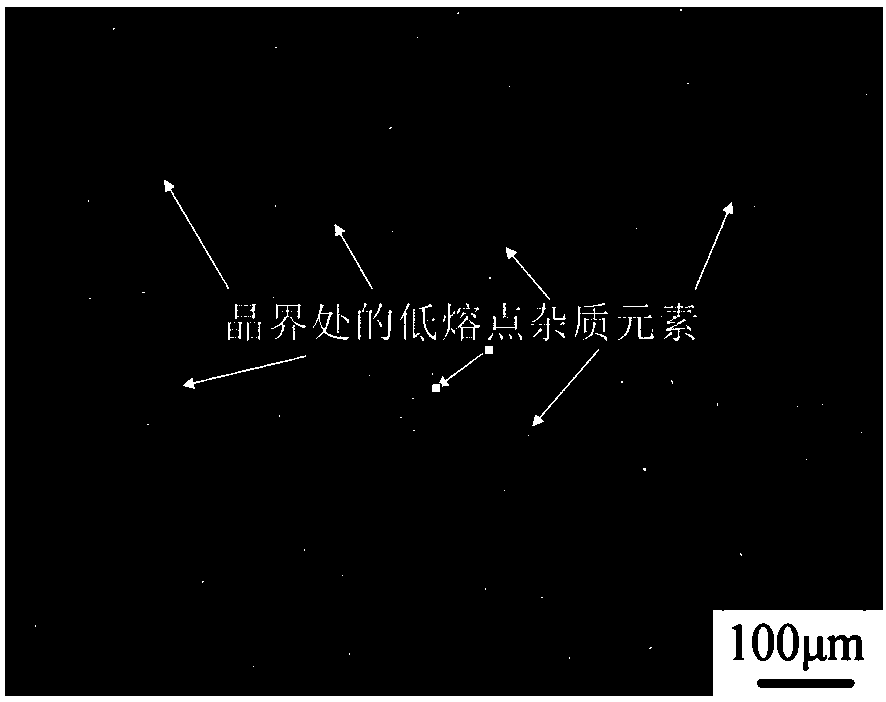
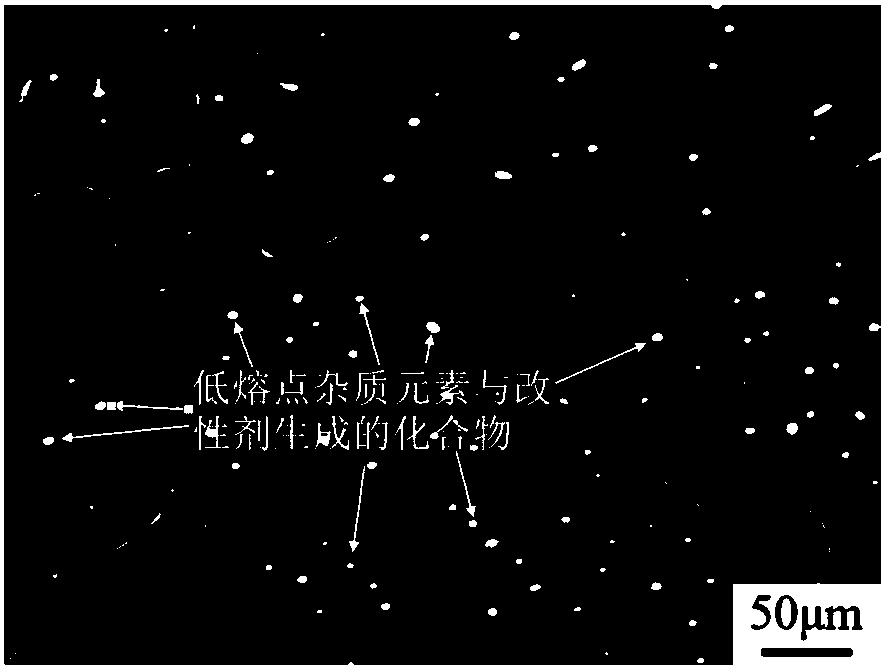
Modifier and modification method of low melting point impurity element lead in copper and copper alloy
A technology of impurity elements and low melting point, which is applied in the field of modification of low melting point impurity elements and can solve problems such as hazards
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
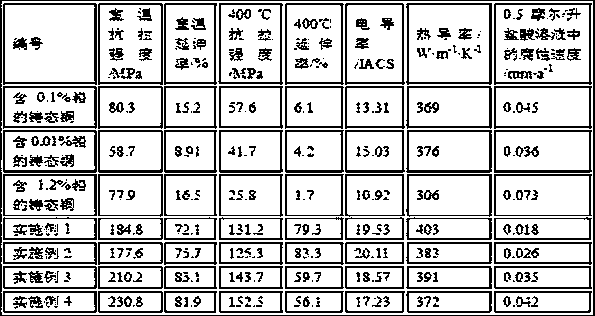
[0033] Example 1 A process for modifying lead as an impurity element with a low melting point in copper. The specific steps are to melt 9.91 kg (by weight percentage) of miscellaneous copper containing 0.1% lead at 1190 ° C, and cover the surface of the copper liquid with a Layer thickness is the charcoal layer of 5 centimeters, add 21 grams of copper-phosphorus master alloys of phosphorus content 13%, react for 0.5 hours, then take samples and analyze before furnace, measure the phosphorus content and oxygen content in copper liquid by direct-reading spectrometer, wherein, copper The phosphorus content in the liquid is controlled at 70-80ppm, and the oxygen content is controlled at 0-3ppm; after pre-deoxidation, the temperature of the copper liquid is raised to 1250°C, and 33 grams of low melting point impurity element modifiers are added, including 7.1 grams of lanthanum, cerium 18.3 grams, 4.7 grams of yttrium, 2.9 grams of neodymium, electromagnetic stirring for 22 minutes,...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Example 2 A process for modifying lead as an impurity element with a low melting point in copper. The specific steps are to melt 9.99 kg (by weight percentage) of miscellaneous copper containing 0.01% lead at 1200 ° C, and cover the surface of the copper liquid with a The thickness of the charcoal layer is 5.5 cm. Add 20 grams of copper-phosphorus master alloy with a phosphorus content of 14%, react for 0.7 hours, then take a sample and analyze it before the furnace, and measure the phosphorus content and oxygen content in the copper liquid by a direct-reading spectrometer. Among them, copper The phosphorus content in the liquid is controlled at 80-100ppm, and the oxygen content is controlled at 0-5ppm; after pre-deoxidation, the temperature of the copper liquid is raised to 1260°C, and 3.1 grams of low melting point impurity element modifiers are added, including 0.7 grams of lanthanum, cerium 1.8 grams, 0.5 grams of yttrium, 0.1 grams of neodymium, electromagnetic stir...
Embodiment 3
[0035] Example 3 A process for modifying lead as an impurity element with a low melting point in copper. The specific steps are to melt 10.27 kg (by weight percentage) of miscellaneous copper containing 0.5% lead at 1180 ° C, and cover the surface of the copper liquid with a Layer thickness is 5.8 centimeters charcoal layer, add 18 grams of copper-phosphorus master alloys with phosphorus content 12%, react for 0.6 hours, then take samples and analyze before furnace, measure phosphorus content and oxygen content in copper liquid by direct-reading spectrometer, wherein, copper The phosphorus content in the liquid is controlled at 75-85ppm, and the oxygen content is controlled at 0-8ppm; after pre-deoxidation, the temperature of the copper liquid is raised to 1255°C, and 98 grams of low melting point impurity element modifiers are added, including 19.6 grams of lanthanum, cerium 58..8 grams, 9.8 grams of yttrium, 9.8 grams of neodymium, electromagnetic stirring for 23 minutes, aft...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com