Acid-resistant, ethanol-resistant and acetic acid-resistant Acetobacer pasteurianus
A technology of acetic acid bacteria and ethanol resistance, applied in the direction of bacteria, microorganism-based methods, microorganisms, etc., can solve the problems of poor tolerance to acetic acid, high fermentation temperature, intolerance to ethanol and acetic acid, etc., and achieve a wide range of environmental tolerance Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] Example 1 Preliminary separation and purification of high-temperature-resistant high-alcohol acetic acid bacteria
[0024] (1) Selection of acetic acid bacteria isolation source: vinegar grains from Danyang Vinegar Factory;
[0025] (2) Preliminary separation and purification of high-temperature-resistant high-alcohol acetic acid bacteria
[0026] ① Enrichment culture of acetic acid bacteria:
[0027] Add 1g of vinegar unstrained spirits from a vinegar factory (multiple) with traditional solid-state fermentation technology to 100mL of water, culture at 30°C for 5-8 days, obtain 5mL of natural fermentation liquid, put it into a conical flask containing 100mL of enriched medium, 30°C, Cultivate at 180r / min for 2 days to obtain acetic acid bacteria enriched culture solution.
[0028] Enrichment medium composition: 2% glucose, 2% yeast powder, 0.01% MgSO 4 , and the rest is distilled water;
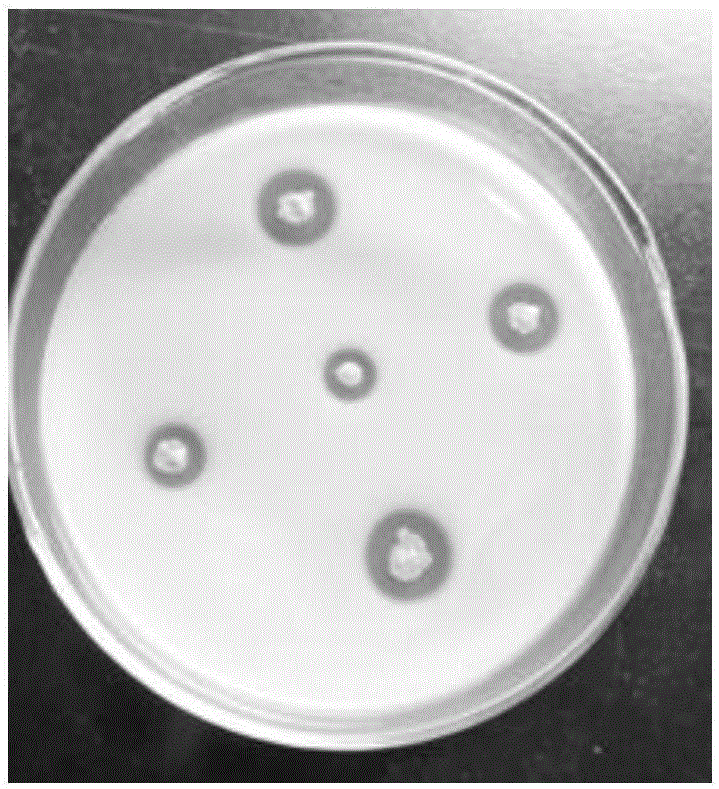
[0029] ②Qualitative experiment of acetic acid bacteria:
[0030] Take 20 mL o...
Embodiment 2
[0033] The identification of embodiment 2 acetic acid bacteria
[0034] (1) ZJ17 strain was identified morphologically, physiologically and biochemically according to the "Common Bacterial System Identification Manual" and "Bergey's Bacterial Identification Manual" eighth edition (Table 1).
[0035] Table 1 Physiological and biochemical characteristics of ZJ17 and AS1.41
[0036]
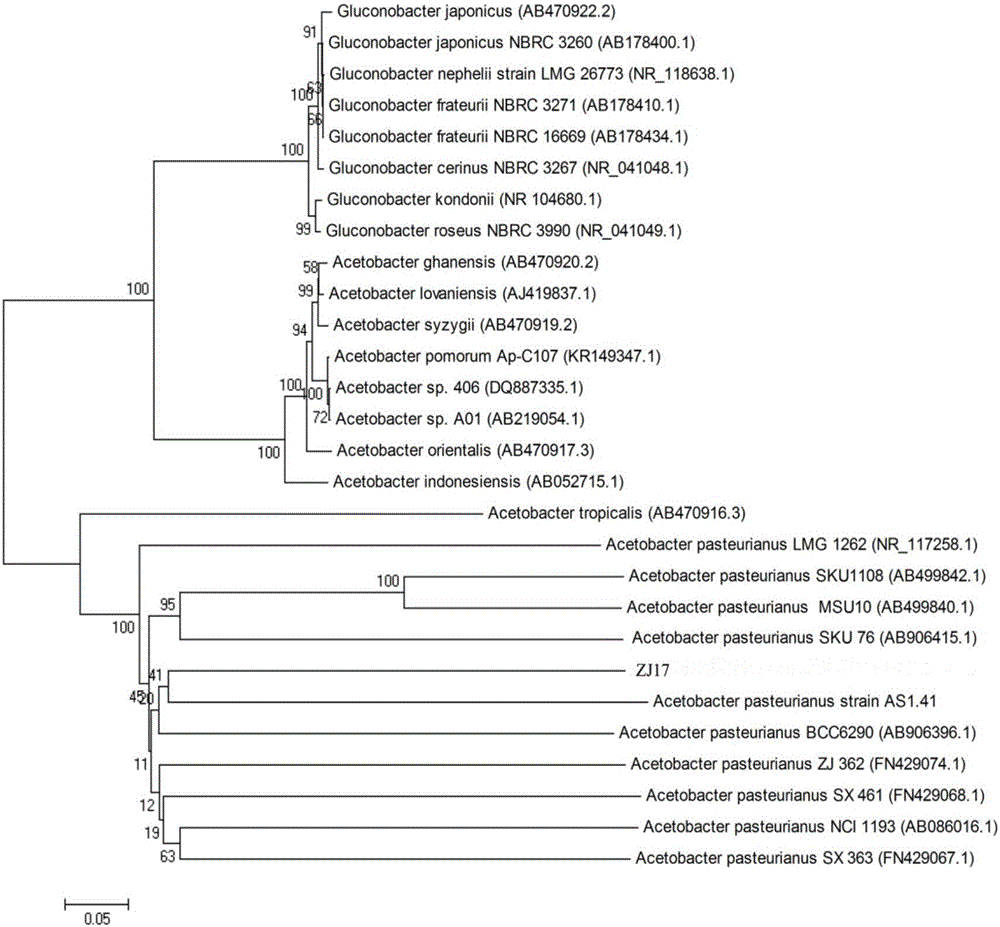
[0037] (2) 16Sr DNA identification:
[0038] Pick acetic acid bacteria ZJ17 and inoculate them in 10mL / 100mL Erlenmeyer flask liquid medium, shake and cultivate in a constant temperature shaking incubator at 30°C and 180r / min for 24h, take 2mL of the bacteria liquid in a centrifuge tube, centrifuge at 12000r / min for 2min, and remove the supernatant Genomic DNA of the bacterial strain was extracted according to the instructions of the SK1201-MNIQ-10 Column Bacterial Genomic DNA Extraction Kit from Shanghai Sangon Bioengineering Technology Service Co., Ltd. as a template. Select universal primers...
Embodiment 3
[0047] Example 3 High temperature resistance experiment
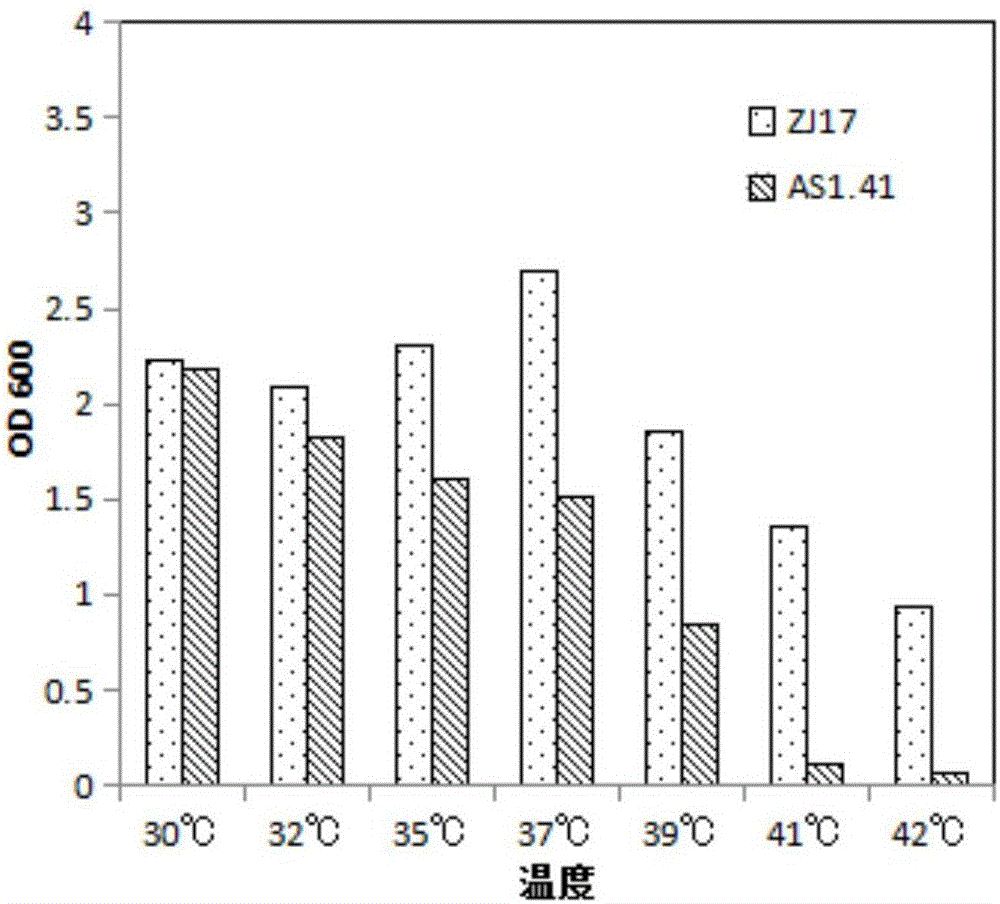
[0048] Take the logarithmic period Acetobacter pasteμ rianμ s 4mL of ZJ17 and AS1.41 bacteria solution were respectively added to 96mL liquid medium (2% glucose, 2% yeast powder, 0.01% MgSO 4 , 4% absolute ethanol) in a 500mL Erlenmeyer flask, shake culture at 30°C, 32°C, 35°C, 37°C, 39°C, 41°C, 42°C, shaker speed 180r / min, every day Measure the OD of bacterial growth 600 value and acid production until growth OD 600 value and acid production reached a stable level, draw a graph and compare the final growth and acid production ( Figure 3-A , Figure 3-B ).
[0049] in conclusion: Acetobacer pasteurianus ZJ17 has relatively stable growth and acid production at 30-42°C under the condition of 4% ethanol ( Figure 3-A ), and both perform better than AS1.41 ( Figure 3-A , Figure 3-B ); the optimum fermentation temperature of AS1.41 is 30°C, while the optimum fermentation temperature of ZJ17 is 37°C (the ethano...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com