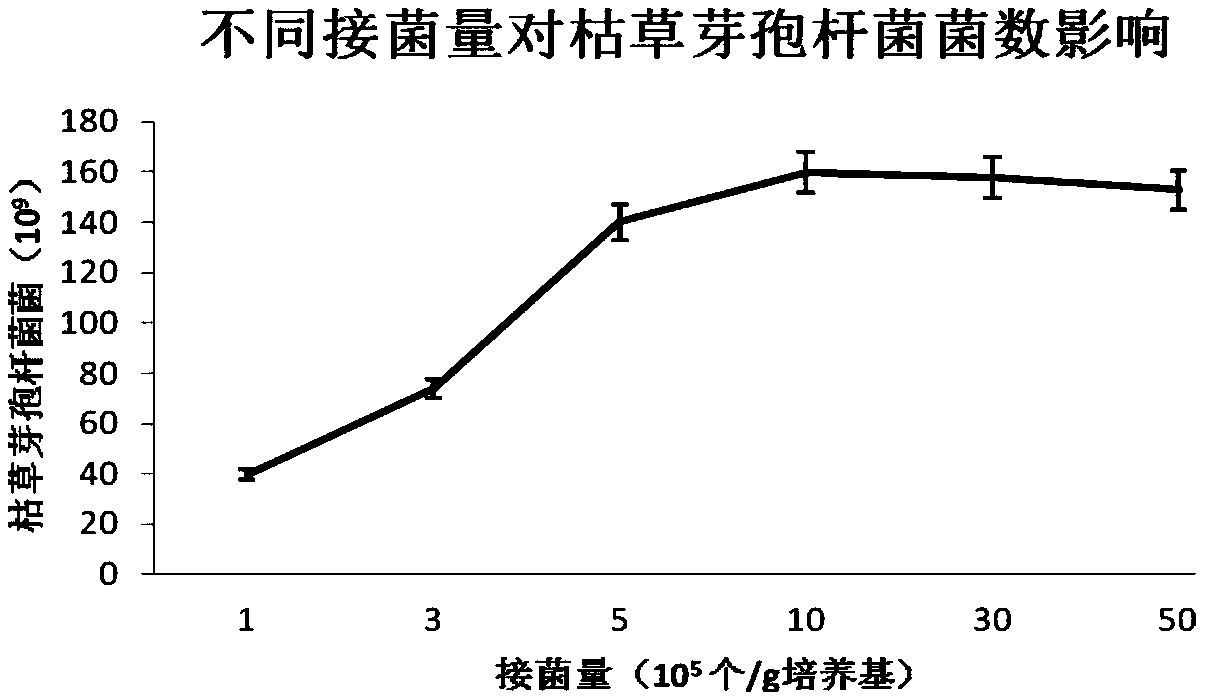
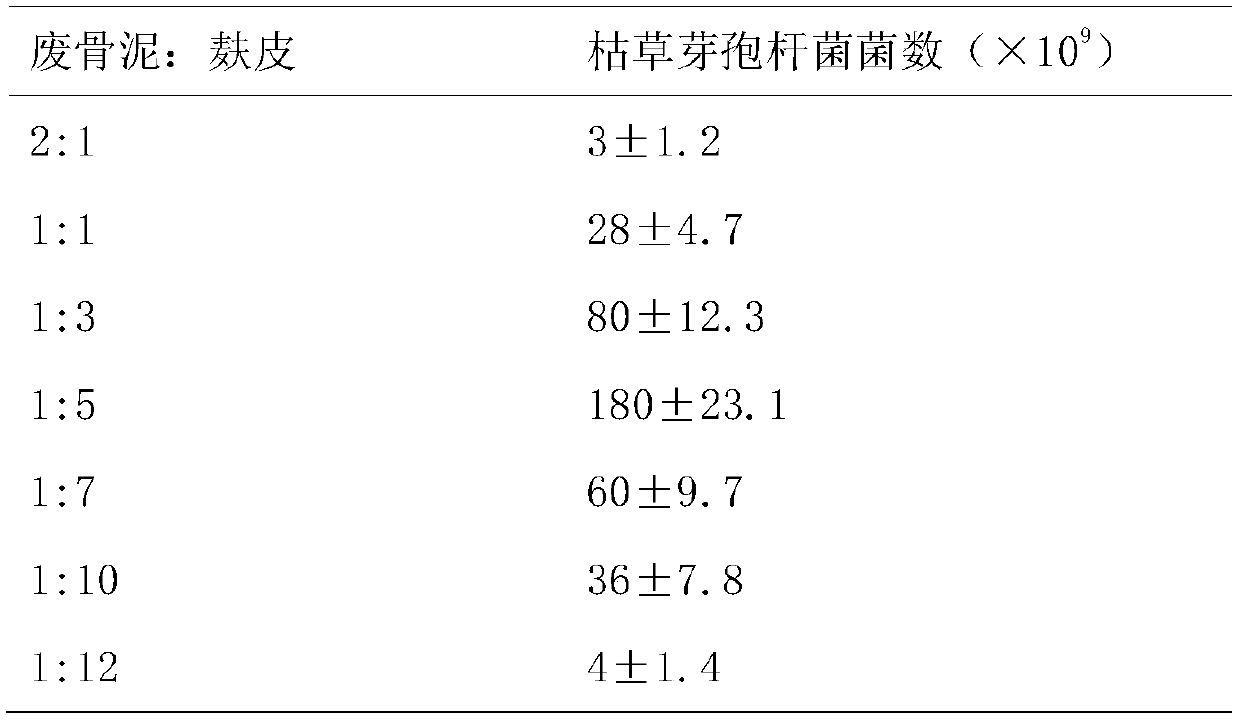
A method for producing Bacillus subtilis by solid fermentation using chondroitin sulfate to produce industrial waste bone sludge as raw material
A technology of Bacillus subtilis and chondroitin sulfate, which is applied in the field of microorganisms to achieve the effects of easy operation, lower price, and convenience for industrialized large-scale production and application
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Example 1: Prepare 100 kg of solid fermentation medium according to the mass ratio of waste bone mud, bran and water 3:20:60, stir evenly, sterilize at 120°C for 20 minutes, press 5×10 5 Bacillus subtilis was inserted into the culture medium per g, solid fermentation at 35-37°C for 48 hours, the fermentation process was divided into two stages: static culture was adopted for 1-8 hours, after 8 hours, the temperature was controlled by sterile air at 35-37°C, and stirring was started every 6 hours 20rpm time 10min. After 48 hours of fermentation, the fermentation product was collected. Dried at 50-60°C until the water content is lower than 8%, crushed and passed through an 80-mesh sieve to obtain Bacillus subtilis for feed. According to GB / T 26428-2010 "Detection of Bacillus subtilis in microbial preparations for feed" method to detect the number of Bacillus subtilis >6.0×10 10 pcs / g.
Embodiment 2
[0028] Example 2: Prepare 100 kg of solid fermentation medium according to the mass ratio of waste bone mud, bran and water 8:30:80, stir evenly, sterilize at 120°C for 20 minutes, press 1×10 6 Bacillus subtilis was inserted into the culture medium per g, and solid fermentation was carried out at 35-37°C for 60 hours. The fermentation process is divided into two stages: static culture is adopted for 1-8h, and after 8h, the temperature is controlled by sterile air at 35-37°C, and stirring is started at 20rpm for 10min every 6h. After 60 h of fermentation, the fermentation product was collected. Dried at 50-60°C until the water content is lower than 8%, crushed and passed through an 80-mesh sieve to obtain Bacillus subtilis for feed. According to GB / T 26428-2010 "Detection of Bacillus subtilis in feed microbial preparations" method to detect the number of Bacillus subtilis > 1.0×10 11 pcs / g.
Embodiment 3
[0029] Example 3: Prepare 100 kg of solid fermentation medium according to the mass ratio of waste bone mud, bran, and water 3:10:20. After stirring evenly, sterilize at 120° C. for 20 minutes, and press 5×10 6 Bacillus subtilis was inserted into the culture medium per g, and solid fermentation was carried out at 35-37°C for 72 hours. The fermentation process is divided into two stages: static culture is adopted for 1-8h, and after 8h, the temperature is controlled by sterile air at 35-37°C, and stirring is started at 20rpm for 10min every 6h. After 72 hours of fermentation, the fermentation products were collected. Dried at 50-60°C until the water content is lower than 8%, crushed and passed through an 80-mesh sieve to obtain Bacillus subtilis for feed. According to GB / T 26428-2010 "Detection of Bacillus subtilis in microbial preparations for feed" method to detect the number of Bacillus subtilis >8×10 10 pcs / g.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com