Novel arthrobacter gandavensis strains
A technology of Tsarthrobacter and strains, which is applied in the direction of bacteria, medical raw materials derived from bacteria, animal feed, etc., and can solve the problems of reducing the efficacy of antibiotics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0076] Example 1: Isolation of rumC+ bacterial strains
[0077] Search for culturable strains carrying rumC-like genes from pig cecum and ileum microbiota.
[0078] In the first stage, the bacteria were cultured in the following media:
[0079] -M17: Promote the growth of Lactococcus
[0080] -LB: Allows Bacillus and Enterococci to grow
[0081] -BEA: media for reverse screening of Bacteroides groups
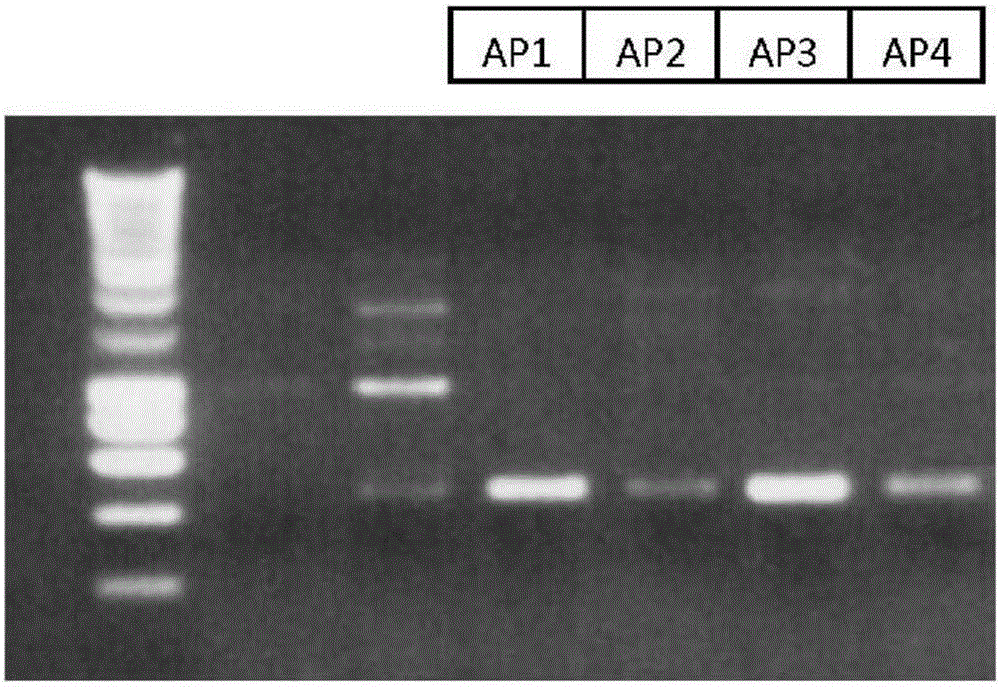
[0082] Clones were then screened for their ability to inhibit the growth of C. perfringens. Thus, the presence of the rumC gene was shown by PCR ( figure 1 ).
[0083] Table 1: List of primers used to amplify different target DNA fragments
[0084]
[0085] Four strains were retained: AP1, AP2, AP3 and AP4.
Embodiment 2
[0086] Example 2: Identification of Retained Strains
[0087] 2.1 rDNA 16S
[0088] The gene fragment encoding rRNA 16S (approx. 1550bp) (corresponding to positions 8-1541 in the E. coli numbering system), followed by sequencing.
[0089] The sequences obtained are aligned in databases using a sequence homology study program of the "BLAST" type.
[0090] Strain AP1 (SEQ ID No.) => 99.45% identical to Arthrobacter ghentii R 5812
[0091] Strain AP2 (SEQ ID No.) => 99.37% identical to Arthrobacter ghentii R 5812
[0092] Strain AP3 (SEQ ID No.) => 99.44% identical to Arthrobacter ghentii R 5812
[0093] Strain AP4 (SEQ ID No.) => 99.31% identical to Arthrobacter ghentii R 5812
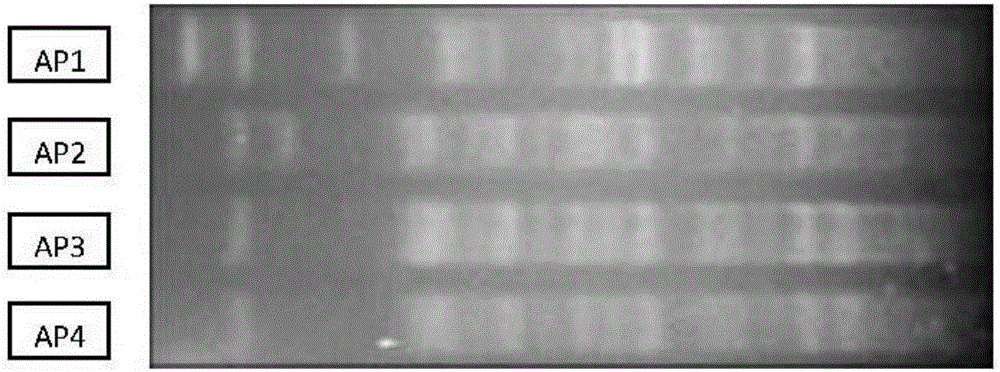
[0094] 2.2. PFGE identification
[0095] The strains AP1, AP2, AP3 and AP4 belonging to the genus Arthrobacter must have genetic differentiation at the gene level. The reference technique for the identification of bacterial strains at the intraspecific level is mainly to assemble their chromos...
Embodiment 3
[0097] Example 3: Characterization of strains
[0098] 3.1 Resistance to pH and to bile salts
[0099] Strains were subjected to two treatments to determine their resistance to acidity and to bile salts.
[0100] - Acidity: 0.85% NaCl buffer, pH 2, containing pepsin (1 mg / mL).
[0101] - Bile salt isotonic buffer (1.24% K 2 HPO 4 , 0.76%H 2 PO 4 , 0.1% trisodium citrate, 0.6% [NH 4 ] 2 SO 4 , pH 6.7), containing 0.2% cholate (50% sodium cholate, 50% sodium deoxycholate).
[0102] Table 2: Survival percentages of different strains
[0103]
[0104] BS: bile salts; ND: not determined
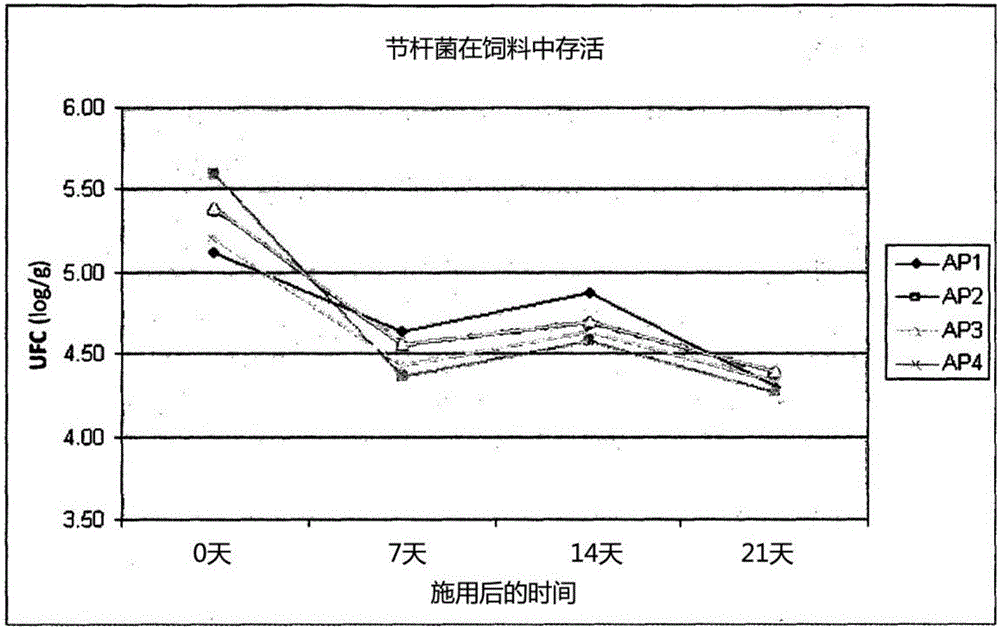
[0105] The AP4 strain was better able to resist conditions that mimic the gastric matrix. In general, all strains were more sensitive to bile salts, however, with the exception of the AP1 strain, the other strains survived adequately.
[0106] 3.2 Fermentation parameters
[0107] For the culture supernatants obtained after semi-anaerobic growth in BHI-YH, their fermentation par...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com