Epitaxial wafer for GaN-based light-emitting diode, and growth method for epitaxial wafer
A technology of light-emitting diodes and a growth method, which is applied to the epitaxial wafer of GaN-based light-emitting diodes and its growth field, can solve the problems of high fragmentation rate, lattice mismatch, large thermal expansion coefficient, etc. The effect of reducing the temperature difference
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
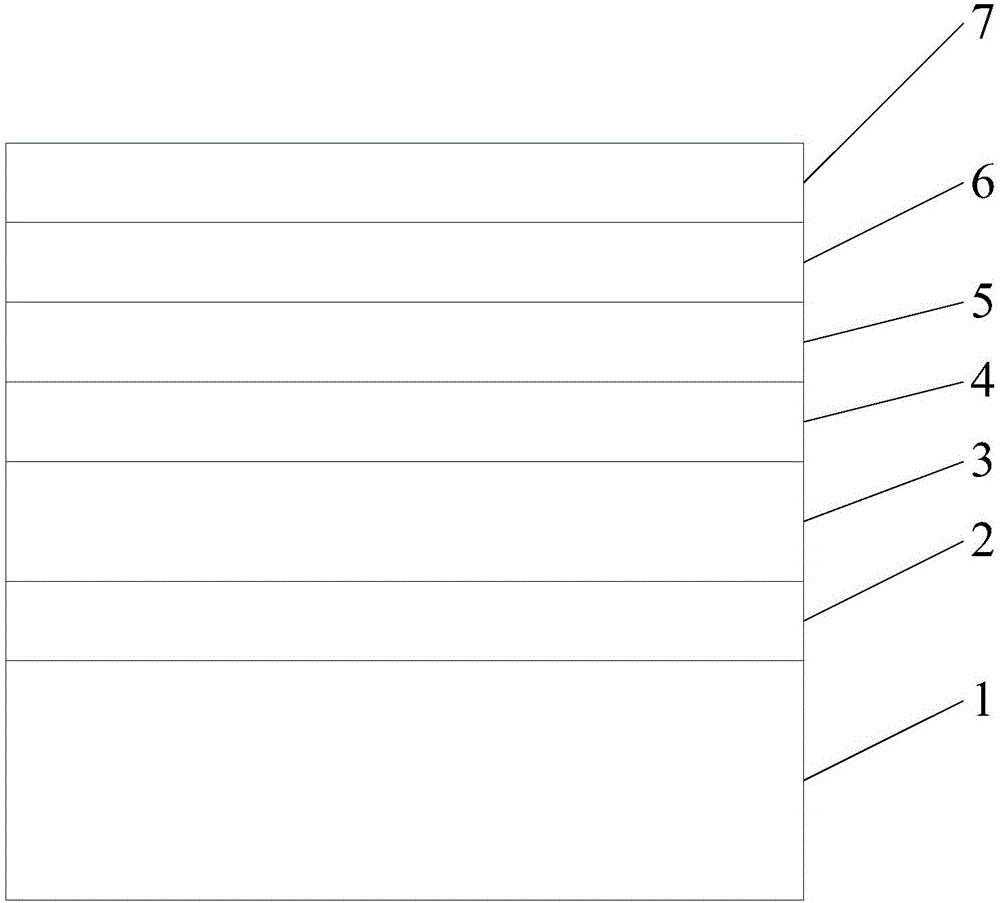
[0029] An embodiment of the present invention provides an epitaxial wafer of a GaN-based light emitting diode, see figure 1 , the epitaxial wafer includes a sapphire substrate 1, and a buffer layer 2, an undoped GaN layer 3, a stress release layer 4, an N-type layer 5, a multi-quantum well layer 6, and a P-type layer stacked sequentially on the sapphire substrate 1. Layer 7.
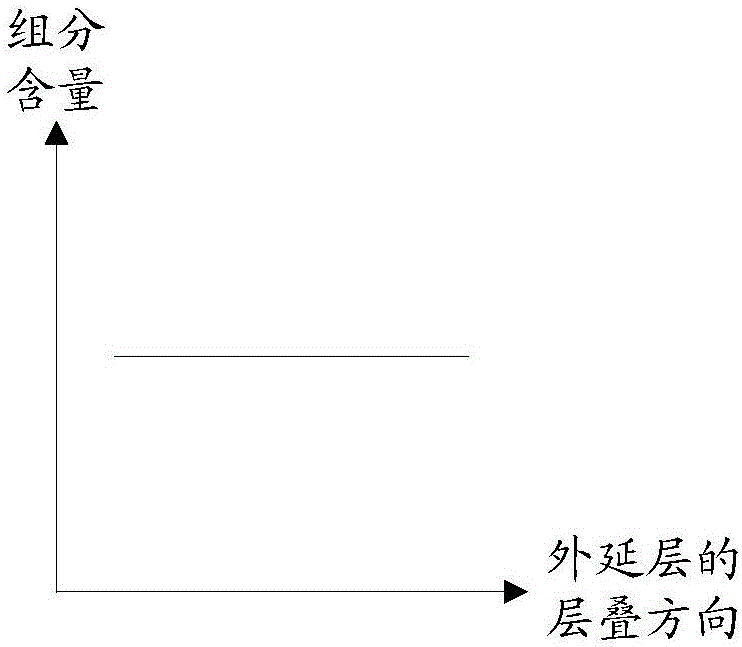
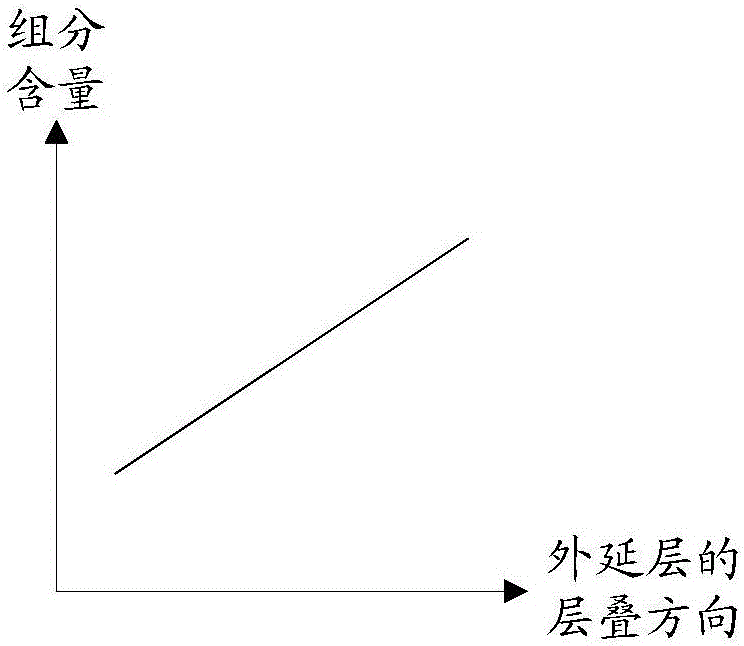
[0030] In this embodiment, the stress release layer includes alternately stacked undoped Al x Ga 1-x N layer and SiN layer, 0≤x Figure 2a shown), linearly increasing along the stacking direction of the epitaxial wafer (such as Figure 2b shown), linearly decreases along the stacking direction of the epitaxial wafer (such as Figure 2c shown), the single layer remains unchanged and increases layer by layer along the stacking direction of the epitaxial wafer (such as Figure 2d shown), the single layer remains unchanged and decreases layer by layer along the stacking direction of the epitaxial wafer (s...
Embodiment 2
[0037] An embodiment of the present invention provides a method for growing an epitaxial wafer of a GaN-based light-emitting diode, which is suitable for growing the epitaxial wafer provided in Embodiment 1, see image 3 , the growth method includes:
[0038] Step 201: Provide a sapphire substrate.
[0039] Step 202: growing a buffer layer, an undoped GaN layer, a stress release layer, an N-type layer, a multi-quantum well layer, and a P-type layer sequentially on the sapphire substrate.
[0040] In this embodiment, the stress release layer includes alternately stacked undoped Al x Ga 1-x N layer and SiN layer, 0≤x<1. The Si component content in the SiN layer changes in any of the following ways: remains constant, increases linearly along the stacking direction of the epitaxial wafers, decreases linearly along the stacking direction of the epitaxial wafers, remains constant for a single layer and increases along the stacking direction of the epitaxial wafers. The direction...
Embodiment 3
[0049] The embodiment of the present invention provides a method for growing epitaxial wafers of GaN-based light-emitting diodes, which is a specific realization of the growth method provided in Embodiment 1, and is realized with high-purity hydrogen (H 2 ) or nitrogen (N 2 ) as carrier gas, trimethylgallium (TMGa), trimethylaluminum (TMAl), trimethylindium (TMIn) and ammonia (NH 3 ) as Ga, Al, In and N sources respectively, with silane (SiH 4 ), Magnesium (Cp 2 Mg) as N and P type dopants respectively.
[0050] Specifically, see Figure 4 , the growth method includes:
[0051] Step 301: The temperature of the substrate is first raised to 500°C, then raised to 800°C and stabilized for 30s, then raised to 1000°C and stabilized for 30s, then raised to 1230°C and stabilized for 10 minutes, and then heat-treated in a pure hydrogen atmosphere.
[0052] It should be noted that the purpose of heat treatment is to clean the substrate surface.
[0053] Step 302: Lower the tempera...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com