Recombinant strain for producing shikimic acid, and preparation method and application thereof
A kind of technology of recombinant Escherichia coli, bacterial strain, applied in the recombinant bacterial strain of producing shikimic acid and preparation field thereof, can solve the problems such as unfavorable industrial production, output is not ideal enough
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
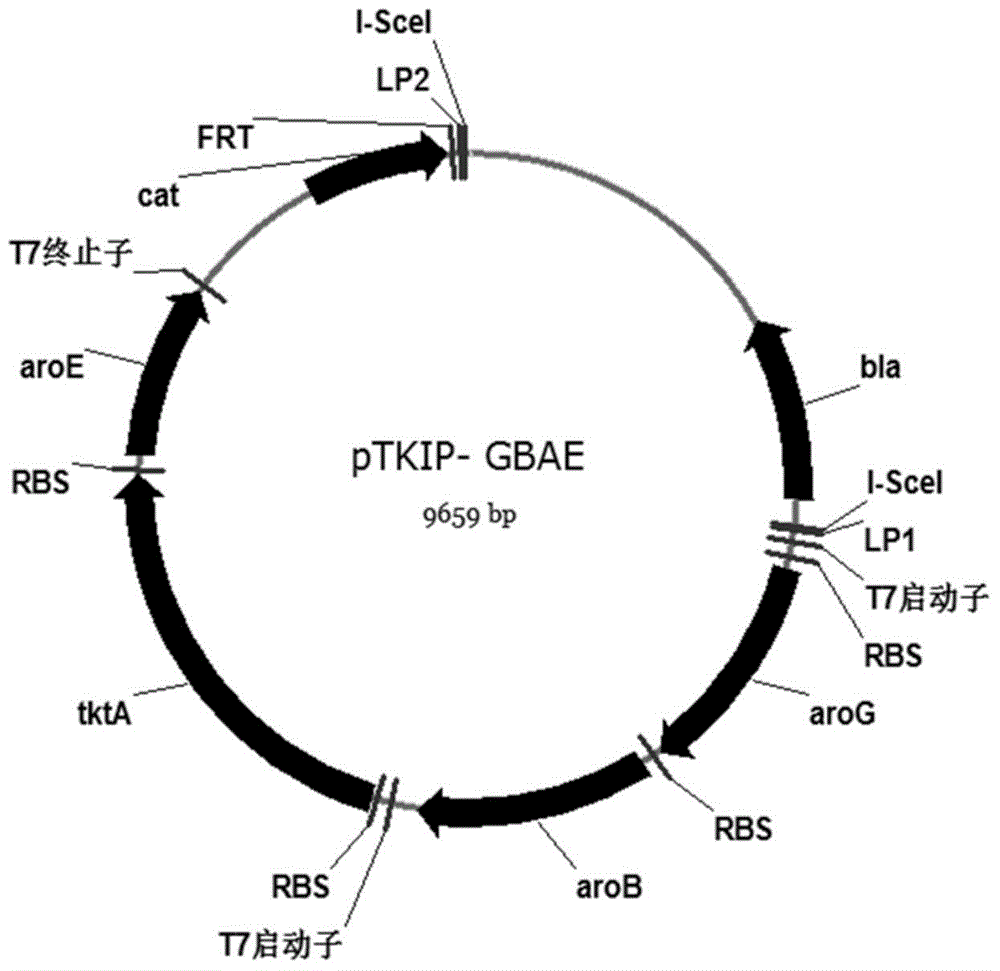
[0053] Construction of targeting plasmid pTKIP-GBAE
[0054] (1) All required genes were amplified using the chromosome of strain BW25113 as a template. The gene aroG was amplified with primers G1 (SEQ ID NO: 1) and G2 (SEQ ID NO: 2), and the PCR amplification conditions were as follows: PCR system (20 μL): template 10 ng, 10 μM primers 1 μL each, 2 × pfu enzyme PCR Reaction mixture 10μL, add ddH 2 0 to 20 μL. Amplification program: pre-denaturation at 94°C for 5 min; denaturation at 94°C for 30 s, annealing at 68°C for 30 s (minus 0.5°C for each cycle), extension at 72°C for 1 min / kb, a total of 35 cycles; extension at 72°C for 10 min.
[0055] The amplified gene aroG and plasmid pETDuet-1 were digested with restriction endonuclease BamH I and ligated to obtain plasmid pETDuet-G; amplified with primers B1 (SEQ ID NO: 3) and B2 (SEQ ID NO: 4) To obtain the gene aroB, the gene aroB and the plasmid pETDuet-1 were digested with restriction endonucleases BamH I and Hind III and...
Embodiment 2
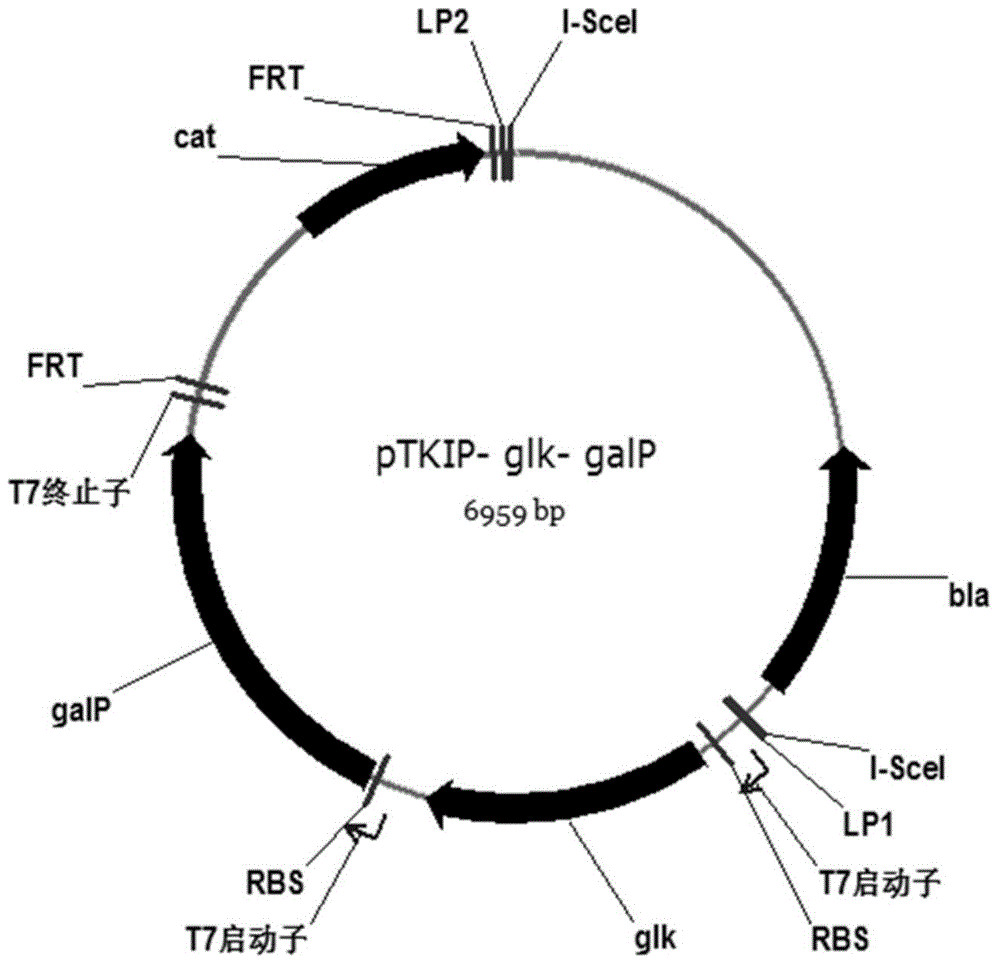
[0059] Construction of targeting plasmid pTKIP-glk-galP
[0060] (1) Using the bacterial strain BW25113 as a template, use primers glk1 (SEQ ID NO: 15) and glk2 (SEQ ID NO: 16) to amplify the gene glk fragment, the amplification conditions are the same as above, and use restriction The plasmid pETDuet-glk was obtained after digestion with endonucleases EcoR I and Pst I; the gene galP fragment was amplified with primers galP1 (SEQ ID NO: 17) and galP2 (SEQ ID NO: 18), and the amplification conditions were the same as above , digest it with the plasmid pETDuet-glk with restriction endonucleases Bgl II and Xho I and connect it to obtain the plasmid pETDuet-glk-galP;
[0061] (2) Gene glk and galP on the plasmid pETDuet-glk-galP are amplified with primers Duet-F (SEQ ID NO: 13) and Duet-R (SEQ ID NO: 14) together with their respective rbs sequences and the T7 promoter terminator Amplification is obtained, the amplification conditions are the same as above, digested with restricti...
Embodiment 3
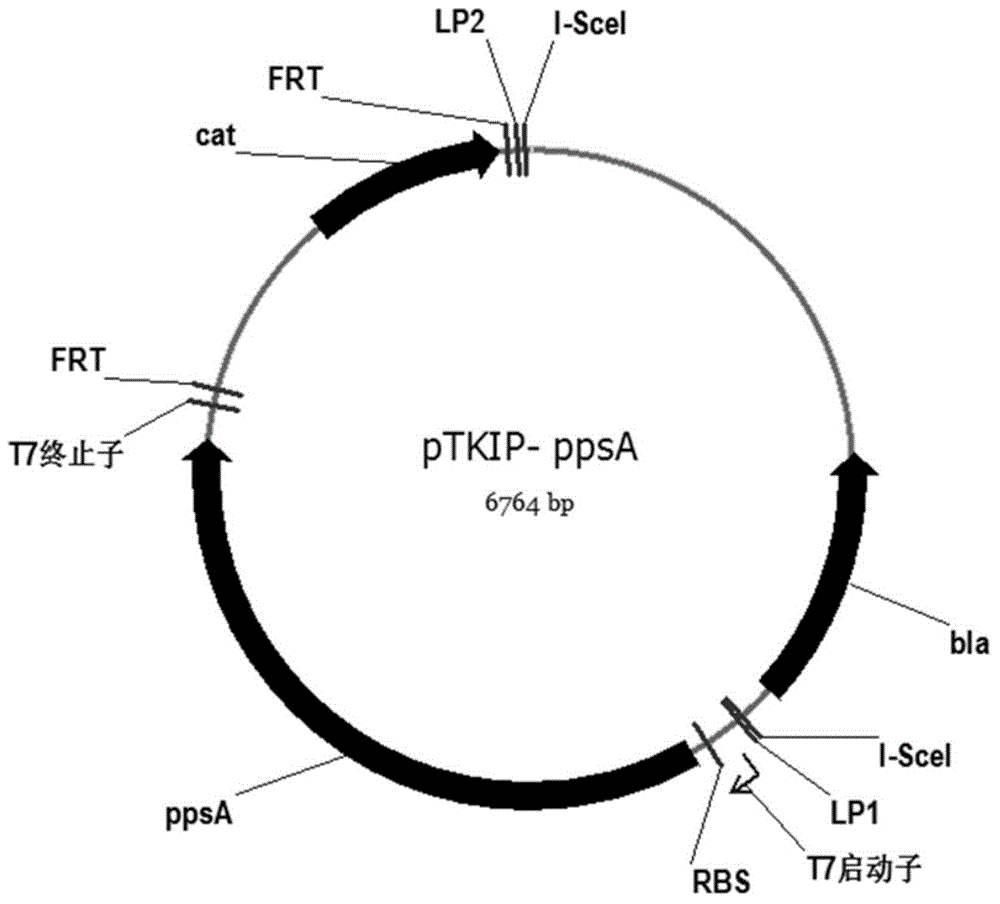
[0063] Construction of targeting plasmid pTKIP-ppsA
[0064] (1) Using the bacterial strain BW25113 as a template, the gene ppsA fragment was amplified with primers ppsA1 (SEQ ID NO: 19) and ppsA2 (SEQ ID NO: 20). The plasmid pETDuet-ppsA was obtained after digestion with endonucleases EcoR I and Xho I;
[0065] (2) The gene ppsA on the plasmid pETDuet-ppsA together with its rbs sequence and T7 promoter terminator were amplified with primers Duet-F (SEQ ID NO: 13) and Duet-R (SEQ ID NO: 14). The multiplication conditions are the same as above, and the restriction endonucleases Apa I and Nhe I are digested and connected to the plasmid pTKIP-cat to obtain the plasmid pTKIP-ppsA, whose structure is as follows: image 3 shown.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com