Plug-in type gas blaster igniter and cracking device
A technology for detonating device and blaster, which is applied to valve devices, blasting cylinders, compressed gas generation and other directions, can solve the problems of high manufacturing cost, low heat release efficiency, long time consumption, etc., and achieves high mixing uniformity and heat release effect.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
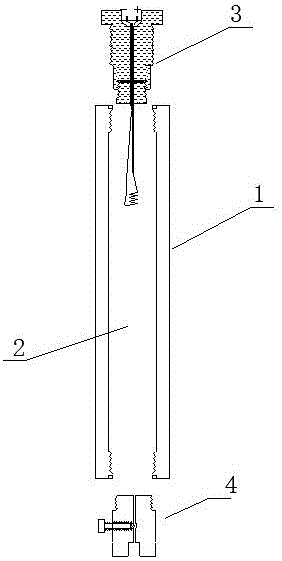
[0066] A plug-in gas blaster detonating device, such as figure 1 As shown, it includes a housing 1, a filling chamber 2, an ignition mechanism 3 and an inflatable mechanism 4. The housing 1 is filled with a chamber 2, and the housing 1 is sealed to connect the ignition mechanism 3 and the inflatable mechanism 4. The pressure resistance of the housing 1 The strength is greater than 5.045Mpa; the shell 1 is a carbon steel cylinder or a stainless steel cylinder, and the inflation mechanism 4 and the ignition mechanism 3 are respectively connected to both ends of the shell 1;
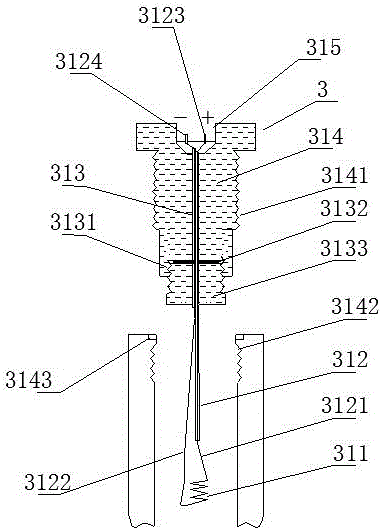
[0067] Such as figure 2 As shown, the ignition mechanism 3 includes a heating wire 311, a wire 312, a wire through hole 313, a sealing base 314 and a socket 315, the heating wire 311 is connected to the wire 312, the axial center of the sealing base 314 is a wire through hole 313, and the plugging groove 315 is located on the upper part of the wire through hole 313, and the positive pole pin 3151 and the ...
Embodiment 2
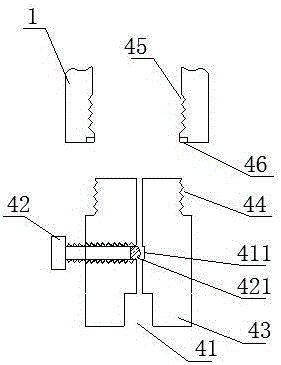
[0073] The difference with embodiment 1 is: as Figure 4 As shown, the housing 1 includes a first segment body 11 and a second segment body 12, the first segment body 11 and the second segment body 12 are connected through a threaded structure, and are matched with a threaded sealing ring 13 for Sealing; the inflation mechanism 4 and the ignition mechanism 3 are respectively connected to both sides of the first segment body 11 and the second segment body 11; this structure is convenient for charging.
Embodiment 3
[0075] The difference with embodiment 1 is: as Figure 5As shown, the housing 1 is a composite layer tube containing fiber material, the housing 1 is made of composite layers, the housing 1 includes a matrix layer 101, a fiber layer 102 and a hardened layer 103, and the hardened layer 103 is located at The outer layer of the fiber layer 102, the matrix layer 101 is located in the inner layer of the fiber layer 102; the two ends of the housing 1 are respectively sealed and wrapped with a first metal joint 111 and a second metal joint 112, and the first metal joint 111 and the second metal joint 112 are sealed and wrapped respectively. Two metal joints 112 are respectively connected to the inflation mechanism 4 and the ignition mechanism 3 ;
[0076] As a further description of the above embodiment, the base layer 101 is made of polyethylene (PE); the fiber layer 102 is made of glass fiber; the hardened layer 103 is made of epoxy resin.
[0077] As a further description of the ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Compressive strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Inner diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com