Method for preparing porous membrane by virtue of non-solvent induced phase method
A non-solvent, porous membrane technology, applied in the field of materials, to achieve the effect of shortening the cleaning cycle
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Example 1: A method for preparing a porous membrane by a non-solvent phase-induced method, using a non-solvent phase-induced method to dope submicron metal oxides to prepare hollow fiber, flat and tubular membranes with catalytic, hydrophilic, and antibacterial properties;
[0038] Prepare materials according to the following components (weight ratio):
[0039] PVDF resin content 30,
[0040] Submicron level metal oxide content 10,
[0041] Additive 80,
[0042] Organic salt dispersant 10,
[0043] Solvent 70.
[0044] The additive is one or more of polyvinylpyrrolidone, polyethylene glycol, polymethyl methacrylate and polyacrylonitrile with different molecular weights.
[0045]Submicron metal oxides have different particle sizes, in the range of 0.10-1000 microns, transition metals such as nickel oxides, iron oxides, aluminum oxides, magnesium oxides, copper oxides, and zinc oxides One or more of oxides and their oxyhydroxides.
[0046] One or a mixture of organi...
Embodiment 2
[0049] Embodiment 2: A method for preparing a porous membrane by a non-solvent phase-induced method, comprising the following steps;
[0050] Table 1:
[0051]
[0052] The specific implementation formula,
[0053] Do test 1, test 2, test 3, test 4, test 5, test 6 according to the formula in Table 1:
[0054] Test Characterization of Trials:
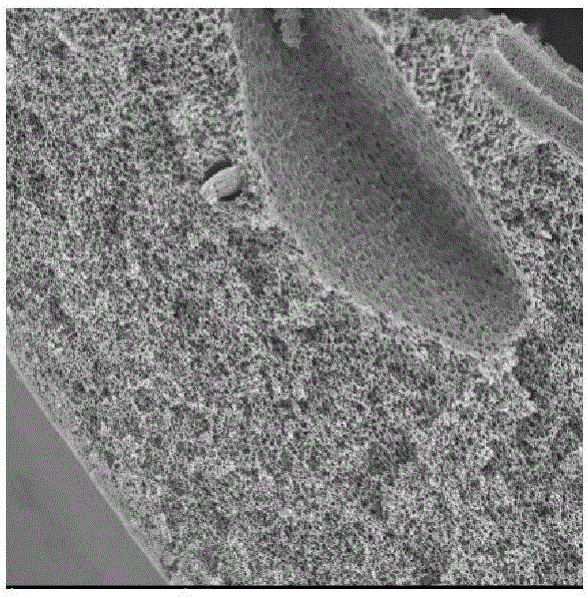
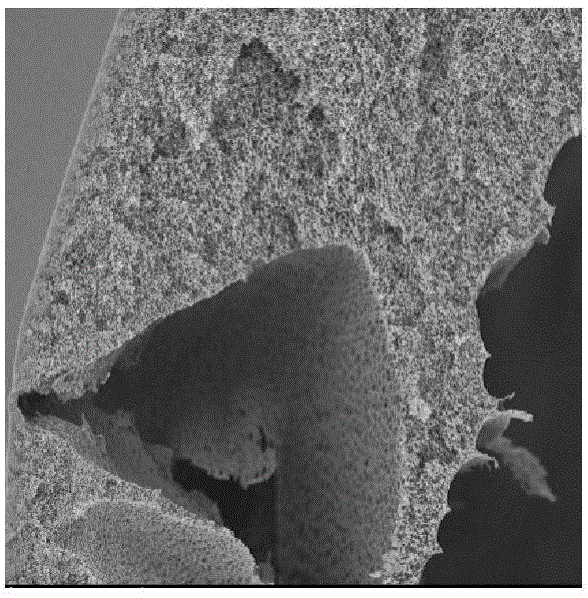
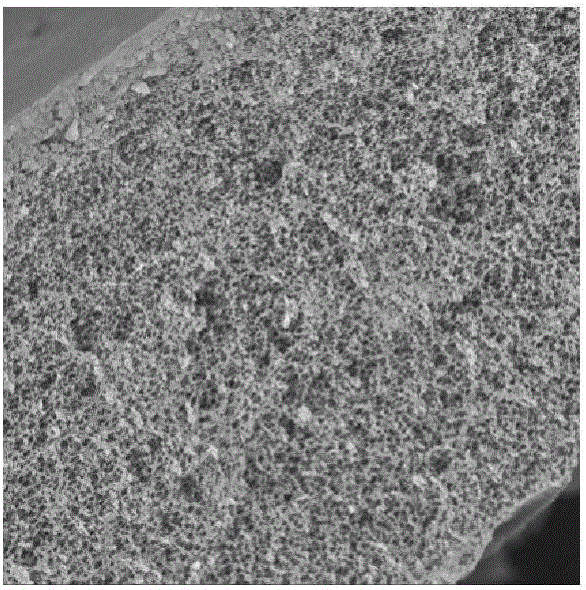
[0055] Electron microscope photos such as figure 1 (test 4), figure 2 (test 5), image 3 (Test 6) shows:
[0056] Test 1, Test 2, Test 3 and Test 4, Test 5, and Test 6 are comparative tests using nickel oxides, iron oxides, aluminum oxides, magnesium oxides, Copper oxide, zinc oxide and other transition metal oxides and one or more of their oxyhydroxides,
[0057] The test mainly illustrates the following rules:
[0058] 1. The transition metal oxides and their oxyhydroxides with larger particles are not easy to be lost, but the catalytic effect is poor;
[0059] 2. The antibacterial effect decreases with the increase of tra...
Embodiment 3
[0062] Example 3: A method for preparing a porous membrane by a non-solvent-induced phase method, using a non-solvent-induced phase method to dope submicron metal oxides to prepare hollow fiber, flat and tubular membranes with catalytic, hydrophilic, and antibacterial properties;
[0063] Prepare materials according to the following components (weight ratio):
[0064] Polyvinylidene fluoride resin content 15,
[0065] Submicron level metal oxide content 0.1,
[0066] additive 10,
[0067] Organic salt dispersant 0.1,
[0068] Solvent 40.
[0069] The additive is one or more of polyvinylpyrrolidone, polyethylene glycol, polymethyl methacrylate and polyacrylonitrile with different molecular weights.
[0070] Submicron metal oxides have different particle sizes, in the range of 0.10-1000 microns, transition metals such as nickel oxides, iron oxides, aluminum oxides, magnesium oxides, copper oxides, and zinc oxides One or more of oxides and their oxyhydroxides.
[0071] One ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com