Circulation harmlessness treatment method of colistin fermentation bacterial residue
A harmless treatment, colistin technology, applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, fermentation, etc., can solve the problems of environmental pollution, high treatment costs, high incineration costs, etc., to reduce production costs, The effect of changing physical properties and simple process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
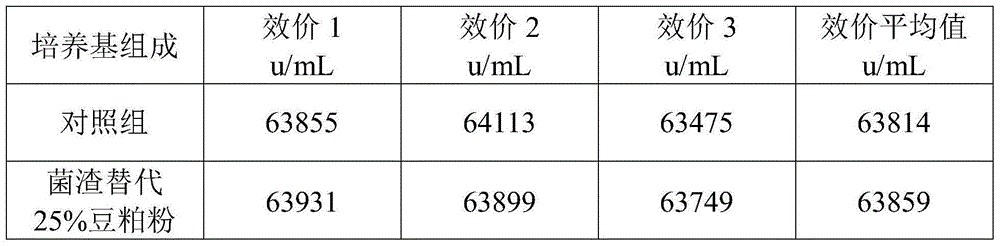
[0035] a. 1 kg of fresh colistin wet fungus slag filtered by ceramic membrane in the extraction workshop, its water content is 77%, add 40g of bran, 40g of bran, and 50g of distiller's grain to the wet fungus slag, stir and mix evenly, after mixing Squeeze with plate and frame to obtain the premix of fungus residue.
[0036] The moisture content of the premix was determined to be 42%.
[0037] b. Carrying out the solid-state fermentation of the fungus residue premix in step a, the temperature of the fermentation process is controlled at 28-40° C., and the fermentation period is 158 hours to obtain a solid-state fermentation product.
[0038] No residue of colistin was found in the fermentation product.
[0039] c. The solid-state fermentation product of the fungus residue in step b is dried at 85-95° C., crushed, and passed through a 60-mesh sieve to obtain the fungus residue powder.
[0040] After testing, the protein content of the fungus residue powder is 38%, the fat con...
Embodiment 2
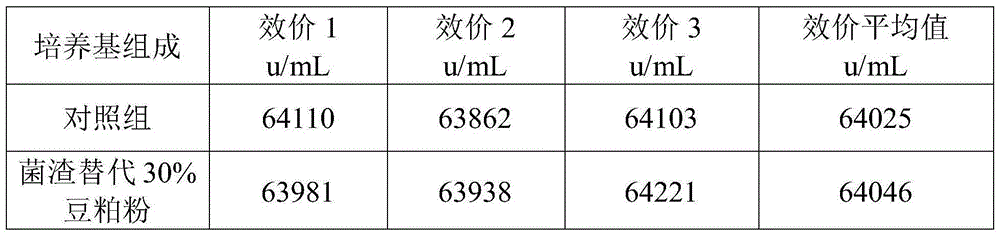
[0044] a. 1 kg of fresh colistin wet fungus residue filtered by ceramic membrane in the extraction workshop, and its moisture content is measured to be 73%. Add 30g of bran, 30g of bran and 40g of distiller's grains to the wet fungus residue, stir and mix evenly, after mixing Squeeze with plate and frame to obtain the premix of fungus residue.
[0045] The moisture content of the premix was determined to be 44%.
[0046] b. Carrying out the solid-state fermentation of the fungus residue premix in step a, the temperature of the fermentation process is controlled at 28-40° C., and the fermentation period is 171 hours to obtain a solid-state fermentation product.
[0047] No residue of colistin was found in the fermentation product.
[0048] c. The solid-state fermentation product of the fungus residue in step b is dried at 85-95° C., crushed, and passed through a 60-mesh sieve to obtain the fungus residue powder.
[0049] After testing, the protein content of the fungus residu...
Embodiment 3
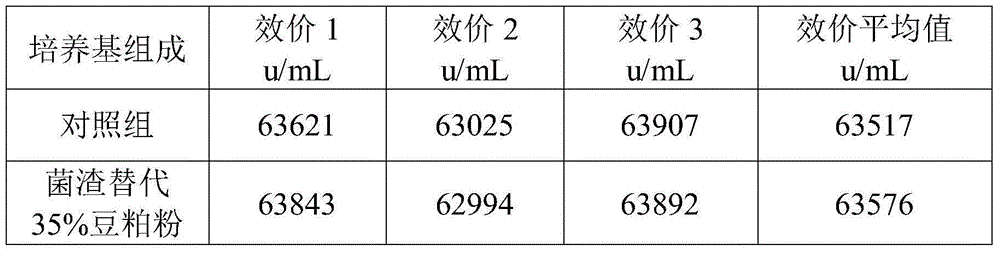
[0053] a. 1 kg of fresh colistin wet fungus slag filtered by ceramic membrane in the extraction workshop, its water content is 75%, add 35g of bran, 35g of bran, and 45g of distiller's grain to the wet fungus slag, stir and mix evenly, after mixing Squeeze with plate and frame to obtain the premix of fungus residue.
[0054] The moisture content of the premix was determined to be 43%.
[0055]b. Carrying out the solid-state fermentation of the fungus residue premix in step a, the temperature of the fermentation process is controlled at 28-40° C., and the fermentation period is 169 hours to obtain a solid-state fermentation product.
[0056] No residue of colistin was found in the fermentation product.
[0057] c. Preparation of fungal residue powder: the solid-state fermentation product of fungal residue in step b is dried at 85-95° C., pulverized, and passed through a 60-mesh sieve to obtain fungal residue powder.
[0058] After testing, the protein content of the fungus re...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com