A LED epitaxial growth method for improving luminous efficiency
A technology of epitaxial growth and luminous efficiency, applied in the direction of crystal growth, single crystal growth, single crystal growth, etc., can solve the problems of low luminous efficiency, low hole concentration, and low hole mobility of LED, and improve hole migration. rate, increase hole concentration, and improve the effect of antistatic ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
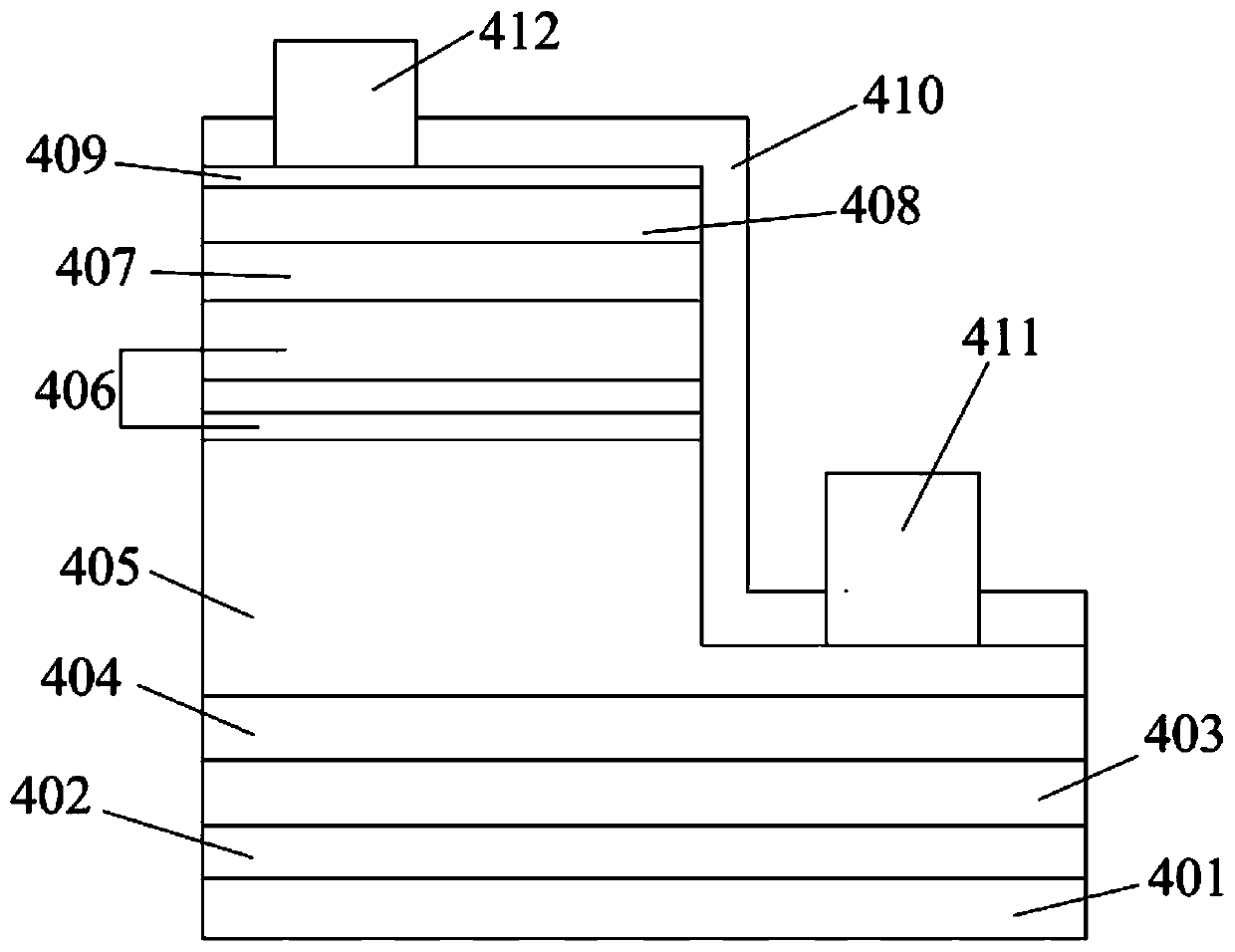
[0048] Such as figure 2 As shown, it is a schematic diagram of the LED structure of the epitaxial growth method for improving LED luminous efficiency described in this embodiment. The method described in this embodiment solves the problem of the LED epitaxial layer in the prior art.
[0049] The technical problems of low hole concentration, low hole mobility, and low LED luminous efficiency.
[0050] In this example, MOCVD (metal organic compound chemical vapor deposition) is used to grow high-brightness GaN-based LED epitaxial wafers, using high-purity H 2 or high purity N 2 or high purity H 2 and high purity N 2 The mixed gas as the carrier gas, high-purity NH 3 As the N source, the metal-organic sources trimethylgallium (TMGa) and triethylgallium (TEGa) are used as the gallium source, trimethylindium (TMIn) is used as the indium source, and the N-type dopant is silane (SiH 4 ), trimethylaluminum (TMAl) as the source of aluminum, and the P-type dopant as magnesocene (C...
Embodiment 2
[0066] On the basis of Example 1, this embodiment describes the specific content of the overall growth of the LED epitaxial layer in the present invention. The structural schematic diagram of the LED is as follows figure 2 shown. The LED epitaxial growth method for improving luminous efficiency described in this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0067] Step 501, process the patterned sapphire substrate: Into the reaction chamber of the metal organic chemical vapor deposition system with the substrate placed, simultaneously feed NH with a flow rate of 10000-20000 sccm 3 , 100-130L / min H 2 , increasing the temperature to 900-1000° C., and processing the substrate for 300s-600s under the condition that the reaction chamber pressure is 100-200mbar.
[0068] Step 502, growing a ZnGaN layer, further:
[0069] Keep the pressure of the reaction chamber at 300-400mbar, the temperature at 900-1000°C, and at the same time feed NH with a flow rate of 30000-40000sccm 3 , 100-...
Embodiment 3
[0084] A conventional LED epitaxial growth method is provided below as a comparative example of the present invention.
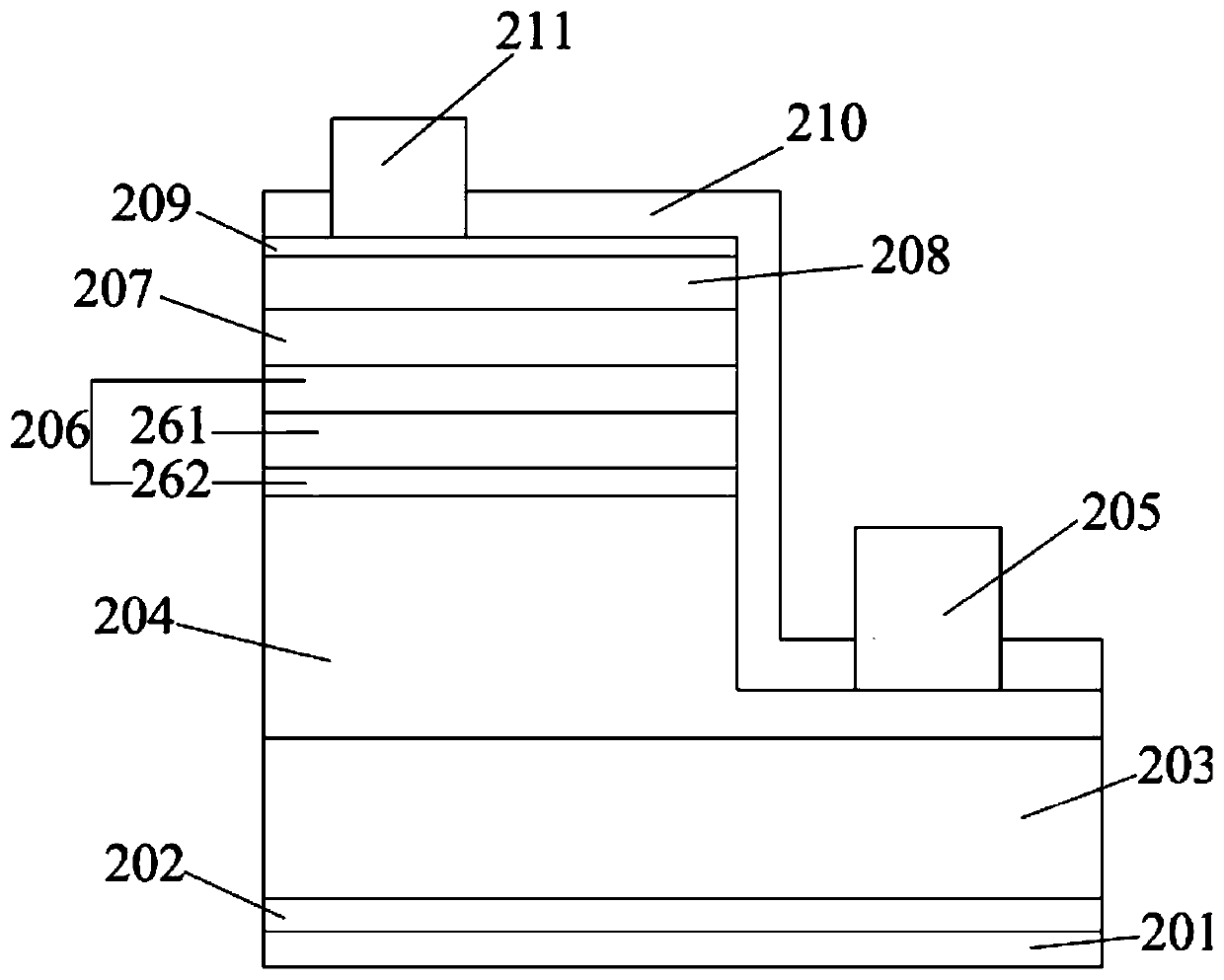
[0085] The growth method of conventional LED epitaxy is (see the epitaxial layer structure figure 1 ):
[0086] Step 101, processing the sapphire substrate: in a hydrogen atmosphere at 1000-1100°C, inject 100L / min-130L / min of H 2 , keep the reaction chamber pressure at 100-300mbar (mbar is the air pressure unit), and process the sapphire substrate for 5-10 minutes.
[0087] Step 102, grow low-temperature buffer layer GaN: lower the temperature to 500-600°C, keep the reaction chamber pressure at 300-600mbar, and feed NH with a flow rate of 10000-20000sccm (sccm notes standard milliliters per minute) 3 , 50-100sccm TMGa, 100L / min-130L / min H 2 1. Growing a low-temperature buffer layer GaN with a thickness of 20-40 nm on the sapphire substrate.
[0088] Step 103, corroding the low-temperature buffer layer GaN into an irregular island shape: raise the tempera...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com