Solvent-promoted method for selective dehydrogenation of tetrahydroisoquinolines
A technology of tetrahydroisoquinoline and compounds, applied in the field of racemization, to achieve the effects of simple reaction operation, high chemoselectivity, and mild reaction conditions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Embodiment 1: optimization of conditions
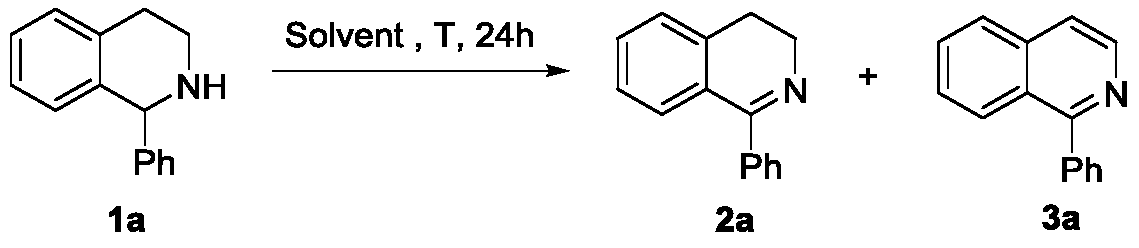
[0033] In air, put substrate 1a (0.2 mmol) into a 25 mL Schlenk bottle, and add 1.0 mL of solvent, then stir at 100°C for 24 hours, then cool to room temperature, remove the solvent under reduced pressure, and determine the conversion rate by crude nuclear magnetic spectrum , and then separated by column. (Eluent: the volume ratio of petroleum ether and ethyl acetate is 5:1), and the target product 1-phenyl-3,4-dihydroisoquinoline was obtained. Its reaction formula is as follows:
[0034]
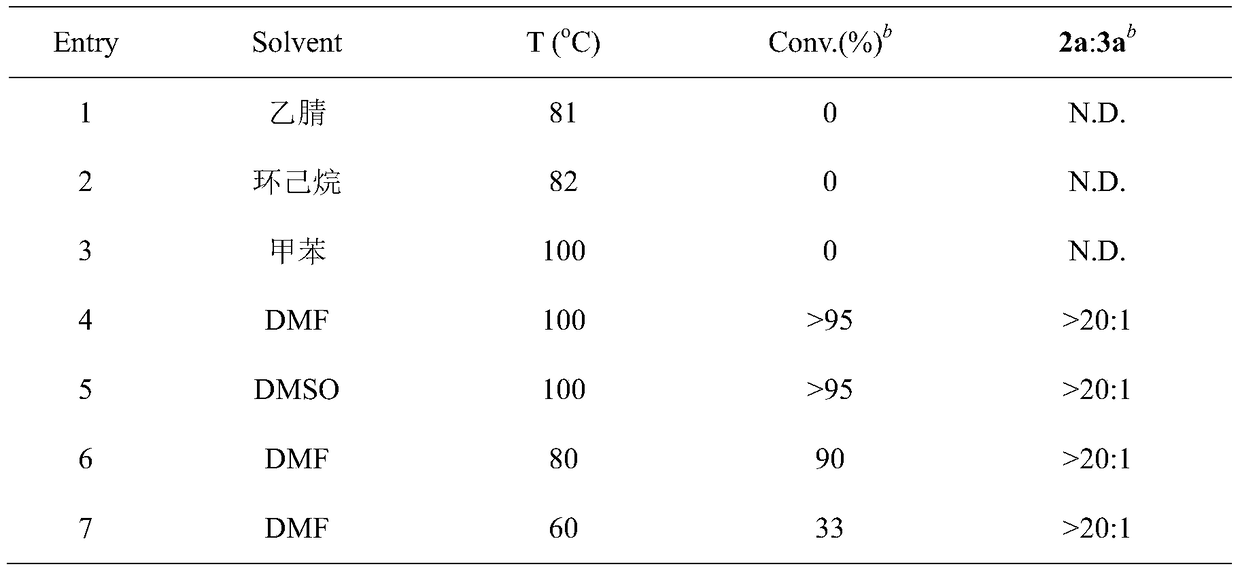
[0035] The conversion rate and the ratio of the two products are determined by the reaction crude product 1 H NMR to determine, see Table 1 for details.
[0036] Table 1. Optimization of reaction conditions for selective dehydrogenation of substituted tetrahydroisoquinolines a
[0037]
[0038]
Embodiment 2
[0039] Example 2: Substrate Expansion
[0040]
[0041] Productivity is the separation yield, separated by column (eluent: the volume ratio of petroleum ether and ethyl acetate is 5:1), the ratio of partial dehydrogenation product and complete dehydrogenation product is determined by nuclear magnetic rough spectrum, see Table 2 .
[0042] Table 2. Tetrahydroisoquinoline Selective Dehydrogenation Synthesis 2 a
[0043]
[0044] Embodiment 2: Gram scale test
[0045]
[0046] In air, the substrate 1-phenyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline (1.0 g, 4.78 mmol) was charged into a 25 mL Schlenk bottle, and 5.0 mL DMF was added, then stirred at 100°C After 3 days, it was cooled to room temperature, and the solvent was removed under reduced pressure. The conversion rate > 95% and the product ratio > 20:1 were determined by crude NMR spectroscopy. 0.827 g was isolated with a yield of 83.5%.
Embodiment 3
[0047] Embodiment 3: chiral tetrahydroisoquinoline racemization test
[0048]
[0049] Add single enantiomer 1-phenyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline substrate (84mg, 0.4mmol, 96.9%ee) into the reaction flask, add DMF to dissolve, heat up to 100°C and stir Reaction for 24 hours, thin-layer chromatographic analysis to detect the reaction process, until the raw materials completely disappeared, then remove the solvent under reduced pressure, without any other treatment, to obtain 1-phenyl-3,4-dihydroisoquinoline, and then to the system Add 3mL of methanol, then add (30mg, 0.8mmol) sodium borohydride in batches, stir the reaction at room temperature, and detect the reaction process by thin-layer chromatography, until the raw material completely disappears, add a small amount of water to quench the reaction, and react with ethyl acetate The aqueous phase was extracted 3 times, the organic phase was combined, washed once with saturated brine, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com