Fuel element and preparation method and application thereof
A fuel element and fuel layer technology, which is applied to fuel elements, reactor fuel elements, and manufacturing reactors, etc., can solve the problems of complicated preparation methods, poor compatibility of molten salts, and high bulk density.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example 1
[0081] The preparation of preparation example 1 spherical phenolic resin base foam carbon
[0082] Take the phenolic resin and hexamethylenetetramine, mix them at a mass ratio of 9:1, and fully dissolve them in absolute ethanol to prepare a resin solution. Put the resin solution into an autoclave, pressurize it to 1MPa with nitrogen gas, and then heat it to 180°C for foaming. After maintaining the temperature for 1 hour, at a temperature of 180° C., the pressure in the reactor was slowly reduced to normal pressure. It was further heated to 300° C., kept at constant temperature for 2 hours, and then cooled to room temperature. The obtained phenolic resin-based foam carbon precursor is carbonized at 900° C. to obtain phenolic resin-based foam carbon.
[0083] Grooves with a width of 1 mm and a depth of 1 mm are opened on the surface of the phenolic resin-based foam carbon by machining, and there are 8 grooves in the warp direction and 8 grooves in the weft direction.
Embodiment 1
[0084] Embodiment 1 The preparation of the fuel element without the fuel layer in the innermost layer
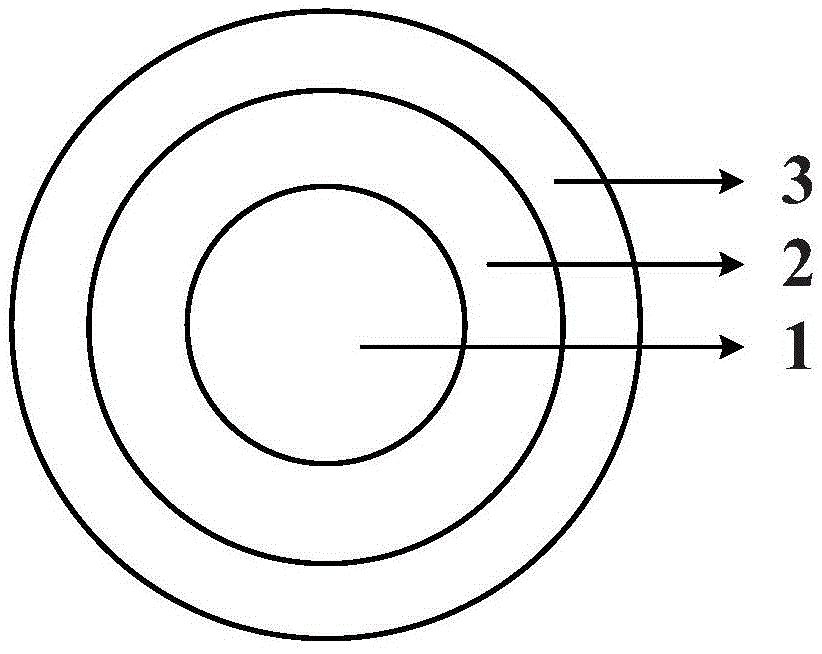
[0085] (1) The density prepared by Preparation Example 1 is 0.5-1.2g / cm 3 1. Grooved phenolic resin-based foamed carbon with a compressive strength of 40-90 MPa, which is used as the fuel-free layer (1);
[0086] (2) Using a quasi-isostatic pressing process or a coating process, the raw material of the fuel layer (2) is evenly coated outside the fuel-free layer (1); the raw material of the fuel layer (2) is formed by mixing TRISO particles and matrix graphite powder. The matrix graphite powder described is 64% natural flake graphite, 16% artificial graphite and 20% phenolic resin, and the matrix graphite powder obtained by processes such as kneading, extruding, crushing and sieving obtains sample (12);
[0087] (3) adopt the quasi-isostatic pressing process, press the shell layer (3) raw material outsourcing in the sample (12); the shell layer (3) raw material is 64% natura...
Embodiment 2
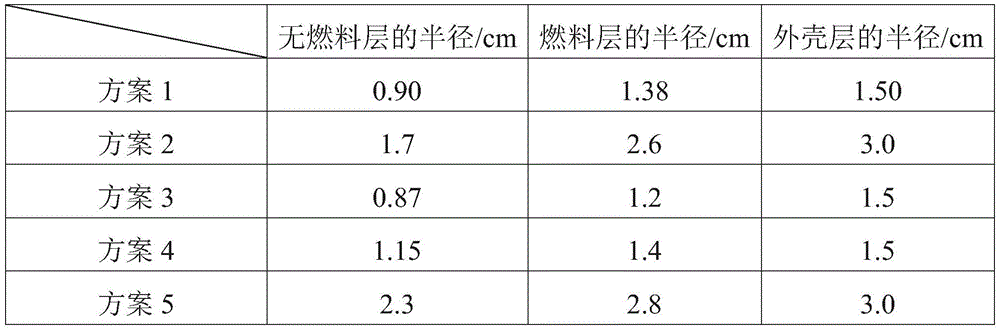
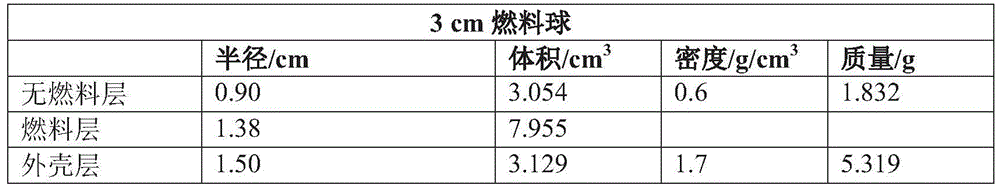
[0089] The fuel element of diameter 3cm that embodiment 2 makes
[0090] With reference to the preparation method of Example 1, a fuel element with a diameter of 3 cm was obtained, and its main parameters are shown in Table 1:
[0091] Table 1
[0092]
[0093]
[0094] The present embodiment single sphere density is 1.70g / cm 3 , the bulk density is smaller than that of the single sphere in Comparative Example 2, but the uranium content of each sphere is 1.4 times that of Comparative Example 2. At the same time, the phenolic resin-based foam carbon has good radiation resistance and good mechanical properties. It has nano-scale (20nm) pores inside and has very low thermal conductivity. It is an excellent thermal insulation material, which is beneficial to fuel Layer heat is transported outward. The average pore size of the shell layer is 1μm, and the compressive strength is 40MPa.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Bulk density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Compressive strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Softening point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com